Manganese Dioxide vs Manganese Sulfate presents different options for users depending on their needs. Manganese dioxide is ideal for applications requiring high oxidation, such as specialized batteries. On the other hand, manganese sulfate is more commonly used in electric car batteries and agriculture because it dissolves easily and is more cost-effective. Most battery manufacturers prefer manganese sulfate for electric NMC cathodes due to its affordability and performance. When deciding between manganese dioxide vs manganese sulfate, people should consider which form of manganese suits their specific application and the role it will play.
Manganese dioxide is a dark powder. People use it in batteries and concrete. Manganese sulfate is a pink salt. It is used in fertilizers and animal supplements.
Manganese dioxide does not dissolve in water. It is good for strong, long-lasting batteries. Manganese sulfate dissolves easily in water. It helps plants and animals grow well.
Factories use manganese dioxide to make pure materials. These are for electric car batteries. Farmers use manganese sulfate to fix soil problems. It also helps crops grow better.
Both compounds need careful handling and storage. This keeps workers safe. It also stops health risks from dust or fumes.
You should pick the right manganese compound for your needs. Use manganese dioxide for batteries and water treatment. Use manganese sulfate for farming and supplements.
Manganese Dioxide vs Manganese Sulfate
Key Differences
Manganese dioxide vs manganese sulfate have different chemical and physical traits. Manganese dioxide is a dark powder that does not dissolve in water. Manganese sulfate is a light pink salt that dissolves very well. These differences change how people use them in factories and on farms. Manganese dioxide helps make electric batteries and makes concrete stronger. Manganese sulfate mixes with water fast, so it works well in fertilizers and supplements. Factories can also make manganese sulfate from manganese dioxide, which helps their work.
Tip: Pick manganese dioxide for strong electric batteries. Use manganese sulfate for farming or supplements.
Properties
The table below shows the main properties, uses, solubility, oxidation states, and benefits of manganese dioxide vs manganese sulfate:
Property/Feature Manganese Dioxide (MnO2) Manganese Sulfate (MnSO4) Appearance Dark brown/black powder Light pink crystalline solid Solubility in Water Negligible/insoluble 35.3–62.9 g/100 mL at room temperature Oxidation State +4 +2 Main Industrial Uses Alkaline batteries, lithium-ion cathodes, concrete Fertilizers, supplements, paint dryers, raw material for electrolytic manganese dioxide Benefits High electrochemical activity, low impurities, enhances concrete strength High solubility, promotes plant growth, cost-effective Performance in Batteries Used for high-performance electric cells Preferred for NMC cathodes in electric vehicles due to affordability and efficiency Manganese dioxide vs manganese sulfate also act differently with other chemicals. Manganese dioxide gives batteries great power and keeps them stable. Manganese sulfate dissolves easily and reacts fast, so it is good for plants and paint.
- Manganese dioxide is important for making batteries, like alkaline and lithium-ion types.
- Manganese sulfate helps plants grow and is used in fertilizers and supplements.
Both compounds need manganese to work well. Factories use manganese dioxide to make concrete stronger. Farmers and supplement makers like manganese sulfate because it is easy to use and works well. Making manganese sulfate from manganese dioxide also helps factories save time and money.
Note: The best choice between manganese dioxide vs manganese sulfate depends on how much it dissolves, its oxidation state, and what you need it for. Think about these things to get the best results for your project.

Chemical Properties
Structure and Formula
Manganese dioxide and manganese sulfate are not the same. They have different chemical formulas and structures. Manganese dioxide’s formula is MnO2. It has manganese and oxygen atoms. Its structure is called tetragonal rutile crystal, or β-MnO2. This form is found in nature as pyrolusite. Sometimes, the structure changes if water is present. But β-MnO2 is the most stable form. Manganese sulfate’s formula is MnSO4. It has manganese in the +2 oxidation state and a sulfate ion. Manganese sulfate is a common salt. Its crystal structure is not well described in science books. The biggest difference is the oxidation state and type of compound. Manganese dioxide is a manganese(IV) oxide. Manganese sulfate is a manganese(II) salt.
Appearance
These two compounds look very different in labs. Manganese dioxide is black or brown and solid. It can feel sticky and forms small crystals or lumps. This compound does not dissolve in water. Manganese sulfate looks pale pink when it has water. If it is dry, it is a white crystal. These color and texture differences help people tell them apart.
Tip: You can use color and texture to know which compound you have.
Solubility and Reactivity
Manganese dioxide and manganese sulfate act differently in water and with other chemicals. Manganese dioxide does not dissolve in water. It reacts with hot strong sulfuric acid to make manganese sulfate, oxygen, and water. It also reacts with hydrochloric acid to make manganese chloride and chlorine gas. In basic solutions, manganese dioxide can turn into potassium manganate. These reactions show why factories use manganese dioxide to make manganese sulfate.
Manganese sulfate dissolves fast in water. Plants can take in manganese through roots and leaves because of this. Farmers use manganese sulfate to fix soil problems and help crops grow better. When mixed with sodium hydroxide or ammonia, manganese sulfate makes manganese(II) hydroxide. Hydrogen peroxide can change this hydroxide into manganese dioxide. Making manganese sulfate from manganese dioxide and its easy use by plants make it important for farming.
Compound | Water Solubility | Key Reactions with Acids/Bases |
|---|---|---|
Manganese dioxide | Insoluble | Converts to manganese sulfate with hot acid |
Manganese sulfate | Highly soluble | Forms hydroxide with bases; oxidizes to MnO2 |
Uses
Industrial Applications
Manganese dioxide and manganese sulfate are used in many industries. Steel factories use the most manganese compounds. They add manganese dioxide and alloys to steel. This makes steel stronger and stops it from rusting. Almost all manganese in the world is used for making steel. The chemical industry also needs manganese sulfate. It helps make other chemicals, like manganese dioxide for batteries. More people want manganese dioxide now. This is because electric cars and new energy storage are getting popular.
Battery makers need a lot of manganese dioxide. They use it in batteries as a cathode and depolarizer. It is found in alkaline, zinc-carbon, and lithium-ion batteries. Manganese dioxide helps batteries work better and last longer. Electrolytic manganese dioxide is made in a special way. It is very pure and works well in new battery types. Asia-Pacific uses the most manganese. This is because of steel and battery factories in China and India.
Industrial Sector | Main Compound(s) | Application | Market Share/Trend |
|---|---|---|---|
Steel Production | Manganese dioxide, alloys | Strengthens steel, prevents corrosion | |
Battery Manufacturing | Manganese dioxide | Cathode in batteries, improves performance | Rapid growth with EV adoption |
Chemical Industry | Manganese sulfate | Synthesis, battery materials | Growing with renewables |
Note: Most manganese is used by battery and steel companies.
Agriculture and Supplements
Farmers and animal feed makers use manganese sulfate a lot. It dissolves fast and works well. In farming, manganese sulfate is the best fertilizer for manganese. It is great for spraying on leaves. Plants can take in the nutrient through their leaves. This helps crops like soybeans and wheat get better if they lack manganese. Manganese sulfate also stops nutrients from washing away. This saves money for farmers.
People who make animal feed add manganese sulfate monohydrate. It goes into food for cows, chickens, and other animals. This helps enzymes work, bones grow, and keeps animals healthy. Enough manganese stops growth problems and helps animals do better. More farmers are using manganese sulfate for crops and animals, especially where there are big farms.
Manganese sulfate is best for fixing plant problems.
Spraying manganese sulfate on leaves works fast and well.
Animal feed with manganese sulfate helps animals grow and have babies.
Tip: Always ask an expert about the right amount of manganese sulfate for plants or animals.

Manganese Dioxide in Industry
Electrolytic Manganese Dioxide
Electrolytic manganese dioxide is very important in factories. Workers make it with special hydrometallurgical steps. They start with manganese furnace dust or ores that are not high quality. Dextrin is used to help dissolve the manganese without using a lot of heat. This saves energy and is better for the environment. After the manganese dissolves, the liquid is cleaned to take out bad stuff. Then, in electrowinning, electrolytic manganese dioxide forms on metal plates. This way, factories get more than 90% of the manganese back and spend less money.
Step/Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
Raw Material | Manganese furnace dust or low-grade ores |
Reductant | Dextrin enables direct dissolution |
Leaching | Manganese dissolves into solution |
Purification | pH adjustment removes impurities |
Electrowinning | Electrolytic manganese dioxide deposits on electrodes |
Recovery Rate | Over 90% manganese recovery |
Environmental Impact | Lower energy use, no high-temperature steps |
Electrolytic manganese dioxide has different forms, like akhtenskite, ramsdellite, and nsutite. These forms give it special powers for batteries. More people want emd because batteries need pure manganese dioxide to work well.
Battery Production
Battery makers use electrolytic manganese dioxide for the cathode. This helps batteries work better, especially in electric cars and devices. Electrolytic manganese dioxide lets batteries hold a lot of power, about 300 mAh per gram in lithium-ion batteries. But, the battery can lose power quickly after a few uses, sometimes dropping below half. Still, the voltage stays higher than other cathode materials, so it is good for battery life.
Aspect | Electrolytic Manganese Dioxide (EMD) | Other Cathode Materials |
|---|---|---|
Discharge Capacity | ~300 mAh/g | Lower |
Cycling Stability | Poor, <50% retention after 5 cycles | Better, but lower voltage |
Voltage Profile | 1.5–1.6 V, high hysteresis | Lower voltage |
Reversible Mg2+ Intercalation | Achieved | Limited |
Many companies want electrolytic manganese dioxide for batteries. More electric cars mean more need for good cathode materials. As battery technology gets better, the manganese dioxide market grows because people want high-quality electrolytic manganese dioxide for stronger batteries.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Manganese Dioxide
Manganese dioxide helps many factories. It works as a strong catalyst in water treatment. It cleans water by taking out iron, arsenic, manganese, and radium. This makes water safer to drink. Many water cleaning projects use manganese dioxide because it grabs onto bad stuff well. Factories also use it as an oxidizing agent and catalyst in chemical reactions. It stays stable even when it gets very hot. This makes it good for tough jobs in factories. Battery makers use manganese dioxide for cathodes. This helps batteries store more energy and work better. Manganese dioxide helps the environment by making water cleaner and helping recycle batteries. Builders use it to make materials stronger and last longer. More people want manganese dioxide because batteries and cleaning the environment are important.
Manganese dioxide is easy to move and use. It does not catch fire or explode.
But manganese dioxide has some problems. Some ways to treat water with it cost a lot and need lots of electricity. Methods like adsorption and chemical precipitation can make sludge. This sludge can pollute the environment again. Cleaning water with manganese dioxide can be hard and expensive. Sometimes, chemicals are not used up fully, which can cause more pollution. These problems make companies look for cheaper and easier ways to clean water.
| Treatment Method | Disadvantages Related to Cost and Environment |
|---|---|
| Electrochemical Method | Needs lots of electricity and costs a lot |
| Ion Exchange Method | Can get dirty easily, so it costs more to fix |
| Adsorption Method | Makes sludge that can pollute the environment |
| Chemical Precipitation | Also makes sludge and can cause more pollution |
Manganese Sulfate
Manganese sulfate helps farmers and people who make supplements. Farmers use it to fix manganese problems in plants. It helps plants grow strong and healthy. Manganese sulfate helps plants make food by helping chlorophyll and energy work better. It turns on enzymes that help with nitrogen, fats, and DNA. Manganese sulfate helps plants fight stress and stay healthy. It helps plants take in nutrients like nitrogen and phosphorus. This makes crops bigger and fruit better. Enough manganese sulfate makes plants stronger and helps them fight bugs and sickness. Its slight acidity lowers soil pH and adds sulfur, which helps soil stay healthy. These good things help farmers spend less money and earn more. This makes manganese sulfate popular in farming.
It is important to use the right amount. Testing soil and using manganese sulfate carefully keeps plants safe and the environment clean.
Still, manganese sulfate needs careful use. Using too much can hurt plants and the environment. Farmers must follow rules to use it safely. The price and supply of manganese sulfate depend on how much manganese dioxide factories make.
| Benefit Category | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Photosynthesis Enhancement | Helps plants make more food and grow better |
| Nitrogen Metabolism Activation | Helps plants use nitrogen and grow strong |
| Growth and Yield Improvement | Makes crops bigger and better quality |
| Disease and Pest Resistance | Helps plants fight bugs and sickness |
| Soil Quality Improvement | Lowers soil pH and adds sulfur |
| Economic Benefits | Saves money and helps farmers earn more |
| Application Considerations | Must use the right amount to keep plants and soil safe |
Safety and Handling
Health Risks
Manganese dioxide and manganese sulfate can be risky if not handled right. Manganese is needed for health, but too much is bad. Factory workers might breathe in dust or fumes from manganese. This can cause health problems after a while.
Breathing in manganese dioxide dust at work can hurt the brain and nerves. It can make it hard to move and change how people act.
If someone is around manganese for a long time, it can build up in the brain. Doctors can see this on MRI scans.
Some workers have trouble breathing or have lung problems after being near manganese compounds.
How dangerous manganese is depends on how fast it dissolves. Some types leave the lungs faster than others.
There are safety rules that say how much manganese workers can breathe in. These rules help keep workers safe.
Too much manganese can cause manganism. People with manganism may shake, walk strangely, or move slowly. Some workers may act or think differently. The body can handle a little manganese, but too much is harmful. Factories must follow safety rules to protect workers.
Storage
Storing manganese dioxide and manganese sulfate the right way stops accidents. It also keeps workers healthy. Both should be kept in closed containers. Store them in cool, dry places away from acids and oxidizers. Workers should label all containers and keep them off the floor. Good airflow in storage rooms helps lower dust and fumes.
Manganese Compound | Storage Requirement | Safety Tip |
|---|---|---|
Airtight, dry container | Avoid contact with acids | |
Sealed, moisture-free area | Keep away from oxidizers |
Workers need gloves, masks, and special clothes when using these chemicals. Cleaning storage areas often stops dust from building up. Safety lessons teach workers what to do if there is a spill or if someone is exposed.
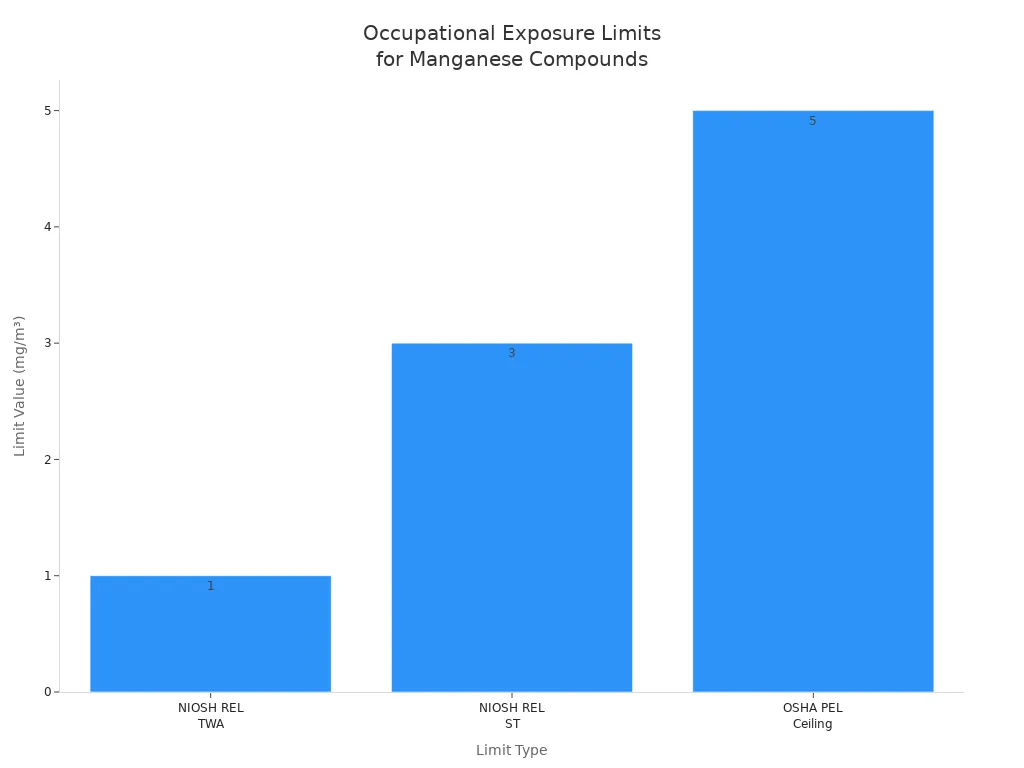
Workplace safety groups set limits for manganese exposure. The table below shows the safe amounts:
Manganese Compounds and Fume (as Mn) | Exposure Limit Type | Limit Value |
|---|---|---|
NIOSH REL | TWA (Time-Weighted Average) | 1 mg/m³ |
NIOSH REL | ST (Short Term) | 3 mg/m³ |
OSHA PEL | Ceiling (C) | 5 mg/m³ |
Workers should stay under these limits to stay healthy. Checking air and having medical checkups helps keep everyone safe.
Manganese dioxide and manganese sulfate do different jobs. Manganese dioxide is used in batteries. It is important for electric cars and devices. It needs to be very pure for these uses. Manganese sulfate is good for fertilizers and animal feed. It helps crops grow and keeps animals healthy. Experts say to pick the right one for your needs. You should think about what you need and how pure it must be. The table below gives advice from experts:
Application Area | Manganese Compound | Expert Recommendation / Market Insight |
|---|---|---|
Batteries | Battery grade manganese dioxide (MnO2) | High purity is critical for battery performance and longevity. |
Fertilizers | Manganese sulfate | Essential for correcting soil deficiencies and boosting crop yield. |
Supplements | Manganese sulfate | Supports animal health and growth in feed. |
Always use safety rules when working with manganese compounds. If you want more help, ask an expert or check trusted resources.
FAQ
What is the main difference between manganese dioxide and manganese sulfate?
Manganese dioxide is a black powder. It does not mix with water. Manganese sulfate is a pink salt. It mixes with water very well. Factories use manganese dioxide to make batteries. Farmers use manganese sulfate for plants and animal food.
Can manganese dioxide and manganese sulfate be used interchangeably?
No, you cannot swap them. Each one has its own job. Manganese dioxide is best for batteries and cleaning water. Manganese sulfate is good for farming and supplements. People should pick the right one for what they need.
Is manganese sulfate safe for plants and animals?
Yes, if you use it the right way. Manganese sulfate helps plants grow strong. It also keeps animals healthy. Farmers must use the right amount. Too much can hurt crops or animals. Always ask an expert before using it.
Why do battery makers prefer manganese dioxide?
Battery makers like manganese dioxide because it works well in batteries. It helps batteries last longer and work better. Electrolytic manganese dioxide is very pure. This is important for new batteries.
How should users store manganese compounds safely?
Keep manganese dioxide and manganese sulfate in closed containers. Make sure they stay dry and away from acids or oxidizers. Workers should wear gloves and masks. Good airflow in storage rooms keeps dust and fumes low.
Related Posts

I am Edward lee, founder of manganesesupply( btlnewmaterial) , with more than 15 years experience in manganese products R&D and international sales, I helped more than 50+ corporates and am devoted to providing solutions to clients business.





