When you look at manganese sulfate, you see two sides. Many people say it is good for the environment, but understanding the manganese sulfate environmental impact is crucial. Plants and animals need manganese to stay healthy. However, too much manganese sulfate can hurt nature. For example, studies show high levels can harm fish, leading to slower growth and increased stress.
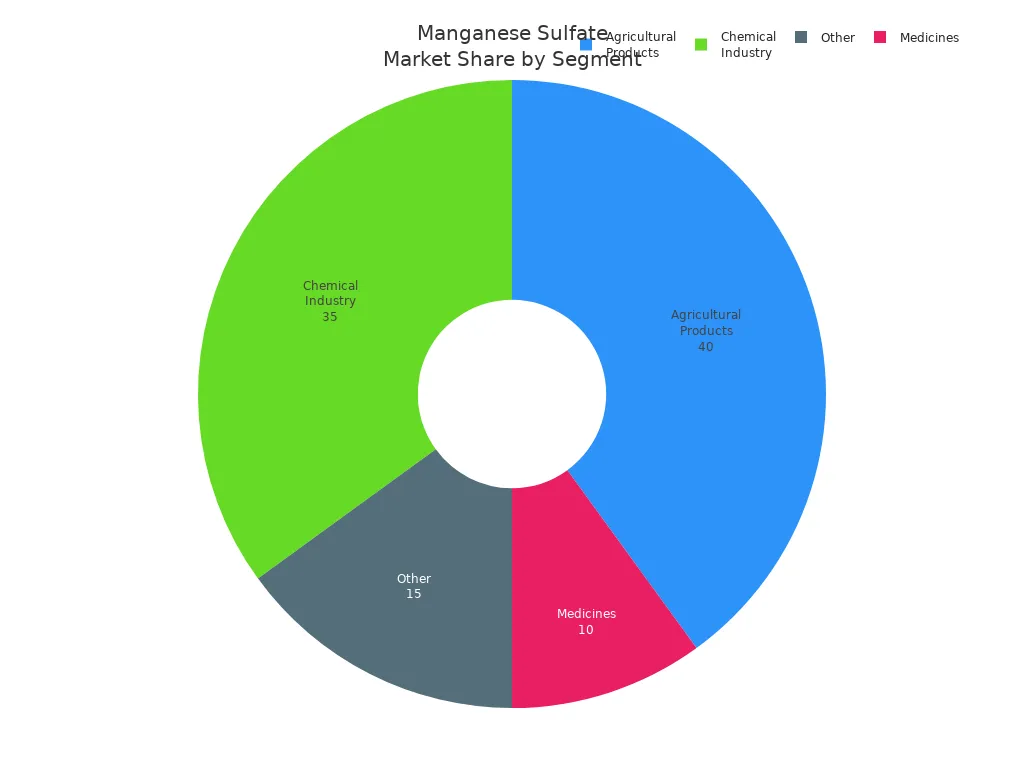
You can find manganese sulfate in many things. Look at the table below to see its main uses:
Application Segment | Market Share (%) | Key Insights |
|---|---|---|
Agricultural Products | It is used in fertilizers to fix manganese problems. This helps crops grow better. | |
Chemical Industry | 35% | It is important for making batteries and other chemicals. |
Medicines | 10% | It is used in supplements to help health and metabolism. |
Other | 15% | It is used for electroplating and making alloys. |
Learning about manganese sulfate’s environmental impact helps you make smart choices. This is important as more people want electric cars and clean energy.
Manganese sulfate helps plants grow well but can hurt nature if used too much. Using manganese sulfate the right way helps crops grow and keeps pollution low. Manganese sulfate can get into water and soil and cause health problems for fish and people. Checking manganese levels in water and soil is important to stop poisoning and keep nature safe. Learning about rules and good ways to use manganese sulfate helps lower its harm to the environment.
Manganese Sulfate Environmental Impact
Air and Water Quality
Manganese sulfate is used in farms and factories. It can get into the air and water. Sometimes, it helps lower pollution from other chemicals. Experts say manganese sulfate is non-toxic and biodegradable. It does not stay in the environment as long as some other things. This makes it better for eco-friendly farming.
But, manganese sulfate environmental impact is not always good. Too much in air or water can cause pollution. Farms and factories can release it through runoff or dust. This can raise levels in rivers, lakes, and the air. Manganese can travel far from where it started.
Tip: Use manganese sulfate in the right amount. This helps keep air and water clean. Too much can pollute and hurt the environment.
Manganese sulfate can move with stormwater or waste. It can build up in plants and animals. When this happens, fish and other animals can get sick. You need to watch for these changes. This helps protect the environment and control pollution.
Soil and Crop Effects
Farmers use manganese sulfate to help crops grow. It keeps soil healthy and helps plants get strong. It fixes manganese problems in soil. This means better crops and stronger plants. Wheat and other grains grow better with manganese sulfate.
Evidence Type | Findings |
|---|---|
Crop Productivity | Manganese sulfate application enhances crop productivity in wheat. |
Soil Characteristics | Improves soil characteristics, leading to better fertility. |
Manganese Concentration | Increases manganese concentration in grains, essential for plant processes. |
Photosynthesis | Mn is crucial for photosynthesis, affecting grain yield and straw. |
Deficiency Effects | Mn deficiency leads to reduced grain setting and yield. |
But, manganese sulfate environmental impact on soil can be bad. Using too much can make manganese build up in soil. This can get into crops. Heavy metals in food can be risky for people and animals. Too much can hurt soil health and make food less safe.
Manganese sulfate helps eco-friendly farming by lowering harmful chemicals.
It keeps soil healthy and crops growing well.
Too much can cause pollution and build up, which can hurt food safety.
You must balance the good and bad sides. The right amount of manganese sulfate keeps pollution low and protects the environment.
Marine and Aquatic Systems
Manganese sulfate can get into rivers, lakes, and oceans. Runoff from farms and factories carries it to water. This can make water cloudy and block sunlight. Plants and fish may have trouble living. Fish may grow slower or get sick. These are signs of manganese sulfate environmental impact on water life.
Manganese runoff makes water cloudy and blocks light.
Fish and other animals can have growth and health problems.
Pollution can cause manganese to build up in fish and shellfish.
Evidence Description | Implications |
|---|---|
Increased manganese in water and biota | Potential toxicity in aquatic organisms and bioaccumulation risks in the food chain. |
Chronic contamination from mine tailings | Long-term source of manganese and trace metals, affecting local ecosystems. |
Elevated manganese in fish tissues | Direct impact on human health through consumption of contaminated species. |
Risks of accumulation in various species | Increased bioaccumulation risks for the local population. |
Toxic effects on aquatic organisms | Induces oxidative stress, tissue damage, and neurodegeneration. |
Watch for manganese building up in the food chain. If fish and shellfish have too much, people can get sick from eating them. Pollution from manganese sulfate can last a long time. It is important to control how much gets into water.
Note: New ways can help clean up manganese sulfate pollution. Some methods take metals from waste. Others trap and remove pollution from soil and water.
You can help protect the environment. By learning about manganese sulfate environmental impact, you help stop pollution and build up. This keeps people, plants, and animals safe.
Human Health Risks

Exposure Pathways
You can come into contact with manganese sulfate in many ways. The most common ways are drinking water, eating food, breathing air, and touching soil. Farms and factories put manganese sulfate into the environment. You might find it in water, crops, or dust. This makes your chance of exposure higher.
If you drink water or eat food with a lot of manganese sulfate, you have a bigger risk of toxicity. Scientists studied how exposure affects people in different places. The table below shows some important results:
Study | Findings | Location |
|---|---|---|
Khan et al. (2011) | Higher water manganese concentrations associated with behavioral problems | Bangladesh |
Wasserman et al. (2006) | Reported neurotoxic effects linked to manganese levels | Bangladesh |
Bouchard et al. (2011) | Association between drinking water manganese and cognitive abilities | Canada |
You should know that water and food can cause manganese toxicity. This risk is higher if you live near farms or factories using manganese sulfate. Kids and older people have more risk because their bodies react more.
Note: You can lower your risk by checking water quality and picking safe food.
Manganese sulfate can also get into your body through the air. Dust from mining or farming can carry manganese particles. Breathing this dust raises your risk of toxicity. Breathing manganese for a long time can hurt your health.
You might touch soil with high manganese levels. This way is less common, but it still adds to your risk. The biogeochemical cycle moves manganese through air, water, and soil. This makes exposure possible in many places.
Organ and Neurological Effects
It is important to know how manganese sulfate affects your organs and brain. Manganese toxicity can hurt your nervous system, heart, and other organs. The risk depends on how much and how long you are exposed.
Manganese toxicity often hurts your brain. Scientists link exposure to diseases and thinking problems. The table below shows how manganese sulfate affects your brain and nerves:
Study Focus | Key Findings |
|---|---|
Cognitive Deficits | Tasks performed by participants can identify cognitive deficits suggesting damage to the basal ganglia, which is involved in memory and attention. |
Long-term Effects | Neurological damage from manganese exposure does not reverse, and symptoms may progress even without ongoing exposure. |
Neuron Type | Impact of Manganese Exposure |
|---|---|
Dopaminergic Neurons | Injured by manganese, leading to dopamine shortages, similar to Parkinson’s disease. |
Cholinergic Neurons | Suspected to be injured by manganese, contributing to cognitive impairment. |
Population | Findings |
|---|---|
Older Adults | High concentrations of manganese in water linked to moderate levels of dementia. |
You may notice memory loss, trouble focusing, and slower thinking. These signs show manganese toxicity in your nervous system. Being exposed for a long time raises your risk of diseases like Parkinson’s.
Your heart can also be hurt by manganese toxicity. Some studies link exposure to heart problems. You may have a higher chance of heart disease if you drink water or eat food with a lot of manganese. Long exposure makes these risks worse.
⚠️ Tip: If you live near a manganese sulfate source, test your water and soil. Early testing lowers your risk and keeps you healthy.
Manganese toxicity can harm your liver and kidneys. These organs help clean toxins from your body. High exposure makes their job harder and raises your risk of organ damage.
The biogeochemical cycle spreads manganese in the environment. This cycle makes your risk of exposure and toxicity higher. You should pay attention to how manganese sulfate moves through air, water, and soil.
You can protect yourself by learning about manganese toxicity and its risks. Watch for symptoms and try to lower your exposure. This helps you avoid brain and heart problems linked to manganese sulfate.
Environmental Regulations
Compliance Challenges
It is hard to follow all the rules for making manganese sulfate. Groups like the EPA and ECHA make strict rules for pollution and waste. These rules help stop toxic pollution in air, water, and soil. You need new machines and safer ways to work to follow these rules. This can take a lot of money and time.
Compliance Challenge | Description |
|---|---|
Stringent Environmental Regulations | Rules from the EPA and ECHA are very strict about pollution and waste. |
Increased Capital Expenditure | You must spend more money on better machines and safe ways to work. |
Evolving Safety Standards | New rules for farm chemicals mean you must test products and get them checked. |
You must keep up with new safety rules. These rules say you need to test products and show they are safe. If you do not follow the rules, you can hurt the coast and people living nearby. You also need to learn about biogeochemistry. This shows how manganese moves in nature. It helps you stop toxic build-up near the coast.
⚠️ Tip: Learn about new rules and buy better machines. This helps you stop pollution and keep the coast safe.
Industry Best Practices
You can stop toxic pollution by using the best ways to work. Many companies use special filters and machines to clean up manganese. These tools help save manganese and make less waste. You can also change how you make crystals to get cleaner products.
Computers and machines help you control work and stop spills.
New materials and ways to make things can save money and lower pollution.
New types of manganese sulfate for farms help keep water clean and protect the coast.
Companies use green ways to make manganese sulfate.
You can recycle to make less toxic waste.
Following rules means you use safe ways to work.
Innovation | Description |
|---|---|
Sustainable production of electrolytic manganese dioxide (EMD) | A new way to make EMD uses less energy and makes less waste. |
Nano One M2CAM Technology | This new process uses less energy, makes less pollution, and cuts down on waste. |
You see new tools like Nano One’s M2CAM and better EMD making. These new ways help you make less pollution and waste. They also help keep manganese moving safely in nature near the coast. By using the best ways to work, you stop pollution and follow the rules.
You can have many risks when you use manganese sulfate. Pollution from manganese can build up in food. This can make people sick. It can hurt the brain and lungs. Sometimes, it is hard to see signs of sickness in kids. Scientists still need to learn more about this. You should think about these risks and pick safe choices. Your choices help companies make safer products. To lower risk, test your water often. Use products that are safe. Support new ways to clean up pollution. Keep learning about risks. Help research for better safety.
FAQ
What is manganese sulfate and why do you use it in agriculture?
Manganese sulfate helps crops grow better. It adds manganese to soil. Plants need manganese to make food. This keeps plants healthy. Farmers put it in fertilizers. It helps crops grow bigger and stronger.
How does manganese sulfate production affect water and fish?
Manganese sulfate can get into water from factories. This can make water dirty. Fish can take in manganese from the water. Too much manganese can make fish sick. You should check water for manganese to keep fish and people safe.
What is a potentially toxic element and is manganese sulfate one?
A potentially toxic element can hurt living things if there is too much. Manganese sulfate is a potentially toxic element. You need to use it safely. Too much can pollute soil, water, and fish.
How does manganese sulfate move in the environment?
Manganese sulfate moves through water, soil, and air. It can travel from farms to rivers. This can make more manganese in fish and soil. The movement can cause more pollution.
How can you lower the risk of manganese contamination?
Test water and soil often for manganese. Use only the right amount of manganese sulfate. Watch fish for signs of sickness. Learn how manganese moves in nature. This helps keep water, soil, and fish safe.
Related Posts

I am Edward lee, founder of manganesesupply( btlnewmaterial) , with more than 15 years experience in manganese products R&D and international sales, I helped more than 50+ corporates and am devoted to providing solutions to clients business.





