MnCO₃ as chemical precursor is very important in industrial chemistry. Manganese carbonate turns into active manganese oxides, which help make effective catalysts. MnCO₃ as chemical precursor also adds color to paints and works as a drying agent in them. Many experts trust MnCO₃ as chemical precursor because it converts efficiently into manganese compounds. Using manganese carbonate carefully keeps people safe and helps produce better catalysts and paints.
Manganese carbonate (MnCO₃) is a stable, light pink solid. It changes into manganese oxides. These oxides are important for making good catalysts. They also help make paints better.
When you heat MnCO₃, it makes manganese oxides. These oxides make chemical reactions happen faster. They help clean up pollution. They also help make batteries and ceramics.
MnCO₃ is a safer drying agent and colorant in paints. It works well in light-colored paints. But it dries slower than cobalt-based agents. People must use it carefully to stop unwanted color changes.
Factories need very pure MnCO₃ to make good catalysts and paints. They follow strict rules to remove impurities. They also protect workers.
People must wear safety gear when handling MnCO₃. Good ventilation is needed to avoid health risks. Companies try to lower harm to the environment by using cleaner ways to make it.
MnCO₃ as Chemical Precursor
Chemical Properties
Manganese carbonate has features that help in industry.
MnCO₃ looks pale pink or white and is a solid crystal.
It stays stable at room temperature, so it is safe to store.
MnCO₃ does not dissolve in water, but it dissolves in weak acids.
The compound breaks down at about 200°C. It gives off carbon dioxide and makes manganese oxide.
Its crystal shape is hexagonal–rhombohedral, like calcite. This makes it strong.
Because it does not dissolve in water, it works well in soil and glazes for ceramics.
MnCO₃ does not have Mn³⁺ impurities. Some hydroxide precursors do, but this helps make pure manganese chemicals.
Making MnCO₃ depends on things like pH, temperature, and stirring speed. These control the size and shape of the particles. You can get round particles that pack tightly.
MnCO₃ as chemical precursor gives good purity and particle shapes. These are important for making manganese compounds that work well.
Transformation to Manganese Oxides
Manganese carbonate helps make manganese oxides for catalysts. When heated between 200°C and 350°C, MnCO₃ breaks down and releases carbon dioxide. This leaves manganese oxide, which is needed in many industries. Scientists often use manganese carbonate to make cryptomelane-type manganese oxides, like OMS-2. These oxides have lots of tiny holes, are acidic, and do not mix with water. They can easily switch between Mn²⁺, Mn³⁺, and Mn⁴⁺. The cryptomelane structure has potassium and manganese in tunnels. It forms double chains of MnO₆ octahedra. This helps the catalyst work well.
Adding copper can make these manganese oxides better at moving oxygen. But it can make them less stable when hot. MnCO₃ as chemical precursor is a good way to make manganese oxides with the right properties. These oxides are used in batteries, ceramics, and making chemicals. Being able to control how pure and what shape the particles are makes manganese carbonate a top choice for making good manganese chemicals.
Catalysts from MnCO₃
Catalyst Types
MnCO₃ is important for making catalysts in many industries. When you heat manganese carbonate, it turns into manganese oxides. These oxides help speed up chemical reactions. Scientists use different catalysts made from manganese carbonate. Some common types are:
Manganese pentacarbonyl bromide helps with Friedel-Crafts alkylation and C-H activation.
Manganese dichloride tetrahydrate is used for electrophilic substitution.
Supported manganese catalysts are made by adding manganese ions to things like apatite or activated carbon. These work in Suzuki-Miyaura coupling and help break down pollution.
Organomanganese reagents come from manganese salts and help with acylation reactions.
Manganese oxide catalysts help with the oxidation of volatile organic compounds.
The table below shows how manganese carbonate can make different catalyst types and what they are used for:
Catalyst Type Derived from Manganese Carbonate | Description and Industrial Use |
|---|---|
Manganese Oxide Catalysts | Made by heating manganese carbonate; used for oxidation reactions and cleaning the environment. |
Manganese Carbonate as Catalyst | Used directly as a green, safe catalyst in making biodiesel and in the viscose process. |
Manganese Dioxide Production | Manganese carbonate helps make manganese dioxide, which is a catalyst in many chemical processes. |
Oxidation Processes
Catalysts made from manganese carbonate are important in oxidation. When MnCO₃ is heated, it becomes manganese oxides. These oxides help turn harmful chemicals into safer ones. The Mars-Van Krevelen mechanism explains how these catalysts work. Carbon monoxide sticks to the catalyst’s surface. Manganese and copper ions help change it into carbon dioxide. Oxygen from the air fills empty spots on the catalyst. This keeps the reaction going. Manganese can switch between different forms, which helps move oxygen. Copper helps by taking in oxygen. This cycle lets the catalyst keep working.
Industries use manganese oxide catalysts to clean air by removing carbon monoxide. These catalysts also help make batteries, ceramics, and glass. Manganese carbonate turns into manganese oxide, which then helps filter water. Chemical plants use these catalysts for hydrogenation and to make other manganese salts.
MnCO₃ makes it easy to get manganese oxides that work well in many oxidation processes. This helps industries keep their work safe and efficient.
Performance Benefits
Manganese carbonate has many benefits as a catalyst precursor. It is easy to find and does not hurt the environment. Manganese has many forms, so it works for different reactions. Unlike iron-based catalysts, manganese does not have problems like the Fenton effect, which can make catalysts stop working sooner. Scientists can change the structure of manganese carbonate to make more active sites. This helps the catalyst work better.
Catalysts made from manganese carbonate work well at low temperatures. They remove nitrogen oxides from air better than vanadium-based catalysts. Vanadium catalysts need higher temperatures and can get ruined by dust. Adding things like magnesium carbonate or carbon makes the catalyst’s surface bigger and helps it last longer. These changes help the catalyst work better and stay strong.
Manganese oxide catalysts on carbon show high conversion rates for nitrogen oxides at low temperatures.
The carrier material helps keep the catalyst stable and lowers costs.
Special shapes, like nanowire networks, help the catalyst handle water and electricity better.
Experiments show that using manganese carbonate as a precursor gives better phase composition and higher surface area. This means the catalyst works better and lasts longer. Chemical plants like these benefits, so manganese carbonate is a top choice for many uses.
Manganese Carbonate in Paints
Drying Agent Role
Manganese carbonate helps alkyd paints dry faster. Paint makers add it to make paint films harden quickly. Manganese acts like a helper in the paint. It breaks down hydroperoxides inside the paint. This makes free radicals form. Free radicals help the paint become solid. Manganese carbonate is slower than cobalt-based drying agents. Paints with manganese carbonate take more time to dry. The paint film may feel softer than those with cobalt driers. Some companies use manganese carbonate because it is less harmful than cobalt. New manganese-based drying agents have been tested. They still do not dry as fast or as hard as cobalt. Iron-based catalysts can sometimes dry paint faster than manganese carbonate. Even so, manganese carbonate is safer for some paint formulas.
Tip: Manganese carbonate is safer than cobalt driers, but paint will dry slower and feel softer.
Colorant and Pigment Use
Manganese carbonate is used as a colorant and pigment in paints. It gives paints pink, purple, or brown colors. The color depends on how much manganese carbonate is used. Paint makers like it because its color stays stable and mixes easily. Manganese carbonate is a pale pink to light brown powder. It does not dissolve in water. It does dissolve in acids. This helps it stay stable in paint mixtures.
Function/Property | Description |
|---|---|
Colorant | Used in paints, coatings, and dyes to give pink, purple, or brown shades depending on concentration and application |
Pigment | Acts as a pigment additive in paint manufacturing |
Physical Form | Pale pink to light brown crystalline powder, insoluble in water but soluble in acids |
Role in Paint | Provides color and serves as a precursor to other manganese compounds used in paint |
Additional Uses | Also used as an additive and flux in ceramics and glass, which relates to its pigment properties |
Manganese carbonate is also used to make other manganese compounds for paint. Paint makers use it in ceramics and glass for color too. Its stable color and easy use make it popular in the industry.
Application in Light-Colored Paints
Paint makers use manganese carbonate in light or white paints in small amounts. Too much manganese carbonate can change the paint’s color. Even a little bit can make paint look pink or brown. To keep paint bright, only a tiny amount is added. This helps avoid unwanted colors but still gives the benefits of manganese. Careful control keeps light-colored paints looking the way they should.
Note: Always check how much manganese carbonate is in light or white paints to stop unwanted color changes.
Production and Safety
Factories make mnco₃ from a rock called rhodochrosite. Workers crush and grind the rock into small pieces. They remove iron and alkali impurities from the ore. Sulfuric acid helps dissolve the ore. After that, they filter out what is left. Oxidation and precipitation take out iron. Sulfide precipitation removes heavy metals. At the end, crystallization makes pure mnco₃ for sale. Some companies use electrolytic manganese metal or manganese dioxide ore. This helps them make very pure manganese carbonate for batteries.
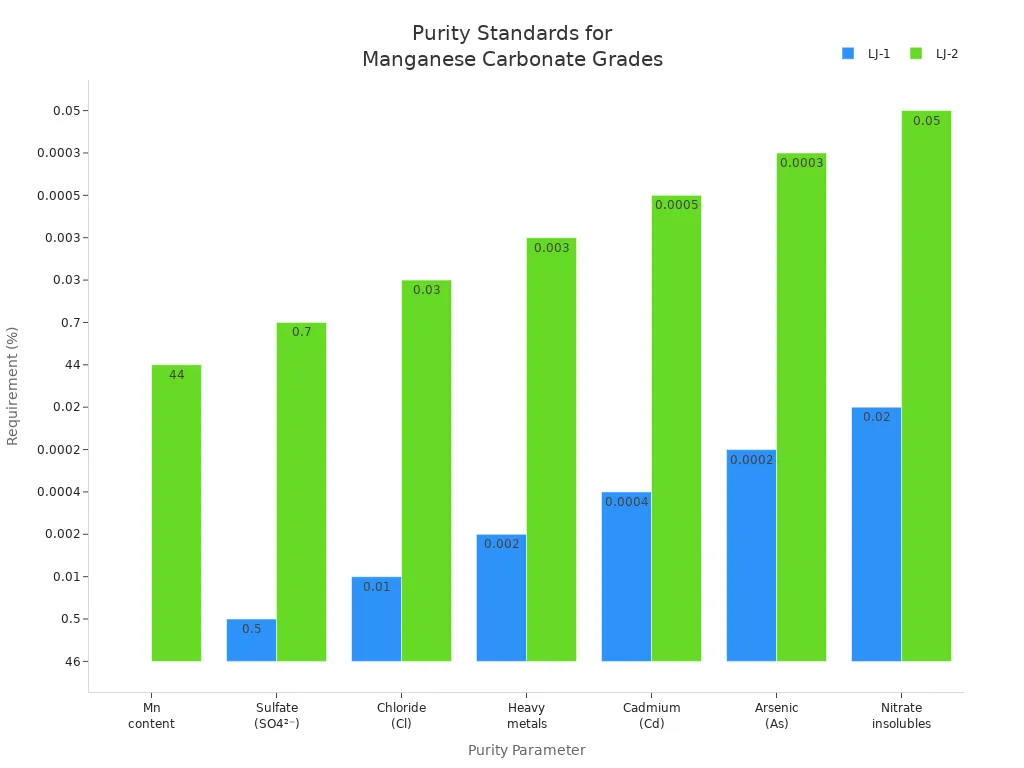
Purity is important for catalysts and paints. The table below shows how much manganese and other things should be in mnco₃. These rules help keep products good and help the battery market grow.
Purity Parameter | Requirement (LJ-1) | Requirement (LJ-2) |
|---|---|---|
Manganese content (Mn) | ≥ 46% | ≥ 44% |
Sulfate (SO4²⁻) | ≤ 0.5% | ≤ 0.7% |
Chloride (Cl) | ≤ 0.01% | ≤ 0.03% |
Heavy metals | ≤ 0.002% | ≤ 0.003% |
Cadmium (Cd) | ≤ 0.0004% | ≤ 0.0005% |
Arsenic (As) | ≤ 0.0002% | ≤ 0.0003% |
Nitrate insolubles | ≤ 0.02% | ≤ 0.05% |
Very pure manganese carbonate is needed for batteries. This helps the market get bigger. More people want batteries, so the market keeps growing.
Handling and Environmental Aspects
Workers must be careful when working with mnco₃. They wear masks, goggles, and gloves to stay safe. Good ventilation keeps the air clean. Companies store mnco₃ in closed containers. They keep it away from water and things it should not touch. If there is a spill, workers block off the area. They wear safety gear and clean up with a special vacuum or scoop it into closed boxes.
Breathing in mnco₃ dust or fumes can make people sick. Short exposure can cause metal fume fever or lung problems. Breathing it for a long time can hurt the brain and nerves. It can cause memory loss, shaking, and weak muscles. Workers must wash up before eating or leaving work.
Mining and making mnco₃ can hurt the environment. Open-pit mines destroy animal homes and make waste. Acid from mines can make water unsafe for fish. Making mnco₃ uses a lot of energy and makes dangerous waste. Companies use cement to lock up waste safely. Some use microbes to make mnco₃ in a greener way. This helps clean up the environment. Using better mining and processing methods helps protect nature and helps the market grow.
The mnco₃ market is getting bigger because more batteries are needed. Companies are using cleaner ways to make mnco₃ and manage waste. This helps them follow rules and meet market needs.
MnCO₃ is important for making catalysts and paints. It helps the market grow over time. Careful drying and changing MnCO₃ keeps it pure and stable. This helps companies make good products. The market likes easy and energy-saving ways to make MnCO₃. These ways help make a lot of it and keep the environment safe. Companies that keep MnCO₃ pure and handle it safely get better results. Their products work well and the business grows. These good habits help the market stay strong and ready for the future.
FAQ
What is the main use of MnCO₃ in catalysts?
MnCO₃ acts as a starting material for making manganese oxides. These oxides help speed up chemical reactions in industries like chemical plants and pollution control.
Can MnCO₃ be used in all types of paints?
Paint makers use MnCO₃ mostly in alkyd and oil-based paints. They add it as a drying agent or colorant. It works best in light-colored paints when used in small amounts.
Is MnCO₃ safe to handle in the workplace?
Workers should wear gloves, masks, and goggles. Good ventilation helps keep dust levels low. MnCO₃ dust can cause health problems if inhaled or touched often.
How does MnCO₃ affect paint color?
Small amounts of MnCO₃ keep paint colors light. Too much can turn paint pink or brown. Paint makers control the amount to avoid unwanted color changes.
Related Posts

I am Edward lee, founder of manganesesupply( btlnewmaterial) , with more than 15 years experience in manganese products R&D and international sales, I helped more than 50+ corporates and am devoted to providing solutions to clients business.





