You can make your crops healthier and get more food by using mnco₃ as a fertilizer. Many farmers have problems with not enough manganese, especially in soil that has high pH or does not have enough air. You may see weaker plants or get less food from your crops in these places. Mnco₃ helps fix these issues because manganese helps plants make chlorophyll and helps important enzymes work.
Not enough manganese can make photosynthesis worse, lower pollen health, and make crops weaker.
Using mnco₃ helps potatoes, soybeans, and wheat grow more.
When you use mnco₃, your plants get stronger and can grow as much as possible.
MnCO₃ gives plants manganese. Manganese is a key nutrient. It helps plants make chlorophyll. It also helps important enzymes work. These enzymes help plants grow strong.
Using MnCO₃ helps photosynthesis. It makes plant cell walls stronger. It helps crops fight diseases. It helps crops handle stress.
Use 0.5 to 1 kg of MnCO₃ for each hectare. Do this early in the growing season. This helps crops like maize, wheat, potatoes, and soybeans grow better.
Test your soil before using MnCO₃. This stops you from using too much. Too much can hurt plants. It can lower crop quality.
Follow safety rules when you use MnCO₃. This keeps you safe. It protects your crops. It helps the environment stay healthy.
MnCO₃ as a Fertilizer
What Is Manganese Carbonate
Manganese carbonate looks pink or light brown and is a crystal. It has a molecular weight of 114.94 g/mol. When you use manganese carbonate, you give crops manganese right away. It is about 26% manganese by weight. This makes it a good way to give plants this nutrient. Manganese carbonate does not dissolve much in water. But it dissolves well in weak acids. This helps manganese ions go into the soil. Plants can then take in the manganese. The compound stays stable at room temperature. If it gets hot, it can turn into manganese oxides. These oxides also help crops grow. Because of these features, manganese carbonate gives plants manganese they can use fast.
Tip: Manganese carbonate works best in soils that need a slow and steady supply of manganese.
Why Use MnCO₃
You may ask why mnco₃ is better than other manganese sources. Mnco₃ is special because plants can use its manganese easily. This means plants get more benefit from it. Studies show that using mnco₃ helps plants grow taller. It also gives more tillers and heavier grains. These results are like those from manganese sulfate. But mnco₃ often works even better. It helps crops use more manganese from the same amount.
Mnco₃ is also in many micronutrient mixes. It helps make soil richer and plants healthier. Farmers use mnco₃ to fix manganese problems in soil. This is helpful in soil with high pH or bad drainage. Adding mnco₃ helps crops grow their best.
Mnco₃ as a fertilizer helps wheat, potatoes, soybeans, and other crops.
You can use it alone or mix it with other nutrients for better soil.
Crop Health Benefits

Chlorophyll and Photosynthesis
Plants need healthy leaves to grow well. Mnco₃ gives plants the manganese they need for chlorophyll. Chlorophyll helps plants use sunlight to make energy. When you add mnco₃, plants build better chloroplasts. Chloroplasts are small parts in cells that use light to make food.
Manganese helps organize thylakoid membranes in plant cells. These membranes are where photosynthesis happens.
If plants do not get enough manganese, their leaves may turn yellow. The photosynthetic system will not work well.
Mnco₃ helps keep the right balance between photosystem I and photosystem II. This balance lets plants use light more efficiently.
When you use mnco₃, plants can store extra manganese in safe places inside their cells. This storage protects them from getting too much manganese at once.
Plants with enough manganese from mnco₃ have stronger photosynthesis. They take in more light and move electrons faster. This helps them grow better.
Enzyme Activation
Mnco₃ helps with more than just photosynthesis. It also turns on important enzymes in plants. These enzymes help plants make energy and build strong roots.
Manganese from mnco₃ turns on nitrate-reducing enzymes. These enzymes help plants use nitrogen, which is important for growth.
Mnco₃ supports enzymes that manage carbohydrates. Plants can make and store starch better.
With enough manganese, plants keep nitrate levels low. This helps roots grow longer and cells stretch out.
Mnco₃ boosts enzyme systems that help with respiration and energy use.
When you use mnco₃, you give plants what they need to grow fast and stay healthy. This is important in farming when you want every plant to do its best.
Plant Strength
Strong plants can fight disease and handle stress. Mnco₃ helps plants build tough cell walls. Manganese helps enzymes make lignin. Lignin makes stems and leaves firm.
Mnco₃ increases lignin in cell walls. This makes plants harder to break and less likely to fall over.
Manganese from mnco₃ helps plants fight off diseases. It boosts antioxidant enzymes like superoxide dismutase. These enzymes protect cells from damage.
When you use mnco₃, plants can block fungi and bacteria. Manganese helps stop harmful enzymes from breaking down cell walls.
Mnco₃ helps plants keep water and food moving through strong vascular tissues.
Plants with enough manganese from mnco₃ show fewer signs of disease. They have thicker cell walls and more phenolic compounds. These act as shields against pests and germs.
You will see a big difference in your crops when you use mnco₃. Plants grow taller, stand stronger, and resist disease better. This makes mnco₃ a good choice for anyone who wants healthy, high-yield crops.
Impact on Yield
Field Results
You can see real changes in your crops when you use manganese carbonate in fields that lack enough manganese. Researchers tested different treatments on sandy loam soils. They measured both grain and straw yields. The table below shows how each treatment affected the results:
Treatment Description | Grain Yield (kg/ha) | Straw Yield (kg/ha) |
|---|---|---|
Control (No Mn) | 4,661 | 7,519 |
MnCO₃ (single dose, early) | 5,054 | 9,131 |
MnCO₃ (single dose, late) | 5,119 | 8,942 |
0.5% MnSO₄·H₂O (foliar spray) | 5,199 | 9,058 |
You can also view the results in the chart below. This chart compares grain and straw yields for each treatment:
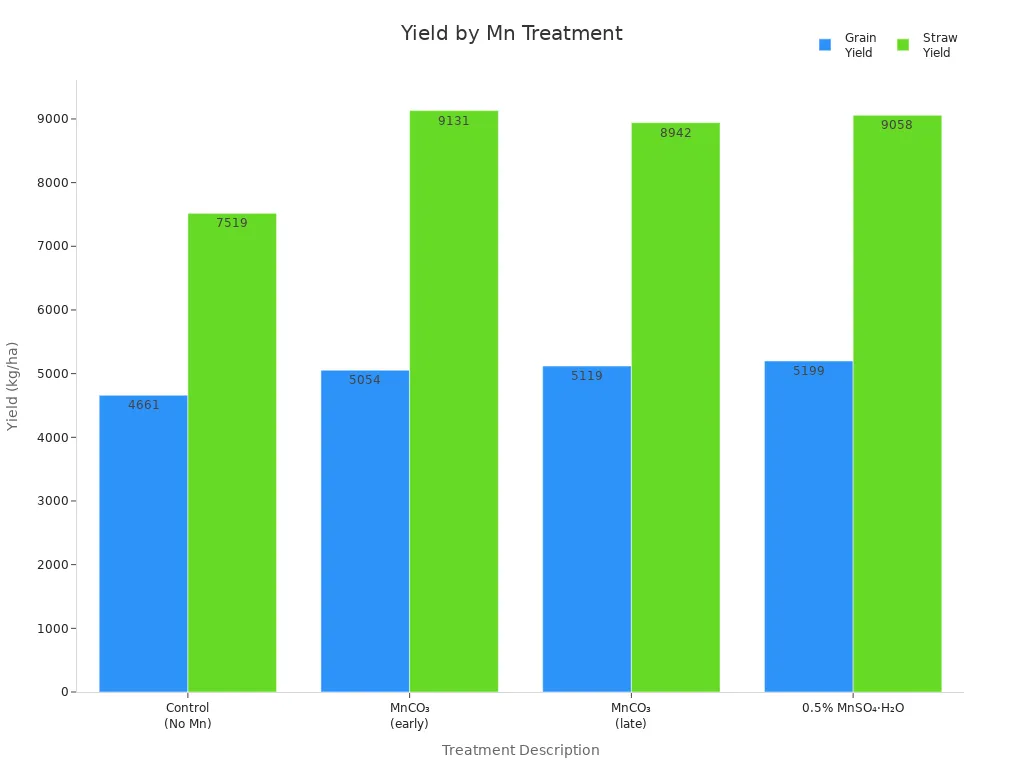
When you add manganese carbonate early in the season, you help your crops grow more grain and straw than if you do not add any manganese. Foliar sprays with manganese sulfate give the highest yields, but manganese carbonate still gives a strong boost. These results show that manganese carbonate works best in soils that do not have enough manganese. You may not see the same effect in soils that already have enough of this nutrient.
Note: You should test your soil before applying manganese carbonate. This helps you target fields that will benefit the most.
Maize and Other Crops
If you grow maize in manganese-deficient fields, you can expect up to a 10% increase in yield when you use manganese carbonate at rates of 0.5–1 kg/ha. Your maize will have greener leaves and fuller kernels. These changes help you meet quality standards in agriculture and may let you earn higher prices for your grain.
Other crops like potatoes, soybeans, and wheat also respond well to manganese carbonate when the soil lacks manganese. You will see stronger plants and better harvests. However, most studies focus on maize, so you should watch your other crops closely and adjust your practices as needed.
Greener leaves and stronger plants mean your crops use sunlight better and resist stress. This leads to better harvests and healthier fields.
Application and Best Practices

Rates and Timing
Farmers should use 0.5 to 1 kg per hectare of manganese carbonate. Most people see good results with these amounts. It is best to add it early. You can put it on before planting or when plants are small. This helps young plants get manganese for strong roots and leaves. If you see yellow leaves or weak stems, try a foliar spray for fast help. Always look at your soil test before choosing how much to use.
Tip: Use manganese carbonate on days with little wind. This stops it from blowing away.
Suitable Crops
Many crops do well with manganese carbonate. You can use it for maize, wheat, potatoes, and soybeans. These crops often need more manganese in cool or wet soils. Sandy soils and soils with high pH also need extra manganese. Watch your plants for yellow between leaf veins or slow growth. These signs mean your crops need more manganese. Manganese carbonate works in most soils, but do not use it if your soil already has enough manganese.
Crop | Best Timing | Soil Type |
|---|---|---|
Maize | Early growth | Sandy, high pH |
Wheat | Pre-planting | Cool, wet |
Potatoes | Early growth | Poor drainage |
Soybeans | Pre-planting | Sandy, high pH |
Safety Tips
You must be careful when using manganese carbonate fertilizer:
Read and follow all label rules.
Treat all fertilizers with care, even natural ones.
Know what is in the fertilizer and how to use it.
Wear gloves and goggles when using it.
Use it on calm days to stop drift and runoff.
Keep fertilizer out of water.
Keep pets and animals away from treated spots.
Wait before letting people or pets back in.
Store it in the original container in a cool, dry place.
Know who to call in an emergency.
Breathing in dust from manganese carbonate can hurt your health. Use dust control and wear a mask if needed. Store fertilizer in a dry, airy place to keep it safe. Clean up spills right away to protect nature. Always follow local rules for using fertilizer.
Note: Being safe keeps you, your crops, and nature healthy.
Challenges and Solutions
Overuse Risks
Some people think using more manganese carbonate helps crops. But too much can hurt plants and soil. Plants may get brown spots on old leaves. Young leaves can have yellow dots. Growth may slow down, and you might get less food. Too much manganese harms photosynthesis and enzymes. It also stops plants from taking in iron, zinc, copper, and calcium. This makes cell walls weak and plants less stable.
If your soil has low pH, bad drainage, or lots of water, watch for these signs. These things make manganese easier for plants to take in. Too much can cause problems.
Brown spots on older leaves
Yellow dots on young leaves
Slow growth and less food
Weak stems and plants that fall over
Check manganese levels often. Use the right amount of fertilizer to stop these problems.
Soil Compatibility
Check your soil before using manganese carbonate. Soil pH, drainage, and organic matter change how much manganese plants can use. Acidic soils with pH below 5.5 and wet fields give plants more manganese. This can cause too much and hurt plants. Sandy soils and soils with lots of organic matter may need more manganese. But always test first.
Take plant samples to check for too little or too much manganese.
Look for yellow between leaf veins.
Check problem spots every year, especially if pH is below 5.0 or above 6.5.
If you think there is a problem, use both soil and plant tests before adding more nutrients.
Practical Solutions
You can fix manganese problems with easy steps. Keep soil pH between 5.5 and 6.5. Add lime to raise pH if soil is too acidic. Make sure water drains well to stop waterlogging. Add organic matter to help roots and keep nutrients in the soil. Use both manure and fertilizer to help soil and crops.
Solution | Benefit for Crops | How It Works |
|---|---|---|
Lime application | Lowers manganese problems | Raises pH and makes manganese less easy to take in |
Organic matter addition | Helps keep nutrients in soil | Helps roots grow and take in micronutrients |
Balanced fertilization | Stops nutrient problems | Gives plants the right mix of food and nutrients |
Drainage improvement | Lowers risk of too much manganese | Stops water from building up in the soil |
Write down where you see problems and test soil often. This helps you use fertilizer the right way and keep crops healthy.
You can help your crops grow better by using manganese carbonate (MnCO₃) fertilizer. This micronutrient helps plants make food from sunlight. It also helps them use nitrogen and turn on important enzymes. These things make plants stronger and help them give you more food. MnCO₃ gives manganese to crops slowly. This means your plants get a steady supply of this nutrient.
Test your soil before you use MnCO₃.
Use the right amount at the right time.
Talk to local experts if you need help.
For more ideas on good farming, look at trusted farm guides or ask university extension services.
FAQ
How do you know if your crops need MnCO₃?
Look for yellowing between leaf veins or slow growth. You can test your soil for manganese levels. If your soil test shows low manganese, your crops will benefit from MnCO₃.
Can you mix MnCO₃ with other fertilizers?
Yes, you can mix MnCO₃ with most common fertilizers. Always check the label for compatibility. Mixing helps your crops get a balanced supply of nutrients.
Is MnCO₃ safe for the environment?
MnCO₃ is safe when you use it as directed. Avoid overuse to protect water and soil. Store it properly and clean up spills right away.
Which crops benefit most from MnCO₃?
| Crop | Benefit Level |
|---|---|
| Maize | High |
| Wheat | High |
| Potatoes | Medium |
| Soybeans | Medium |
You will see the best results in maize and wheat, especially in soils low in manganese.
Related Posts

I am Edward lee, founder of manganesesupply( btlnewmaterial) , with more than 15 years experience in manganese products R&D and international sales, I helped more than 50+ corporates and am devoted to providing solutions to clients business.





