For homes with iron, manganese, or hydrogen sulfide in their water, the manganese sand vs. greensand plus debate centers on which filtration media delivers high-quality filtration solutions. Manganese sand features a natural sand substrate with a manganese oxide coating, while greensand plus uses a more durable silica base and advanced coating. Both media effectively remove contaminants that cause staining, discoloration, and unpleasant odors. Selecting the right option depends on careful water testing and matching the media’s strengths to those specific conditions.
Manganese sand uses solid manganese dioxide and offers stronger oxidation, higher flow rates, and longer lifespan, making it ideal for large or high-demand water systems.
Greensand Plus has a silica core with a manganese oxide coating, making it lighter, easier to handle, and better suited for smaller systems with lower flow and budget limits.
Both media effectively remove iron, manganese, and hydrogen sulfide when regularly regenerated with potassium permanganate or chlorine, ensuring clean, odor-free water.
Testing your water for contaminants, pH, and flow rates is essential to choose the right media and maintain system performance over time.
Greensand Plus requires less maintenance and lower chemical costs, while manganese sand excels in durability and performance for tougher water conditions.
Key Differences
Substrate and Coating
The core difference between traditional greensand media and Greensand Plus lies in their substrate and coating. Traditional greensand media uses a glauconite core with an ionically bound manganese dioxide coating. Greensand Plus, on the other hand, features a silica sand core with a fused manganese dioxide coating. This technical upgrade allows Greensand Plus to withstand a wider range of operating conditions. It performs better in water with low silica, high total dissolved solids, increased hardness, and higher temperatures. The fused coating also provides greater resistance to breakdown, making Greensand Plus a more robust choice for demanding filtration applications.
Durability and Longevity
Durability remains a key factor when comparing filtration media. The table below highlights the main differences:
Aspect | Traditional Greensand Media | Greensand Plus |
|---|---|---|
Core Material | Glauconite | Silica sand |
Coating Attachment | Ionically bound | Fused |
Durability in Challenging Waters | Less durable | More durable |
Temperature Tolerance | Lower | Higher |
Differential Pressure Tolerance | Lower | Higher |
Average Lifespan | Similar or slightly shorter |
Traditional greensand media tends to break down over time, especially under harsh conditions. Greensand Plus offers longer run lengths and a greater margin of error during operation. However, both types may have a shorter lifespan compared to premium manganese oxide media, which can last up to 30 years.
Regeneration Needs
Both traditional greensand media and Greensand Plus require periodic regeneration to maintain their filtration performance. Operators typically use potassium permanganate for this process. Greensand Plus, due to its fused coating, often tolerates more aggressive regeneration cycles and higher differential pressures without rapid degradation. This feature reduces maintenance frequency and helps maintain consistent filtration efficiency, especially in systems with fluctuating water quality.
Manganese Sand vs. Greensand Plus
Performance Comparison
The manganese sand vs. greensand plus debate centers on how each media performs in removing iron, manganese, and hydrogen sulfide from water. Both filters rely on oxidation and adsorption, but their efficiency changes with regeneration and operational conditions. Studies show that using potassium permanganate as a regenerant greatly increases removal rates for both iron and manganese. The following table summarizes key findings from controlled studies:
Parameter | Without Potassium Permanganate (KMnO4) | With Potassium Permanganate (KMnO4) |
|---|---|---|
Iron Removal Efficiency (%) | Outlet Fe < drinking water limits | |
Manganese Removal Efficiency (%) | 27.26 | Outlet Mn < drinking water limits |
Equilibrium Column Capacity for Iron (mg/g) | 5.18 | 12.70 |
Equilibrium Column Capacity for Manganese (mg/g) | 2.16 | 11.29 |
Hydrogen Sulfide Removal Efficiency | N/A | N/A |
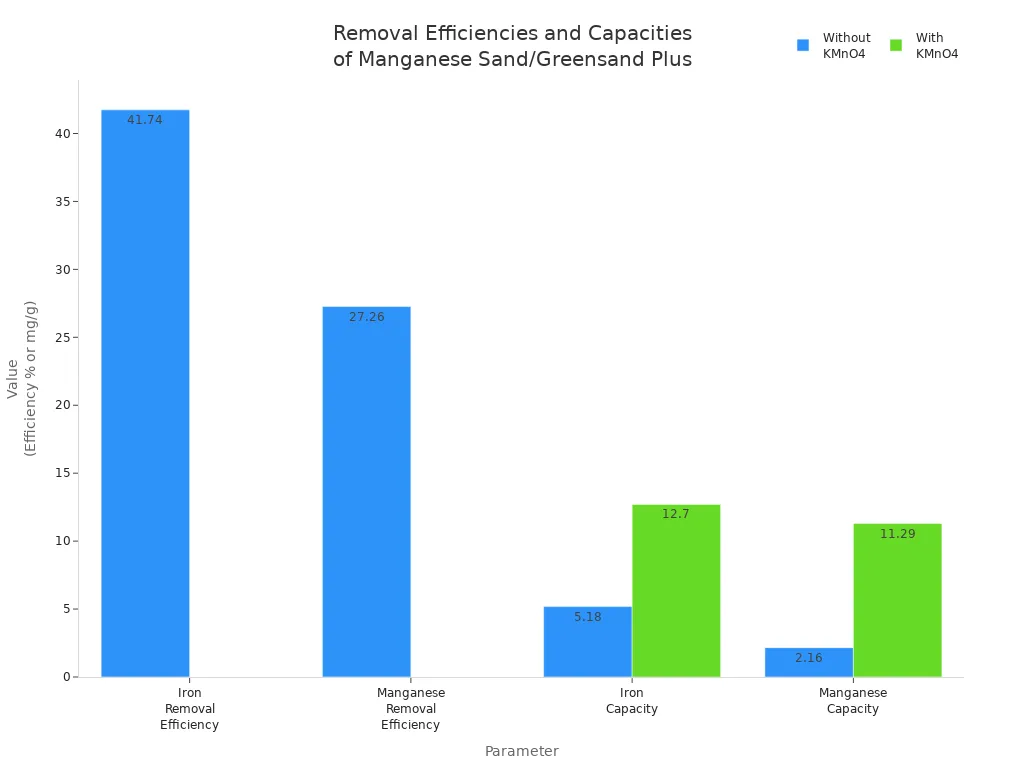
Potassium permanganate boosts the optimal performance of both manganese sand and greensand plus. Iron and manganese removal rates rise sharply, with outlet concentrations dropping below drinking water standards. Hydrogen sulfide removal data remains limited, but field experience suggests both media can reduce odors when properly regenerated.
Greensand plus, with its fused coating and silica core, resists breakdown better than traditional greensand. This durability allows it to maintain high removal rates even under challenging conditions, such as high dissolved solids or temperature swings. Manganese sand, made from solid manganese dioxide, offers even stronger oxidation power and higher service flow rates. This makes it suitable for demanding filtration applications where space and longevity matter.
Application Scenarios
Choosing between manganese sand vs. greensand plus depends on system requirements, water quality, and operational constraints. The following table highlights the main differences in application:
Criteria | Manganese Sand (Solid Manganese Dioxide Media) | Greensand Plus (Coated Manganese Media) |
|---|---|---|
Media Composition | High purity (>80% manganese ore), solid manganese dioxide | Thin manganese oxide coating over silica |
Oxidation Strength | Stronger oxidation capability | Effective but less strong than solid media |
Lifespan | Long lifespan, often decades | Shorter lifespan, typically around 5 years |
Weight | Heavier (120–140 lbs/ft³) | Lighter (around 80 lbs/ft³) |
Backwash Flow Requirement | Requires higher backwash flow rates | Requires less backwash flow |
Service Flow Rate | Higher service flow rates, allowing smaller tanks | Lower service flow rates |
Suitability | Preferred for high performance, longevity, space efficiency | Preferred for systems with low well pump flow, budget constraints, or where lighter media is advantageous |
Note: Manganese sand works best in municipal or industrial treatment plants that need high throughput and long media life. Greensand plus fits residential or small community systems with limited pump capacity or budget.
Regulatory standards also influence the manganese sand vs. greensand plus decision. The U.S. EPA sets secondary limits for iron and manganese in drinking water to prevent staining and taste issues. Both media help water treatment facilities meet these standards. Greensand plus, also known as CalMedia GSR Plus, offers operational advantages such as faster backwash cycles and easier maintenance. It eliminates the need for air-scouring, which reduces wear and extends filter life. Availability can also play a role, as greensand plus often has shorter lead times than traditional greensand.
Water Conditions

Iron and Manganese Removal
Iron and manganese removal remains a primary goal for many water filtration systems. Both manganese sand and greensand plus excel at this task. These media use oxidation and filtration to convert dissolved metals into solid particles, which the filter then captures. Operators often choose these options for efficient iron and manganese removal in municipal and residential water treatment. Manganese sand, with its high manganese dioxide content, provides strong oxidation power. Greensand plus, with its advanced coating, offers reliable performance in a wide range of water conditions. Regular regeneration with potassium permanganate keeps both media effective for long-term use.
Hydrogen Sulfide
Hydrogen sulfide causes rotten egg odors and can corrode plumbing. Greensand plus and other catalytic media remove hydrogen sulfide through oxidation and filtration. The table below compares several media used for hydrogen sulfide removal in water treatment:
Media Type | Description & Composition | Effectiveness in H2S Removal | Certifications & Usage | Field Example & Results |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Greensand Plus | Traditional manganese-based media | Effective at removing hydrogen sulfide and manganese | NSF/ANSI/CAN 61 certified | Used by City of Delano, MN before upgrade; removed manganese to 0.058 mg/L average |
OxiPlus12 | Improved catalytic media with higher MnO2 coating | Faster contaminant removal including hydrogen sulfide | BABAA certified; suitable for municipal & industrial use | After upgrade in Delano, manganese dropped to 0.036 mg/L (38% improvement), better system efficiency |
OxiPlus75 | Natural pyrolusite mineral (~75% manganese dioxide) | Highly efficient for iron, manganese, arsenic, H2S, radium | NSF/ANSI/CAN 61 and BABAA certified | Used in WaterPlus filtration systems; supports higher flow rates and specialized contaminant removal |
Tip: Operators can retrofit existing greensand systems with OxiPlus media for improved hydrogen sulfide removal and better system runtimes.
pH and Other Factors
Water pH affects the performance of all filtration media. Both manganese sand and greensand plus work best when the pH stays above 6.8. Low pH can reduce oxidation efficiency and limit contaminant removal. High levels of dissolved solids, hardness, or temperature may also impact filter life and effectiveness. Operators should always test water quality before selecting a media. Matching the right media to the specific water conditions ensures reliable water filtration and long-term treatment success.
Practical Factors
Installation
Installation of manganese sand and greensand plus filters requires careful planning. Most systems fit into existing plumbing with minimal changes. Technicians often recommend checking the available space and water pressure before starting. Manganese sand filters weigh more than greensand plus filters, so installers may need extra support for larger tanks. Both types of filters work well in whole house or well water systems. Homeowners should always follow manufacturer guidelines to ensure proper setup and safe operation.
Maintenance
Routine maintenance keeps filtration systems running smoothly. Both manganese sand and greensand plus filters need regular backwashing to remove trapped particles. Operators must also regenerate the media with potassium permanganate to restore its filtering ability. Greensand plus filters usually require less frequent regeneration because of their durable coating. Manganese sand filters may need more attention if the water contains high levels of iron or manganese. Technicians suggest checking the system every few months to prevent clogging and maintain water quality.
Tip: Schedule filter inspections and regeneration at the same time to save effort and avoid missed steps.
Cost
Cost plays a major role in choosing a filtration system. Initial costs for whole house or well water filters range from $1,000 to over $4,000. Installation usually adds $200 to $600, depending on system size and complexity. Annual maintenance costs can vary from $80 to $500 or more, especially for systems that need frequent chemical top-ups. Manganese greensand media lasts 6 to 12 years, while greensand plus offers similar longevity. The table below summarizes typical costs:
System Type | Initial Cost Range | Installation Cost Range | Annual Maintenance Cost Range |
|---|---|---|---|
Whole House Systems | $1,000 – $4,000+ | $200 – $500 | $80 – $500+ |
Well Water Systems | $1,000 – $4,000+ | $200 – $600 | $100 – $400 |
Chemical Injector Systems | N/A | N/A | $50 – $500+ |
Greensand plus filters often prove more cost-effective for homes with lower water flow or limited budgets. Manganese sand filters suit larger systems that need higher flow rates and longer service life.
Greensand Pros and Cons
Manganese Sand
Manganese sand stands out for its high purity and solid composition. This media contains more than 80% manganese dioxide, which gives it strong oxidation power. Water treatment systems often use manganese sand when they need to remove high levels of iron or manganese. The solid structure allows for higher service flow rates and longer media life. Many municipal and industrial plants choose manganese sand for its durability and efficiency.
However, manganese sand has a heavier weight, usually between 120 and 140 pounds per cubic foot. This weight requires stronger support structures and higher backwash flow rates. The initial cost is higher than coated media, but the long lifespan can offset this expense over time. Maintenance involves regular backwashing and regeneration, especially in systems with high contaminant loads.
Tip: Manganese sand works best in large-scale applications where performance and longevity matter most.
Greensand Plus
Greensand plus offers a lighter alternative to solid manganese media. It uses a silica core coated with manganese oxide, making it easier to handle and install. Many residential and small community systems prefer greensand plus because it requires lower backwash flow rates and fits well with limited pump capacity.
The table below summarizes the main advantages and disadvantages of greensand plus:
Aspect | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
Composition | Effective for iron and manganese removal | Less durable than solid manganese dioxide media |
Weight | Lighter, easier to handle | Not suitable for high-flow systems |
Lifespan | Suitable for budget constraints, replaced every 5 years | Shorter lifespan than solid media |
Performance | Works well with low well pump flow | Weaker oxidation strength |
Cost | Less expensive upfront | May need more frequent replacement |
Maintenance | Regular backwashing and possible chlorine injection | Maintenance needed to maintain performance |
Suitability | Good for lower flow rates and budget users | Outperformed by solid media in longevity and flow |
Greensand plus provides reliable filtration for homes and small systems. Operators should consider the shorter lifespan and maintenance needs when choosing this media.
Decision Guide
Checklist
Selecting the right filtration media depends on several practical and technical factors. Use this checklist to guide the decision process:
Identify the main contaminants in the water, such as iron, manganese, or hydrogen sulfide.
Test the water for pH, hardness, and total dissolved solids.
Determine the available backwash flow rate and system size.
Assess the need for chemical regenerants and the associated costs.
Consider maintenance requirements and available equipment.
Review the expected lifespan and replacement frequency of the media.
Evaluate the ease of integrating new media into existing systems.
The table below summarizes key factors for comparison:
Factor | Manganese Green Sand | Greensand Plus (GSP) |
|---|---|---|
Chemical Regenerant | Requires potassium permanganate | Uses chlorine only |
Regenerant Cost | Higher (permanganate is expensive) | Lower (chlorine costs about one-fifth) |
Maintenance Equipment | Needs chemical feed pumps and storage tanks | No extra chemical feed equipment needed |
Physical Properties | Standard media properties | Identical to manganese green sand |
System Compatibility | Needs specific backwash/service rates | Can substitute directly without changes |
Note: Greensand Plus offers cost savings and simpler maintenance by using chlorine for regeneration. It can often replace manganese sand without major system changes.
Flowchart
A simple flowchart helps clarify the selection process for water filtration media:
Does the water contain high levels of iron, manganese, or hydrogen sulfide?
If yes, proceed to step 2.
If no, consider other filtration options.
Is the system equipped to handle potassium permanganate safely?
If yes, both manganese sand and Greensand Plus are suitable.
If no, Greensand Plus is preferred due to chlorine regeneration.
Is minimizing maintenance and chemical costs a priority?
If yes, choose Greensand Plus.
If no, either media can be used based on other factors.
Does the system require high flow rates and long media life?
If yes, manganese sand may offer better performance.
If no, Greensand Plus provides a lighter, easier-to-handle option.
Tip: Always test water quality before making a final decision. Consult a water treatment professional for complex systems.
Manganese sand excels in high-flow, long-life applications with heavy iron or manganese, while Greensand Plus fits homes needing lighter media and simpler maintenance. Experts advise starting with a professional water test to match media to contaminants.
Media Type | Best For |
|---|---|
Manganese Dioxide | Well water with iron, sulfur, arsenic |
Greensand Plus | Residential iron and manganese removal |
Common mistakes include skipping water analysis, ignoring flow rates, and choosing the wrong system. Test water first and consult a specialist for the best results.
FAQ
What is the main difference between manganese sand and Greensand Plus?
Manganese sand uses solid manganese dioxide, while Greensand Plus features a silica core with a manganese oxide coating. This difference affects durability, oxidation strength, and suitability for various water conditions.
Can both media remove hydrogen sulfide from water?
Both manganese sand and Greensand Plus can remove hydrogen sulfide when properly regenerated. Operators often choose Greensand Plus for residential systems due to its lighter weight and easier maintenance.
How often should the media be regenerated?
Regeneration frequency depends on contaminant levels and water usage. Most systems require regeneration every few days to weeks. Regular regeneration ensures optimal performance and extends media lifespan.
Which is better for high iron or manganese levels?
For high iron or manganese, manganese sand often provides stronger oxidation and longer service life. Greensand Plus works well for moderate levels and systems with lower flow rates.
Related Posts

I am Edward lee, founder of manganesesupply( btlnewmaterial) , with more than 15 years experience in manganese products R&D and international sales, I helped more than 50+ corporates and am devoted to providing solutions to clients business.





