Manganese dioxide water pollution treatment uses a special mineral. It cleans water by taking out harmful metals and pollutants. This process works in three main ways. Oxidation changes toxic things into safer forms. Adsorption grabs unwanted particles on its surface. Filtration traps impurities in the water. Manganese dioxide often works better than other filtration materials. It removes heavy metals like lead and copper well. Its eco-friendly nature makes it good for the environment. It does not cost much, so it is a practical choice for cleaning water.
- Manganese dioxide cleans water in three ways. It oxidizes, adsorbs, and filters harmful metals and pollutants.
- It removes heavy metals like lead, cadmium, copper, and zinc. This makes water safer for people to drink.
- The mineral works best in water that is a little alkaline. It needs good care to keep working well.
- Manganese dioxide filters last for many years. They are good for the environment and cost less than most other materials.
- People use this method in homes, factories, and cities. It helps make water cleaner and removes bad smells.
Manganese Dioxide Water Pollution Remediation
What Is Manganese Dioxide?
Manganese dioxide is a black or brown mineral. It does not mix with water, so it stays solid. This mineral can cause chemical changes called oxidation. It helps turn dangerous things into safer ones. Manganese dioxide has many tiny holes in it. These holes trap and hold bad stuff from water. Because of these features, it is great for cleaning water.
Manganese dioxide comes in different types, like pyrolusite and birnessite. Each type has a slightly different structure, but all are good for water treatment. Some types, like α-MnO2, have open channels. These channels help them grab and remove more impurities.
Why Use Manganese Dioxide?
Many scientists and engineers pick manganese dioxide for water pollution solutions for many reasons:
Manganese dioxide is a catalyst. It helps remove dissolved manganese by turning it into a solid that can be filtered out.
The process works faster and better with manganese dioxide. Without it, removing manganese from water is slow and does not work as well.
Manganese dioxide is safe for people and the environment. It is even used to treat mineral water.
The technology is trusted and tested. You can pick different types of manganese dioxide to match the water for the best results.
Manganese dioxide water pollution treatment also saves money. Makers can mix manganese dioxide with things like bamboo carbon or guava leaf powder. These mixes cost less and make it easier to clean lots of water. The materials are simple to make and can be used again and again with little loss in how well they work.
Aspect | Summary |
|---|---|
MnO2 mixes with natural materials are cheap and good for the planet. | |
Preparation | Easy ways let people make a lot for less money. |
Performance | Removes a lot of bad stuff and stays strong, even after reuse. |
Comparison | Works better than many carbon-based materials in price and strength. |
Regeneration | Can be used again, so it is more eco-friendly. |
Manganese dioxide water pollution remediation is a smart, green, and low-cost way to take out harmful things from water.
Pollutants and Heavy Metals Removed

Targeted Heavy Metals
Manganese dioxide helps clean water by removing heavy metals. It works best for lead, cadmium, copper, and zinc. These metals are dangerous if people drink them. Manganese dioxide grabs the metal ions and holds them on its surface. The process works better when the water’s pH is just right.
Heavy Metal Ion | Removal Rate at 600 min (%) | Removal Capacity at Breakthrough (mg/g) | Treatable Bed Volume (BV) |
|---|---|---|---|
Pb(II) | 2.1 × 10^6 | 320 | |
Cd(II) | >98 | 1.1 × 10^6 | 233 |
Cu(II) | >98 | 6.7 × 10^5 | 267 |
Zn(II) | >98 | 5.2 × 10^5 | 213 |
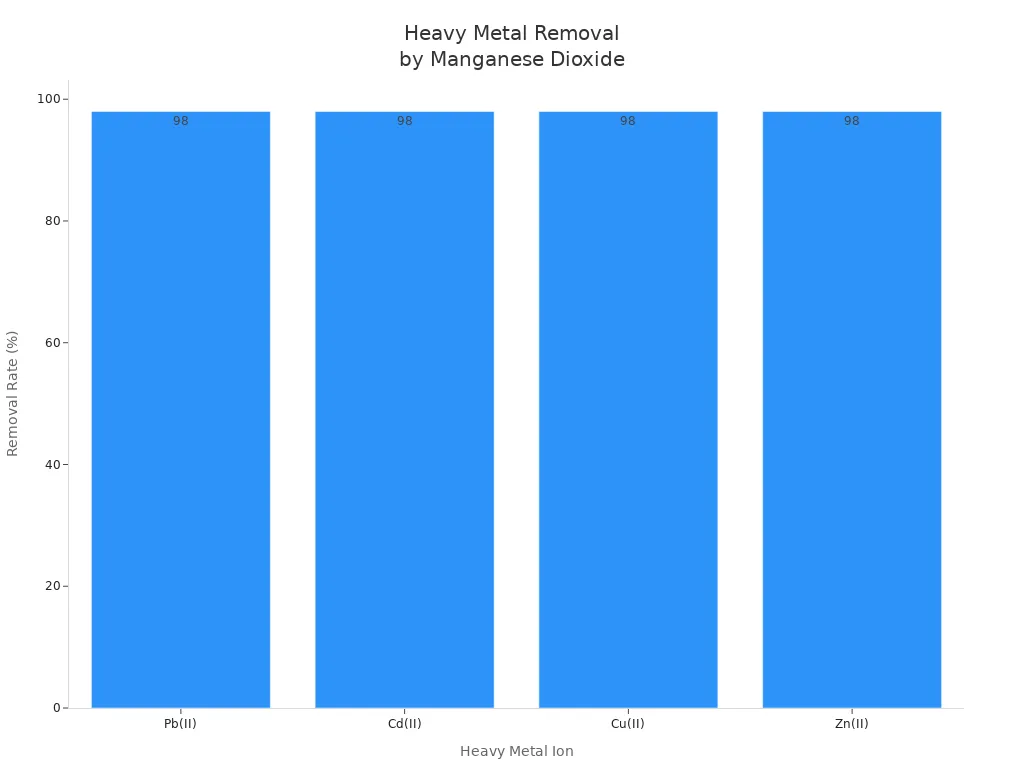
Manganese dioxide composites can take out almost all the lead in water. They can hold a lot of lead. The process works best when the water is a little acidic.
Organic Pollutants
Manganese dioxide also helps remove organic pollutants. These include antibiotics and chemicals from factories. It can trap molecules like tetracycline and oxytetracycline. These are often found in dirty water. The mineral uses adsorption and oxidation to break down these pollutants.
Pollutant | Form of Manganese Dioxide Used | Removal Efficiency / Adsorption Capacity | Removal Mechanism(s) |
|---|---|---|---|
Tetracycline (TC) | Hydrous manganese dioxide hydrogel composite | Adsorption, chemisorption, pH dependent | |
Oxytetracycline (OTC) | MnO2@PSA hydrogel composite | Adsorption, oxidative degradation |
Manganese dioxide can also remove other organic pollutants. It attracts molecules with certain shapes and charges. Some types can even break down strong chemicals like 3-chlorophenol. They do this using reactive oxygen species. This makes the cleaning process quick and strong.
Iron and Manganese
Manganese dioxide also helps remove iron and manganese from water. These metals are often found in groundwater. They can stain pipes and make water taste bad. Manganese dioxide changes the metals into solids. These solids get stuck in filters.
Treatment Method | Iron Removal Efficiency (%) | Manganese Removal Efficiency (%) |
|---|---|---|
Open-aeration + Chlorine | 62.5 | |
Chlorine only | 67.7 | 58.0 |
Tray aerators (Physical only) | 57.0 | 48.7 |
Sand filtration only | 42.6 | 38.9 |
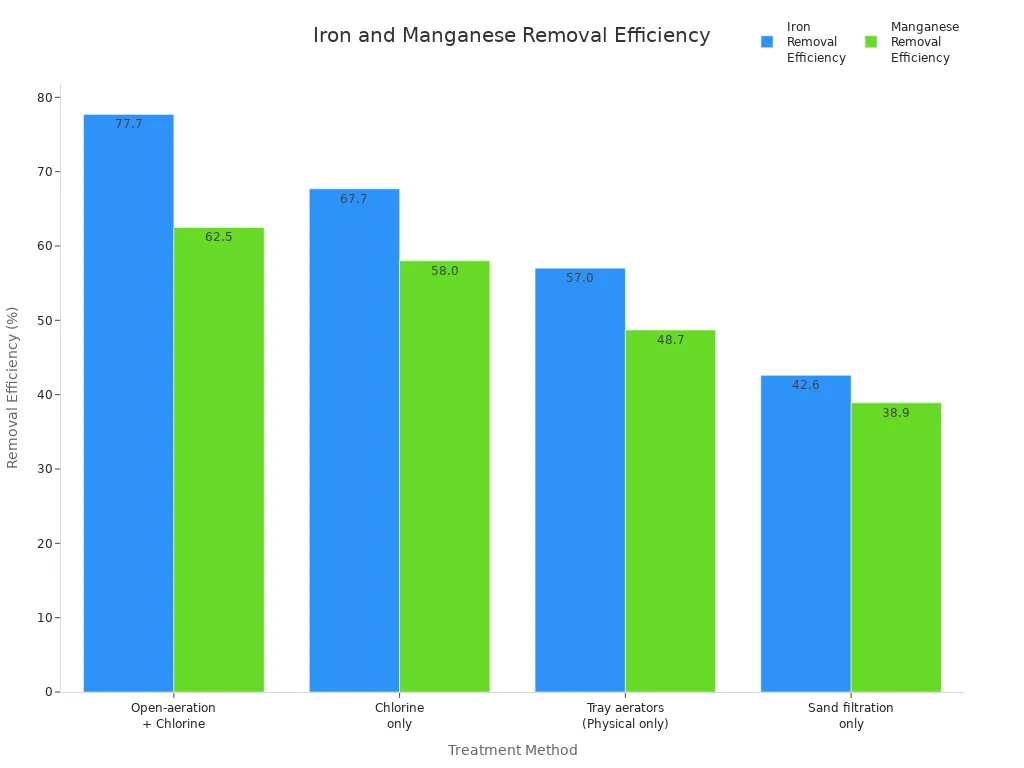
Manganese dioxide uses oxidation to turn iron and manganese into particles. Filters can catch these particles. The best results come from using both chemical and physical methods together.
Removal Mechanisms
Oxidation
Manganese dioxide is a strong oxidizer in water treatment. When water moves through manganese dioxide, it makes harmful things safer. This works well for metals like iron and manganese. Manganese dioxide changes dissolved iron and manganese into solid bits. These solids are easy to filter out.
Manganese dioxide pulls dissolved manganese to its surface.
It uses surface-catalyzed oxidation to change manganese from Mn(II) to Mn(III/IV).
The solid bits are simple to remove with filters.
Manganese dioxide also helps break down many organic chemicals. It works best on things like phenols, bisphenol A, and some pesticides. The mineral can keep working for many years, sometimes up to 25 years. Some water plants use manganese dioxide on sand to help oxidation. This method works well for stormwater and city water.
Biofiltration can make oxidation stronger. Tiny microbes living on manganese dioxide help speed up the process. This makes manganese dioxide water treatment work better and last longer.
Adsorption
Adsorption means manganese dioxide grabs and holds pollutants on its surface. The mineral has a big surface area with lots of tiny holes and channels. These spaces trap heavy metals like lead, cadmium, copper, and zinc. The structure of manganese dioxide, like birnessite or cryptomelane, changes how much it can hold.
Manganese Oxide Mineral | Structure Type | Cd Adsorption Capacity (mmol/kg) | Co Adsorption Capacity (mmol/kg) | Cu Adsorption Capacity (mmol/kg) | Zn Adsorption Capacity (mmol/kg) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Birnessite | Layered Mn(IV) | ~1830 | ~1040 | ~1080 | ~1270 | ~1210 |
Cryptomelane | Tunnel Mn(IV) | ~293 | ~89 | ~76 | ~133 | ~87 |
Todorokite | Tunnel Mn(IV) | ~284 | ~85 | ~117 | ~191 | ~67 |
Hausmannite | Low-valence Mn | ~105 | ~3 | ~44 | ~189 | ~43 |
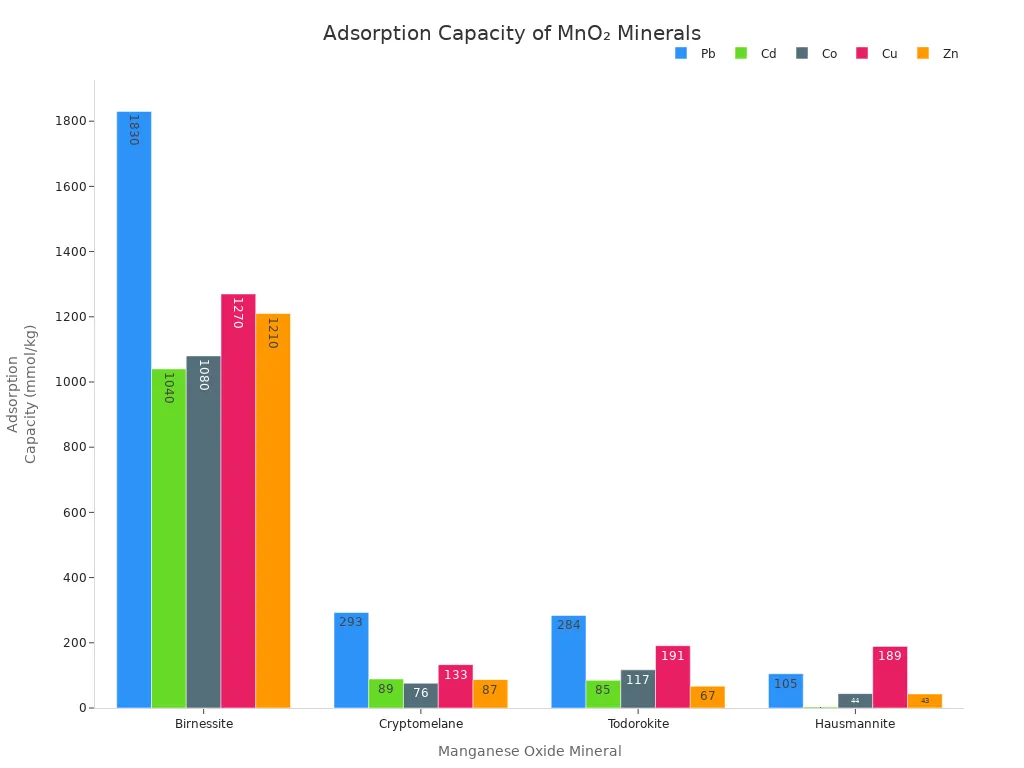
Special types of manganese dioxide, like Fe3O4/MnO2 core–shell nanocomposites, make adsorption better. These nanosorbents have a large surface area and are magnetic. The magnetic core lets people remove them with magnets. The MnO2 shell has spots for trapping heavy metals. These materials work best in water that is a little acidic or neutral.
Some composites can be used again after cleaning with acid. This saves money and makes less waste.
Filtration
Filtration is the last step in manganese dioxide water treatment. After oxidation and adsorption, the solid bits and trapped pollutants must be removed. Manganese dioxide acts as a filter media inside special tanks. Water flows through the media, and the solid bits get stuck.
The media helps oxidize iron, manganese, and hydrogen sulfide.
It traps the solids, making water clearer and taste better.
The filter media can be cleaned by backwashing to remove the solids and keep working.
There are two main kinds of manganese dioxide filter media:
Coated media, like Greensand or Birm, have a thin layer of manganese dioxide and need extra chemicals.
Solid media, such as Pro-OX or Pyrolox, use pure manganese dioxide and last longer but need faster water flow for cleaning.
Advanced filtration systems use manganese dioxide-coated sand or membranes for even better results. These systems can remove very tiny particles and work in homes, factories, and city water plants.
Manganese dioxide media not only filters out solids but also removes bad smells from hydrogen sulfide. This makes water safer and nicer to use.
Applications in Water Treatment
Household Filters
Many people use manganese dioxide in home water filters. Makers put manganese dioxide on filter materials like manganese greensand. These filters work best for whole-house systems, especially with well water. They help remove manganese, iron, and hydrogen sulfide. The filter changes dissolved manganese into a solid. This solid gets trapped in the filter. Homeowners like these filters because they are easy to care for. You just need to backwash and use potassium permanganate to keep them working. People pick these filters because they are reliable and simple to use. They also help lower iron and manganese without hard work.
Tip: Manganese greensand filters are great for taking out iron and manganese. They are popular in country areas.
Industrial and Municipal Use
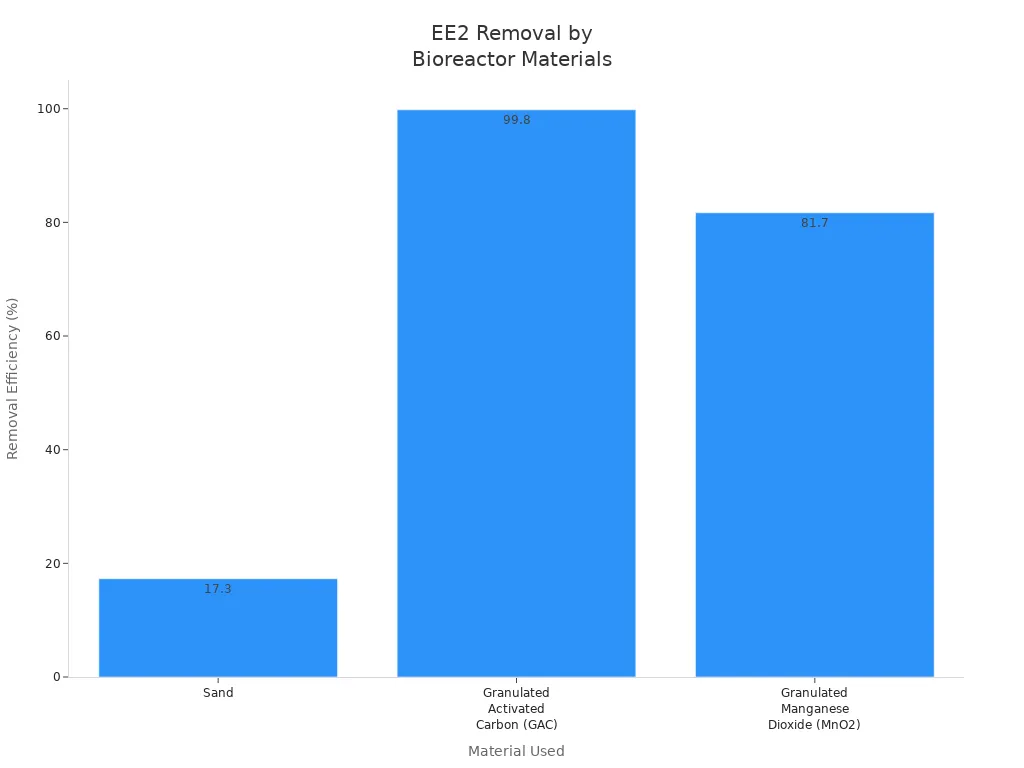
Factories and cities use manganese dioxide for better water cleaning. They often use granulated manganese dioxide in bioreactors to clean tough pollutants. For example, this material can remove up to 81.7% of EE2, a hard-to-remove chemical. The process uses adsorption and catalytic oxidation together. This works better than just using sand filters.
Material Used in Bioreactor | EE2 Removal Efficiency | Main Mechanism |
|---|---|---|
Sand | 17.3% | Filtration |
Granulated Activated Carbon | >99.8% | Adsorption |
Granulated MnO2 | 81.7% | Adsorption + Catalytic Oxidation |
City water plants also use manganese dioxide filters to clean water for everyone. For example, the Baldwin Pond Water Treatment Plant in Wayland, Massachusetts, used this method. They took out iron and manganese by using oxidation and filtration. This made the water better for the people in the town.
Activated Sludge and Modified Materials
Engineers make activated sludge systems better by adding manganese dioxide, often as nanoparticles. In special reactors, manganese dioxide helps bacteria move electrons faster. This helps break down pollutants like azo dyes more quickly. Manganese dioxide nanoparticles make the sludge conduct electricity better. They also help more acidogenic bacteria grow. This means the system removes more chemical oxygen demand and makes wastewater lose its color faster.
Manganese dioxide-modified activated carbon helps move electrons.
The Mn4+/Mn2+ cycle makes microbes work harder.
More acidogenic bacteria grow, and fewer methanogenic archaea are present.
Scientists have also made new membranes and magnetic adsorbents with manganese dioxide. These materials remove heavy metals like lead and manganese very well. They are easy to collect and use again.
Performance Factors
pH and Chemistry
The pH of water affects how well manganese dioxide works. When the pH is high, it removes more contaminants. For example, manganese removal goes from 8% at pH 2 to 99% at pH 9. At low pH, manganese stays as Mn²⁺ ions. These ions are hard to take out. Divalent ions like calcium and magnesium can lower removal rates. They compete for the same spots on the manganese dioxide. Monovalent ions like sodium and potassium do not change much.
Factor | Effect on Removal Efficiency |
|---|---|
pH > 9 | |
pH < 9 | Lower removal; Mn stays dissolved |
Divalent ions (Ca²⁺) | Moderate reduction due to competition |
Monovalent ions (Na⁺) | Minimal impact |
Tip: Keep water a little alkaline. Try to limit calcium and magnesium. This helps manganese dioxide work its best.
Dosage and Contact Time
How much manganese dioxide you use matters. The more you use, the more surface area there is. This helps pollutants stick better. A normal dose is about 10 grams per liter. Water should touch the manganese dioxide for at least 30 minutes. This gives good results. The best pH for removing manganese is between 6 and 10. Ozone can make reactions faster. But keep the pH between 6.5 and 8.0 to avoid problems.
Parameter | Optimal Value | Notes |
|---|---|---|
Dosage | ~10 g/L | More dosage means more adsorption |
Contact Time | ~30 minutes | Needed for effective removal |
pH Range | 6 to 10 | Alkaline pH works best |
Maintenance
Manganese dioxide filters need regular care to keep working well. Operators should backwash the filters to clean out solids. Some systems use chemicals like potassium permanganate to recharge the filter. Acid washing can help the adsorbent work again. Most filters last for many cycles if you take care of them. Water treatment rules say you must check pH, flow, and chemical levels often. Doing these things keeps water safe and clean.
Note: Always be careful with chemicals like potassium permanganate. Store them safely and follow local rules for water treatment.
Benefits and Limitations
Advantages
Manganese dioxide has many good points for cleaning water. It takes out iron and manganese from water very well. This helps stop stains and bad taste in drinking water. The media acts as a catalyst. It makes oxidation happen faster. This helps metals turn into solids that are easy to filter. Manganese dioxide lasts longer than other filter materials. You do not need to replace it often. Operators can clean the media by backwashing. This saves money and cuts down on waste.
Property | Manganese Dioxide Media | Activated Carbon | Quartz Sand |
|---|---|---|---|
Main Function | Removes iron, manganese | Removes organics, odors | Filters particulates |
Filtration Efficiency | High for metals | High for organics | Moderate for particulates |
Lifespan | 6–12 months | 3–5 years | |
Regeneration | Backwashing | Replacement needed | Backwashing |
Cost | Moderate | Higher | Low |
Strengths | Durable, eco-friendly | Good for taste, odor | Affordable, durable |
Weaknesses | Not for organics | Not for metals | Limited chemical removal |
Studies show manganese dioxide works as a catalyst for oxidation. Natural types like birnessite make redox reactions and ion exchange better. This makes manganese dioxide great for cleaning groundwater.
Drawbacks
Manganese dioxide has some problems too. Operators must watch pH closely. If pH is wrong, the media wears out and does not work well. It cannot remove manganese that is stuck to organic matter. Special steps are needed for that. Fast gravity filters cannot take out dissolved manganese unless it is oxidized first. Changing manganese levels in water make dosing and treatment harder.
Limitation/Drawback | Explanation |
|---|---|
pH Control and Media Exhaustion | Needs careful pH management; media wears out over time |
Ineffective for Organics | Cannot remove organic contaminants |
Disinfection Byproducts | Residual manganese can react with chlorine, forming harmful byproducts |
Customer Complaints | High manganese causes discoloration, taste issues, and pipe scaling |
Regulatory Limits | Strict standards require close monitoring |
Operators must follow health rules and limits. The USEPA says manganese in water should not go over 0.05 mg/L.
Safety and Disposal
Manganese dioxide is safe for water treatment if used right. But manganese compounds can be toxic if they get into nature. Mining and making manganese dioxide can pollute rivers and lakes. Too much manganese hurts fish and plants. It can cause yellow leaves and spots. Manganese is a toxicant for people. It can harm the brain and other organs.
Manganese pollution can hurt nature and people.
Toxicity depends on how much, how, and what species.
Microorganisms can help clean up manganese pollution.
Operators should throw away used manganese dioxide media the right way. Follow local rules to keep people and nature safe.
Manganese dioxide water pollution treatment takes out heavy metals and other bad stuff from water. It uses oxidation, adsorption, and filtration to make water safer to drink. People like it because it is good for the environment and lasts a long time. Manganese dioxide works best when the water has the right pH and when workers take care of the system. There are some limits, like needing to watch the pH closely. Many people pick this method to get clean and safe water.
FAQ
What does manganese dioxide remove from water?
Manganese dioxide takes out heavy metals like lead and copper. It also removes cadmium, zinc, iron, and manganese. Some organic pollutants are also taken out. This helps make water safer for drinking and using.
Is manganese dioxide safe for home water filters?
Yes, manganese dioxide is safe if used the right way. Many home water filters use it. People should always follow the maker’s directions for best results.
How long does manganese dioxide filter media last?
Most manganese dioxide filter media work for 5 to 7 years. Cleaning the filter by backwashing helps it last longer. Good care keeps water clean and the filter working well.
Can manganese dioxide remove bad smells from water?
Manganese dioxide can take away bad smells from hydrogen sulfide. It changes the smelly gas into a solid that gets trapped. This makes water taste and smell much better.
Does water pH affect manganese dioxide performance?
Yes, water pH changes how well manganese dioxide works. It removes more metals when water is a little alkaline. Operators should check the pH often to get the best results.
Related Posts

I am Edward lee, founder of manganesesupply( btlnewmaterial) , with more than 15 years experience in manganese products R&D and international sales, I helped more than 50+ corporates and am devoted to providing solutions to clients business.





