Manganese Dioxide in Water Treatment is a reliable method for purifying water. This mineral plays a crucial role in removing iron, manganese, and hydrogen sulfide from water systems. Manganese dioxide in water treatment works by oxidizing and filtering out these contaminants, providing consistent and effective results. The presence of manganese in water can lead to stains and unpleasant odors, but Manganese Dioxide in Water Treatment effectively addresses these issues. Iron and manganese can also affect the taste and color of water, making Manganese Dioxide in Water Treatment a preferred choice among water professionals. This media efficiently removes iron, manganese, and other harmful substances, ensuring cleaner and safer water.
Manganese dioxide helps clean water. It changes harmful metals like iron and manganese into solids. Filters can then catch these solids. This makes water taste and smell better.
This mineral works as a catalyst and filter media. It makes water treatment faster and better. It also lasts a long time.
Filters with manganese dioxide remove iron, manganese, hydrogen sulfide, arsenic, and radium. This helps keep water clear and safe. It also stops stains from forming.
To keep systems working well, operators should check pH between 6.5 and 8.5. They should backwash filters often. They also need to check the media every six months.
Manganese dioxide is safe and natural. People use it in homes and cities. It is a trusted way to get clean and healthy water.
Manganese Dioxide in Water Treatment
Catalyst and Oxidant
Manganese Dioxide in Water Treatment helps clean water in two ways. It acts as a catalyst and as an oxidant. This mineral makes chemical reactions happen faster but does not get used up. In water, Manganese Dioxide in Water Treatment starts oxidation. It turns iron and manganese in water into tiny solid pieces. These solids are easy to catch with a filter. Oxidation also gets rid of hydrogen sulfide. Hydrogen sulfide makes water smell like rotten eggs. This process makes water look clear and smell better.
Tip: Oxidation works best when the pH is just right. Most systems work well if the pH is between 6.5 and 8.5.
Manganese Dioxide in Water Treatment is special because it does more than just filter. It changes the form of contaminants. This makes it work better than many other ways to treat water.
Filtration Media
Granular manganese dioxide is the main part of many filters. The small, hard pieces have a lot of surface area. Water moves through a bed made of these granules. As water goes through, iron and manganese change into solids. These solids stay in the filter bed.
Most water treatment systems use tanks with granular manganese dioxide. These tanks can clean a lot of water at once. They are used in homes, schools, and big water plants. The media lasts a long time because it does not break down or dissolve fast.
Manganese dioxide comes from natural rocks. Mining companies dig it up and get it ready for water treatment. The mineral is strong, so it does not need to be replaced often. This saves money and time for people who use it.
Note: Backwashing the filter bed often keeps it working well.
Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
Natural Origin | Safe and eco-friendly |
High Durability | Long service life |
Large Surface Area | Efficient oxidation and filtration |
Compatibility | Works in many water treatment systems |
Contaminants Removed

Remove Manganese
Manganese dioxide is very good at taking out manganese from water. When water goes through a filter with manganese dioxide, the media acts like a helper. It makes the process of changing dissolved manganese into solids happen faster. These solid pieces get stuck in the filter. The water that comes out has much less manganese.
Scientists found that biofilters with extra nutrients can remove up to 91% of manganese. Some systems use both electrocoagulation and manganese dioxide filters. These systems can lower manganese to safe levels set by the World Health Organization and Health Canada. This means the water is safe to drink.
Note: Taking out manganese stops black stains on sinks and clothes. It also makes water taste and look better.
Iron and Hydrogen Sulfide
Manganese dioxide media is also great for removing iron from water. The media starts a reaction that changes dissolved iron into solid bits. This step lets the filter catch the iron before it gets to your tap. Taking out iron keeps red stains off sinks and makes water clear.
Hydrogen sulfide makes water smell like rotten eggs. It also reacts with manganese dioxide. The media turns hydrogen sulfide into safe particles the filter can hold. This step takes away bad smells and makes water nicer to use.
- Removing iron helps protect pipes and machines.
- Taking out hydrogen sulfide makes water better for drinking and washing.
- Manganese dioxide media works in homes and big city water systems.
Arsenic and Radium
Manganese dioxide coated filters, like GreensandPlus™, help take out arsenic and radium from groundwater. These filters use special reactions to target many bad things in water. Some systems use both electrocoagulation and manganese dioxide filters. They can lower arsenic by more than 99%. The final amount of arsenic can be less than 0.1 μg/L, which is much lower than the safe limit.
- Manganese dioxide media grabs and changes manganese in water.
- Arsenic is often removed with iron, as iron helps trap arsenic.
- Radium is also taken out, but the amount depends on the system.
Tip: Cleaning the filter with chlorine often keeps it working well.
| Contaminant | Removal Method | Typical Result |
|---|---|---|
| Manganese | Catalytic oxidation, filtration | Below 100 μg/L (WHO standard) |
| Iron | Oxidation, filtration | Clear, stain-free water |
| Hydrogen Sulfide | Oxidation, filtration | No odor, improved taste |
| Arsenic | EC + manganese dioxide filtration | Below 0.1 μg/L |
| Radium | Adsorption, oxidation | Reduced to safe levels |
Effectiveness
Oxidation Process
Manganese dioxide works well for cleaning water. It uses oxidation to make harmful things safer. When water goes through the filter bed, manganese dioxide reacts with iron and manganese in the water. This reaction changes them into solid pieces. The filter catches these solids, so they do not get into your tap water. Oxidation also takes away hydrogen sulfide, which makes water smell bad.
Operators see the best results when the pH is between 6.5 and 8.5. This pH range helps manganese dioxide react faster with iron and manganese. The process does not use up the manganese dioxide, so the filter lasts a long time. Many water plants use this method because it keeps water clear and stops stains.
Oxidation takes out manganese and iron from water.
The process also makes water taste and smell better.
Filters need to be backwashed often to keep working well.
Adsorption Properties
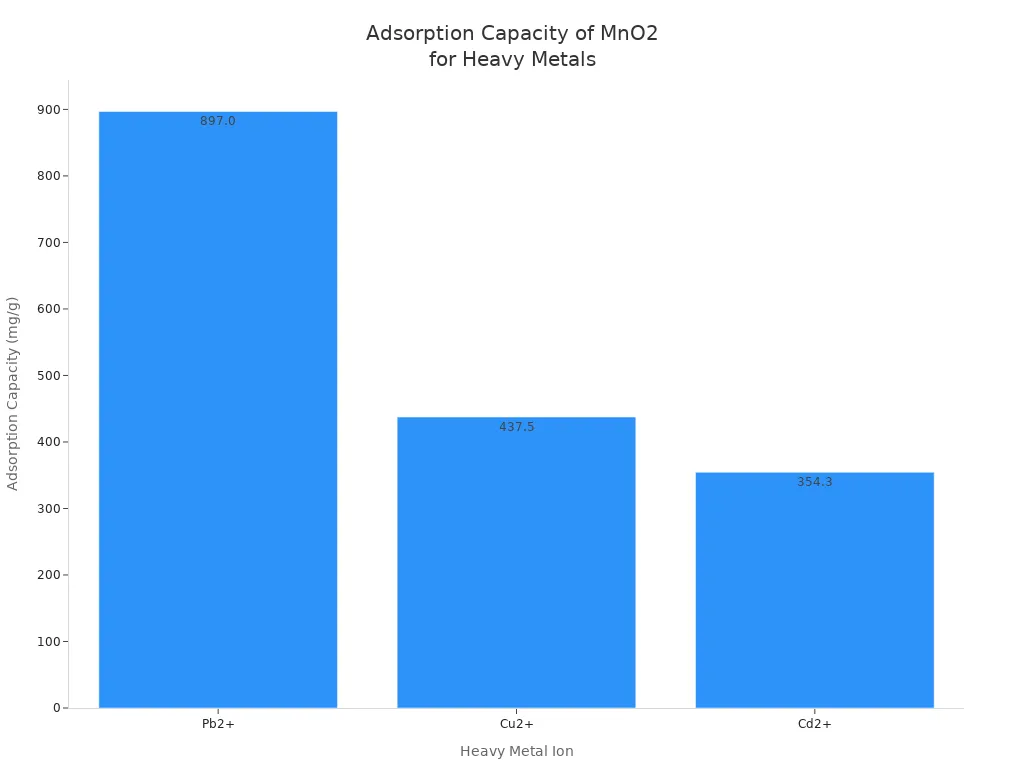
Manganese dioxide does more than just oxidation. It also acts as a strong adsorbent. Its special crystal structure, especially in δ-MnO2, gives it a big surface area. This helps it remove manganese, iron, and heavy metals from water. The adsorption process uses different ways, like physical adsorption, electrostatic pull, and ion exchange. These actions trap bad things on the surface of the manganese dioxide granules.
The table below shows how well manganese dioxide can adsorb different metals:
Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
Adsorbent Type | Hollow mesoporous structured MnO2 nanosorbent (HMN) |
Pb2+: 897.0, Cu2+: 437.5, Cd2+: 354.3 | |
Adsorption Mechanisms | Physical adsorption, electrostatic adsorption, surface complexation, ion exchange |
Structural Advantage | Layered crystal structure of δ-MnO2 leads to higher adsorption capacity |
Stability | Good stability under acidic conditions |
Environmental Application | Effective removal of heavy metals from wastewater and soil |
Performance Compared to Others | Superior adsorption capacity compared to most reported manganese dioxide adsorbents |
MnO2 Phase | Adsorption Capacity for Pb2+ (mg/g) | Structural Feature |
|---|---|---|
δ-MnO2 | 200–300 | Layered crystal structure |
Other MnO2 phases | Lower adsorption capacities | Non-layered or less favorable structure |
Note: Manganese dioxide can hold a lot of metals, so it is great for taking out manganese and other metals from water.
Applications in Water Treatment
System Types
Many water treatment systems use manganese dioxide as a main part. These systems are found in homes, schools, factories, and big city plants. The most common types are:
Pressure Filters: Water is pushed through a bed of manganese dioxide granules. The media takes out iron, manganese, and other bad things.
Gravity Filters: Water moves by gravity through the filter bed. These filters are good for treating lots of water at once.
Greensand Filters: These filters use greensand coated with manganese dioxide. They remove iron, manganese, and hydrogen sulfide.
Mixed Media Filters: Some filters mix manganese dioxide with other filter materials. This helps take out more contaminants.
Operators pick a system based on water quality, flow speed, and what needs to be removed. In special batteries, manganese dioxide electrodes need careful control of flow and pump power. The thick paste in these batteries means pumping can use 8% to 50% of the system’s power. Engineers try to use less energy but still clean water well.
Usage Tips
Operators can get the best results from manganese dioxide systems by following these tips:
Monitor pH Levels: Keep pH between 6.5 and 8.5. This helps oxidation and contaminant removal work well.
Backwash Regularly: Clean the filter bed often to get rid of trapped solids. Backwashing keeps the system working right.
Check Flow Rates: Make sure the flow matches the system’s design. Too fast means less contact time, too slow can lower how well it works.
Inspect Media Condition: Change the manganese dioxide media if it looks worn or does not work as well.
Use Pre-Treatment: Sometimes, treat water first to remove big particles or fix pH before it goes into the main system.
Tip: Always follow the maker’s rules for care. Good care gives safe water and makes the system last longer.
A table below shows the best ways to care for the system:
Maintenance Task | Frequency | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
Backwashing | Weekly/As needed | Stops clogging |
pH Monitoring | Daily | Keeps oxidation working well |
Media Inspection | Every 6 months | Keeps removal working strong |
Flow Rate Adjustment | As needed | Helps remove more contaminants |
These steps help make sure manganese dioxide water systems give safe, clean water for a long time.
Benefits and Limitations
Key Advantages
Manganese dioxide has many good points for cleaning water. This media can take out manganese, iron, hydrogen sulfide, arsenic, and radium. Many people use it because it works as a catalyst and a filter. Some main benefits of manganese dioxide are:
It removes manganese and iron very well.
The media lasts a long time and does not break down fast.
It comes from nature, so it is safe for most water systems.
It works with many kinds of water treatment setups.
If you take care of it, it does not need much work.
Operators often see water that is clear, with no stains or bad smells, after using manganese dioxide filters.
Considerations
Manganese dioxide is strong, but some things can change how well it works. Operators need to watch the water chemistry to get the best results. Here are some things to think about:
How well manganese is removed depends a lot on pH. If the water is acidic (pH below 6), it does not work as well and can even put manganese back in the water.
Low pH makes hydronium ions compete and causes repulsion, so removal is not as good.
Tests show manganese is removed much better when pH is above 6.5. Operators should keep pH between 6.5 and 8.5 for the best results.
The kind of manganese dioxide used matters too. Some forms do not work the same as others.
The amount of other ions in the water does not change manganese removal much.
Factor | Impact on Removal |
|---|---|
pH < 6 | Low removal, possible release |
pH 6.5–8.5 | High removal, stable |
Ionic strength | Little effect |
MnO2 polymorph type | Can change performance |
Note: Checking pH and the filter often helps keep manganese removal strong.
Manganese dioxide is very helpful in today’s filters. It can speed up reactions and help get rid of bad stuff in water. People get cleaner water and do not have to fix the filter as much. This media keeps water clean for a long time. Many experts say manganese dioxide is a good choice for safe and strong water filters.
FAQ
What is manganese dioxide used for in water treatment?
Manganese dioxide helps take out iron, manganese, hydrogen sulfide, arsenic, and radium from water. It works as a catalyst and as a filter. Many city and home water systems use it to make water safe and clean.
How often should operators replace manganese dioxide media?
Operators change manganese dioxide media every 5 to 10 years. The time depends on how clean the water is and how well the system is cared for. Backwashing the filter often helps the media last longer.
Tip: Check the filter bed every six months to keep it working well.
Does manganese dioxide remove all contaminants?
Manganese dioxide can take out many metals and gases, but not everything. It does not get rid of bacteria, viruses, or some chemicals. Operators often use other treatment steps with it to clean water fully.
Contaminant Type | Removed by MnO₂? |
|---|---|
Iron | ✅ |
Manganese | ✅ |
Bacteria | ❌ |
Viruses | ❌ |
Is manganese dioxide safe for drinking water systems?
Yes, manganese dioxide is safe for drinking water if used the right way. It comes from natural minerals and meets safety rules. The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency says it is a good filter media.
For more, visit EPA Water Treatment.
What maintenance does a manganese dioxide filter need?
Operators should backwash the filter once a week, check pH every day, and look at the media every six months. These steps help the system work well and keep water safe.
Backwash: Weekly
pH Check: Daily
Media Inspection: Every 6 months
Related Posts

I am Edward lee, founder of manganesesupply( btlnewmaterial) , with more than 15 years experience in manganese products R&D and international sales, I helped more than 50+ corporates and am devoted to providing solutions to clients business.





