Manganese dioxide grades show how much manganese dioxide is in a sample, like 90%, 95%, or 98%. These grades tell us about the purity and quality of the material. Many industries use manganese dioxide for different things, like batteries and making chemicals. High purity manganese ingots help companies meet tough rules for performance. Manganese dioxide grades are very important in research, where good results need the right mix.
Key Takeaways
Manganese dioxide grades (90%, 95%, 98%) tell us how pure it is. These grades help decide how to use it in batteries, chemicals, and water cleaning. High-purity electrolytic manganese dioxide is best for batteries. It helps batteries last longer and work better. Different ways of making manganese dioxide change its purity and structure. This also changes how it looks and works in products. Picking the right manganese dioxide grade depends on what you need. You should also think about cost and industry rules. This helps keep things safe and gives good results. Always check purity with trusted suppliers. Think about new trends like cleaner ways to make it and more need for high-performance grades.
Grade Meaning
Manganese Dioxide Grades Explained
Manganese dioxide grades tell us how much manganese dioxide is in something. Grades like 90%, 95%, and 98% show how pure the material is. Each grade works best for certain jobs. Battery makers pick higher grades to get better results. Chemical plants might use lower grades if they do not need high purity.
A table below shows how the grades compare:
Grade (%) | Manganese Dioxide Content | Common Use |
|---|---|---|
90 | Lower | Industrial chemicals |
95 | Medium | Water treatment, ceramics |
98 | High | Batteries, electronics |
Note: Higher manganese dioxide grades usually give better results in sensitive uses.
Purity and Structure
Purity means how much of the sample is real manganese dioxide. High purity stops bad reactions from happening. In batteries, even tiny impurities can make them work worse. Electrolytic manganese dioxide is special because it is very pure and has a unique structure. This structure helps it work well in battery cells.
Manganese dioxide can come from nature or from chemical methods. Electrolytic methods use electricity to make very pure manganese dioxide. This process takes out most of the impurities. The structure of electrolytic manganese dioxide is more even. This evenness helps when steady performance is important.
Manganese dioxide grades also change the crystal shape and grain size. These things affect how the material acts in different products. Fine grains help make smooth coatings for battery electrodes. Coarse grains can be better for water treatment.
Key Differences
Chemical Manganese Dioxide vs. Electrolytic Manganese Dioxide
Manganese dioxide comes in two main types. These are chemical manganese dioxide and electrolytic manganese dioxide. Both types have the same chemical formula, MnO2. Manganese is in the +4 oxidation state in both. The biggest differences are in purity, how they are made, and what they are used for.
Electrolytic manganese dioxide is more pure. It is mostly used in batteries because it works better.
Chemical manganese dioxide costs more. People pick it when they need very pure material for special jobs.
Both types have the same basic chemical structure. But their purity and how they are made make them different.
The structure and purity of each type change how well they work in energy storage and as catalysts.
Electrolytic manganese dioxide is made with electricity. This process removes most impurities. It makes the structure more even. This is good for sensitive uses like batteries. Chemical manganese dioxide is made with chemical reactions. This can leave more impurities in the final product. Companies pick the right type based on how pure and strong they need the material to be.
Physical Properties
The way manganese dioxide is made changes its physical properties. Different methods make different crystal shapes, grain sizes, and forms. These changes affect how the material works in real life.
Hydrothermal methods make manganese dioxide with good crystal shape and size. But this needs high heat and pressure.
Template methods are easier but can add impurities.
Solid-phase methods are cheap and work well. But they often make lower purity and clumped particles.
Chemical precipitation gives high purity and uses little energy. But the particles may not all look the same.
Manganese dioxide can form many crystal types. These include α, β, γ, δ, and ε. Each type has a special structure:
α-MnO2 has big tunnels. These help store and move ions.
β-MnO2 has small tunnels. It is not as useful for batteries.
γ-MnO2 mixes tunnel sizes. Some ions can move through it.
δ-MnO2 has layers with wide spaces. This helps ions move and makes it stable.
ε-MnO2 has a messy structure. This makes it hard for ions to move.
The shape and size of manganese dioxide particles matter too. For example, α-MnO2 makes nanotubes. β-MnO2 makes nano-balls. δ-MnO2 can look like flower balls. Smaller particles and bigger surface areas, like in γ-MnO2 and δ-MnO2, help batteries work better. The amount of oxygen vacancies, which help move charges, also changes with each crystal type.
Note: How manganese dioxide is made changes its purity, crystal structure, and how well it works in products.
Performance in Batteries
Manganese dioxide is very important in batteries. The grade, purity, and structure affect battery power, how long it lasts, and how fast it works. Electrolytic manganese dioxide is the best choice for batteries. It is very pure and has a steady structure.
Battery Type | Capacity (mAh) / Specific Energy (Wh/kg) | Cycle Life (cycles) | Discharge Rate (C-rate) | Notes on Performance and Composition |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Li-Manganese Oxide (LiMn2O4) | 1,100–1,500 mAh (18650 cells) / 100–150 Wh/kg | 300–700 | 1C typical, up to 10C continuous, 30C pulse (5s) | Medium capacity, good power and safety, often mixed with NMC for better energy and longer life. |
Lithium Nickel Manganese Cobalt Oxide (NMC) | 2,000–2,800 mAh (18650 cells) | Varies | Up to 20A continuous discharge | Mixed cathodes give more capacity and longer life; silicon anodes give more capacity but may shorten life. |
The table shows that manganese dioxide grade and cathode mix change battery performance. Electrolytic manganese dioxide, with high purity and special structure, helps batteries keep steady power and last longer. The mix of α-MnO2 and γ-MnO2 in the cathode keeps the structure strong during charging and use. This helps the battery last longer and work faster.
Performance Metric | Evidence Summary |
|---|---|
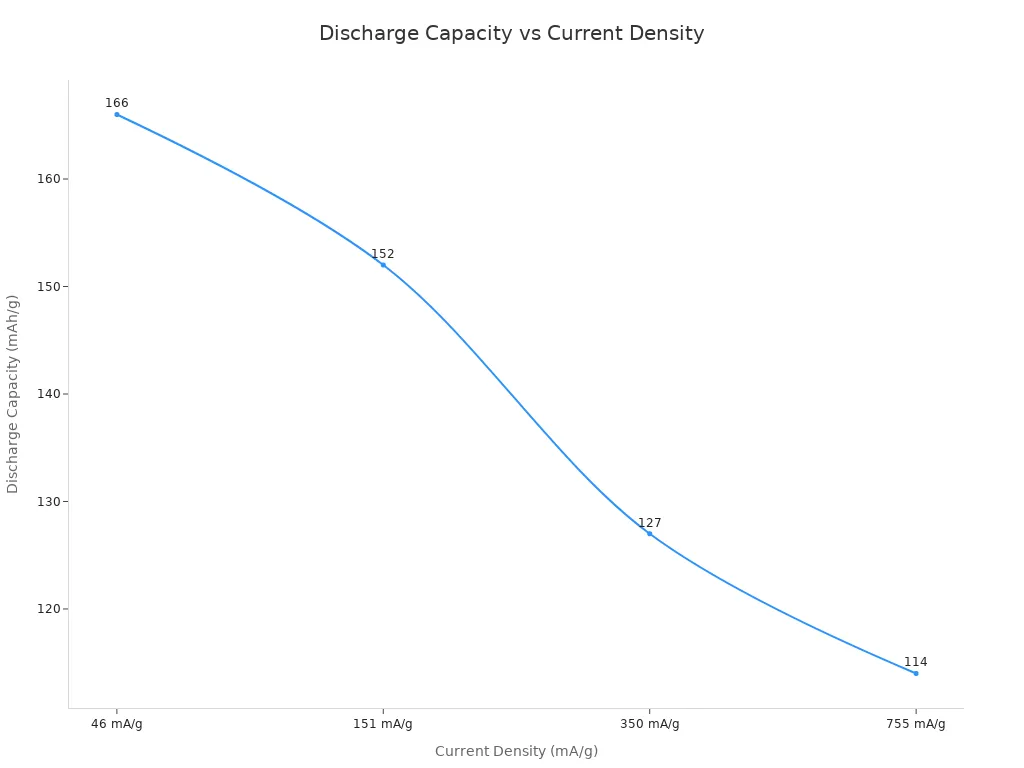
Capacity | EMD cathode gives 166, 152, 127, and 114 mAh/g at current densities of 46, 151, 350, and 755 mA/g (100th cycle). Capacity stays at 82%, 83%, 68%, and 68% at the 100th cycle compared to the first. |
Cycle Life | EMD cathode keeps 84 mAh/g over 400 cycles at 755 mA/g with 66% left compared to the second cycle. Loss of capacity is linked to changes in the crystal structure during use. |
Discharge Rate | EMD cathode works well at high rates because of its large surface area and steady α-MnO2 and γ-MnO2 phases. |
Microstructure Influence | The mix of α-MnO2 and γ-MnO2 keeps the crystal structure strong, helping the battery last longer and work faster. |
Cost and Purity | EMD is very pure, low cost, and active in batteries, making it important for commercial Li/MnO2 batteries. Manganese oxide costs less than cobalt-based materials. |
Flake manganese dioxide is often used in battery electrodes. It gives a large surface area for reactions. This helps batteries work at higher rates and last longer. Picking the right manganese dioxide grade, especially electrolytic types, helps batteries meet strict rules for performance and safety.
Applications
Batteries
Batteries use more manganese dioxide than any other product. In 2023, making batteries used about 91.5% of all manganese dioxide in the world. This is because people need batteries that work well in things like phones, cars, and military gear. Battery makers pick high-purity manganese dioxide to make sure batteries last long and work well. Electrolytic manganese dioxide is best for dry-cell batteries, like alkaline and zinc-carbon ones. These batteries use manganese dioxide as the main cathode. Zinc is the anode, and manganese dioxide helps move electrons. Using both zinc and manganese dioxide gives batteries lots of energy and steady power. Some lithium-ion batteries also have manganese dioxide in their cathodes, mixed with other metals. Companies keep making new manganese dioxide grades to help batteries get better for new technology.
Industrial Uses
Manganese dioxide is used in many factories, not just for batteries. It acts as a catalyst and helps chemical reactions happen faster. The chemical industry uses it to make special chemicals, farm chemicals, and medicines. Water treatment plants use special manganese dioxide to clean water by taking out iron, manganese, and other bad stuff. Pyrolusite ore, which has a lot of manganese dioxide, is made into filters for city and home water systems. In glass and ceramics, technical grade manganese dioxide adds color and makes products stronger. It helps glass and ceramics look better and last longer. The table below shows how different industries use manganese dioxide and what grade they need:
Industry | Application / Use Case | |
|---|---|---|
Glass & Ceramics | Technical Grade | Colorant, decolorizer, property enhancer |
Chemical Industry | Chemical Grade | Catalyst, oxidizing agent in chemical synthesis |
Water Treatment | Specialized Media | Catalyst in filtration systems for contaminant removal |
Battery Industry | Battery Grade | Cathode material in dry-cell batteries and lithium-ion batteries |
Tip: Picking the right manganese dioxide grade helps each factory work better and follow the rules.
Lab and Research
Scientists use manganese dioxide in many lab tests. Combustion experiments need reagent-grade manganese dioxide to study burning and reaction speed. High-purity types give the best results in science tests. In organic chemistry, ‘active’ manganese dioxide is used to help certain reactions happen. Some labs put manganese dioxide on solid supports to help find chemicals in tests. These tests can find things like isoniazid and analgin. Archaeologists study manganese dioxide from old sites to learn about ancient fire-making. Labs like reagent-grade and special types with certain particle sizes and shapes. Manganese dioxide does not dissolve in water, but scientists have made some manganese(IV) complexes that do. Sometimes, labs use manganese dioxide in briquette form to control how it is released in experiments.
β-MnO2 (pyrolusite) is often used in labs but does not react much.
‘Active’ manganese dioxide is better for certain chemical reactions.
Soluble and supported forms let scientists do more kinds of lab work.

Choosing a Grade
Application Needs
Picking the right manganese dioxide grade depends on how it will be used. Each industry needs different levels of purity and performance. These needs help decide which grade is best:
Battery makers, especially for electric cars and gadgets, need high-purity electrolytic manganese dioxide. This type gives strong power and steady results.
Car companies want high-purity grades to make batteries work better and charge faster. These batteries use zinc as the anode and manganese dioxide as the cathode.
Electronics companies choose high-purity grades for small batteries that give steady power.
Alkaline batteries, used at home and in factories, use electrolytic manganese dioxide for lots of energy and long life. Zinc is the anode in these batteries too.
Chemical, fertilizer, glass, and water cleaning companies use chemical or standard grades. These have less purity but still work for speeding up reactions or cleaning.
Companies also try to use greener ways to make manganese dioxide and look for new raw materials.
The market has Battery Grade, Chemical Grade, and Standard Grade manganese dioxide. Battery Grade is most popular because electric cars and energy storage need high purity. Chemical Grade is used more in fertilizers, paints, and coloring. Standard Grade is for jobs that do not need high purity.
Note: The part with more than 99% purity is growing fastest. This is because electronics, medicine, and special chemicals need it. Batteries are still the biggest and fastest-growing use, especially as electric cars and green energy get more common.
Cost and Regulations
Price and rules are important when picking manganese dioxide grades. The table below shows the main differences between 90%, 95%, and 98% grades:
Grade Purity Range | Typical Applications | Performance Suitability | Cost-Effectiveness | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
90% – 95% | Steel production, fertilizers, ferromanganese | Good for cheaper, less important uses | Cheaper and easy to find | Saves money, can be used in many ways | Lower purity can hurt quality; more impurities |
95% – 98% | Specialty alloys, chemical applications | Better for tough jobs and chemical reactions | Costs more because it is purer | Works better and lasts longer | More expensive; only for special uses |
Grades with 90-95% purity are good for cheaper and easier jobs. They cost less and can be used in many ways, but might have more impurities. Grades with 95-98% purity are better for tough jobs and special chemicals, but they cost more.
Some rules say you must use higher purity for batteries, electronics, and water cleaning. These rules help keep products safe and working well. New ways to mine and clean manganese dioxide may make high-purity grades cheaper in the future.
Tips for Buyers and Users
Know what you need it for. Batteries and electronics should use high-purity grades for best results.
Think about zinc in batteries. Using zinc anodes with pure manganese dioxide cathodes makes batteries stronger and last longer.
Check the rules for your industry. Some jobs need certain purity levels for safety and the environment.
Compare price and performance. For simple jobs, standard grades might be the best deal.
Ask suppliers or experts to help you pick the right grade.
Tip: Always check the grade and purity with a trusted supplier. This helps you follow the rules and get good results.
Manganese dioxide grades are not all the same. They have different purity, structure, and how well they work. High-purity grades, like electrolytic manganese dioxide, help make better batteries. Lower grades are used for steelmaking and other factory jobs. Picking the right grade for each job keeps things safe and working well. It also helps follow the rules. New technology keeps making manganese dioxide cleaner and better for the environment. This is important for electric cars and clean energy.
Quick Checklist for Choosing the Right Grade:
Find out what you need it for, like batteries or chemicals.
Make sure you know how pure and strong it must be.
Look at how easy it is to get and how much it costs.
Check the rules for your industry.
Ask an expert if you have special needs.
Getting high-purity manganese dioxide is harder because only a few places make it. Lower grades are easier to get from many places. New research and smart ways to make it will help in the future.
Future Trend / Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
More people want high-performance grades for electric cars and green energy. | |
Sustainable Mining Practices | Companies try to hurt the environment less when mining. |
Smart Manufacturing Integration | Using computers and robots makes manganese dioxide better and faster. |
Expanded Applications | More uses in water cleaning and factories are coming. |
FAQ
What does the percentage in manganese dioxide grades mean?
The percentage tells how much pure manganese dioxide is in the sample. For example, if it says 98%, that means 98% is manganese dioxide. The other 2% is made up of different things.
Why do batteries need high-purity manganese dioxide?
Batteries work better and last longer with high-purity manganese dioxide. If there are impurities, batteries may not work as well. Sometimes, impurities can even make batteries unsafe. That is why battery makers pick high grades.
Can lower grades of manganese dioxide be used in water treatment?
Yes, lower grades like 90% or 95% are used in water treatment. These grades help take out iron and manganese from water. For this job, very high purity is not always needed.
How can buyers check manganese dioxide purity?
Buyers should ask the supplier for a certificate of analysis. They can also get a lab to test the sample. Good suppliers follow the rules and give clear reports about purity.
Are there safety concerns when handling manganese dioxide?
Yes, manganese dioxide dust can bother your lungs and skin. Workers should wear safety gear and follow the rules. The CDC has more tips here: CDC – Manganese.
Related Posts

I am Edward lee, founder of manganesesupply( btlnewmaterial) , with more than 15 years experience in manganese products R&D and international sales, I helped more than 50+ corporates and am devoted to providing solutions to clients business.





