You use MnO₂ and MnCO₃ to remove manganese quickly and well in many industries. If you work in metallurgy, water treatment, or farming, removing manganese helps keep things safe. It also helps you follow the rules. The table below shows how different industries use these compounds for precipitation, cleanup, and taking out heavy metals:
Industrial Sector | Application of MnCO₃ and MnO₂ for Manganese Removal and Remediation |
|---|---|
Metallurgy | Making pure manganese metal and taking out heavy metal impurities |
Ceramics and Glass | Removing color and taking out iron and manganese for better products |
Agriculture | Giving manganese for soil cleanup and animal food |
Water Treatment | Using manganese precipitation to take out heavy metals and clean up |
Chemical Industry | Used as a starter for catalysts and helps clean up heavy metals |
Paints and Coatings | Used as pigment, helps take out heavy metals and control oxidation |
Batteries | Making MnO₂ for batteries after taking out manganese |
Key Takeaways
MnO₂ and MnCO₃ help factories take out manganese fast and safely. This protects nature and follows the rules.
Manganese dioxide works like a helper. It changes dissolved manganese into solid pieces. This makes it easier and faster to remove.
Using MnCO₃ with the right chemicals and pH makes solid manganese carbonate. This solid falls down and is easy to clean up.
There are two steps. First, MnCO₃ is made. Then it is heated to make MnO₂. This helps remove more manganese and makes the product cleaner.
Watching pH, heat, and chemical amounts helps remove manganese better. It also stops problems with other metals.
MnO₂ in Manganese Precipitation
Mechanism and Reactions
Manganese dioxide is used in manganese precipitation because it acts as an oxidant and a catalyst. When you put manganese dioxide into a solution with manganese, it starts a reaction. This reaction changes manganese ions into solid manganese dioxide. This is called manganese oxidation precipitation. The surface of manganese dioxide helps the oxidation of manganese and iron go faster. Air alone cannot remove these metals easily. In water treatment, manganese dioxide media help take out manganese, iron, hydrogen sulfide, arsenic, and radium.
Manganese dioxide takes electrons from manganese ions in the solution. This turns the ions into solid particles that settle down. The manganese oxidation reaction looks like this:
Mn²⁺ (aq) + MnO₂ (s) + 2H₂O → 2MnO(OH) (s) + 2H⁺ (aq)
You can change how fast the reaction goes by changing the solution’s conditions. If you use urea to slowly release ammonium, you get manganese dioxide with a bigger surface area. This makes the catalyst work better and helps remove more manganese. The surface of manganese dioxide has both Mn⁴⁺ and Mn³⁺. The balance between these forms affects how well the catalyst works. Oxygen on the surface also helps the oxidation process.
You can keep using manganese dioxide because you can clean its surface with oxidants like chlorine or potassium permanganate. This lets you reuse the same media for manganese removal. It makes the process more efficient and saves money. Using manganese dioxide for oxidative precipitation is a reliable way to remove manganese from many solutions.
Industrial Advantages
There are many benefits to using manganese dioxide in industry for manganese precipitation. First, manganese dioxide made by heating or oxidation has a special structure. When you heat manganese dioxide to high temperatures, it changes into forms like δ-MnO₂ and Mn₂O₃. These forms have more oxygen defects. That means they hold more active oxygen on their surfaces. This extra oxygen helps the oxidation reaction go faster and more completely. This raises the removal efficiency.
Heating manganese dioxide at high temperatures makes more active sites.
More active oxygen means better oxidation of manganese and other metals.
You get higher removal efficiency and better selectivity for manganese over other metals.
Manganese dioxide also helps you pick which metals to remove. When you use manganese dioxide with other metals like nickel, you can get better selectivity for nitrogen in reactions like selective catalytic reduction (SCR). The special structure of manganese dioxide, especially after heating, helps keep the catalyst stable and active. This is true even if there is water or sulfur dioxide in the solution.
You also make less waste when you use manganese dioxide compared to some other ways. For example, microbially induced carbonate precipitation can make ammonia, which is bad for the environment. The oxidative precipitation method with manganese dioxide mostly makes solid waste. This waste is easier to handle and less harmful.
Tip: To improve manganese removal, focus on the heating temperature and the structure of your manganese dioxide. This helps you get better results in your treatment process.
Manganese dioxide gives you a strong, flexible, and efficient way to handle manganese precipitation. You can use it in water treatment, metallurgy, and chemical manufacturing. The process works well for different solutions and helps you meet strict removal rules. By learning about the reaction and making your manganese dioxide better, you can get high removal efficiency and keep your work running smoothly.
MnCO₃ in Manganese Precipitation
Precipitation Process
MnCO₃ is a strong way to take out manganese in factories. The process starts when you mix a solution with manganese and a carbonate. You often use manganese sulfate or manganese chloride as your starting liquid. Then, you add sodium carbonate or ammonium bicarbonate to it. This makes a reaction that creates solid MnCO₃. The reaction looks like this:
Mn²⁺ (aq) + CO₃²⁻ (aq) → MnCO₃ (s)
You need to keep the solution basic, or alkaline. A high pH helps MnCO₃ form and makes it easier to remove manganese. People usually use stirred tanks to mix the chemicals well. Good mixing helps the reaction happen fast and evenly. You can use sodium carbonate or ammonium carbonate for this step. Both work well and help you get good results.
Start with manganese sulfate or manganese chloride in water.
Add sodium carbonate or ammonium bicarbonate next.
Solid MnCO₃ forms and settles at the bottom.
You filter or spin out the solid to remove it.
Wash and dry the MnCO₃ before using or throwing it away.
You must watch the pH, temperature, and how much of each chemical you use. These things change how well the process works and how clean the water gets. If you keep the pH high and mix well, you remove more manganese. This also lowers the amount of manganese left in the water.
Note: The best way to remove manganese is to keep the solution basic and use the right amount of carbonate. This helps you meet tough treatment rules and gets rid of more manganese.
Process Benefits
Using MnCO₃ to remove manganese has many good points. This method works well and gives steady results. You can use it for water with lots of manganese or just a little. The reaction is simple, and you can change it by adjusting the pH or how much carbonate you add.
High removal: You can take out almost all the manganese.
Selectivity: This method mostly removes manganese, not other metals.
Flexibility: You can use it for many types of water or needs.
Easy to use: It uses common chemicals and simple tools.
Product quality: You can clean the MnCO₃ to make a good product.
This process is safer and better for the environment. The solid MnCO₃ is easy to move and store. You do not make dangerous waste. You can use the MnCO₃ you make in other factories, like for batteries or to make MnO₂.
The MnCO₃ process works for big or small jobs. You can change the steps to fit what you need. You can also use this method with other ways to remove even more manganese.
Tip: Always check the manganese level in your water while you treat it. This helps you get the best results and keep the process working well.
MnCO₃ precipitation is one of the best ways to take out manganese. It gives you control, works well, and helps you reach your treatment goals.
Two-Step Manganese Precipitation Process
MnCO₃ to MnO₂ Conversion
You can remove more manganese by using two steps. First, you make solid MnCO₃ with a simple reaction. Then, you change this solid into manganese dioxide. You do this by heating or using oxidation. This step is called calcination or oxidation. Heat helps the reaction happen and changes the chemical form. This method gives better manganese removal and works more efficiently.
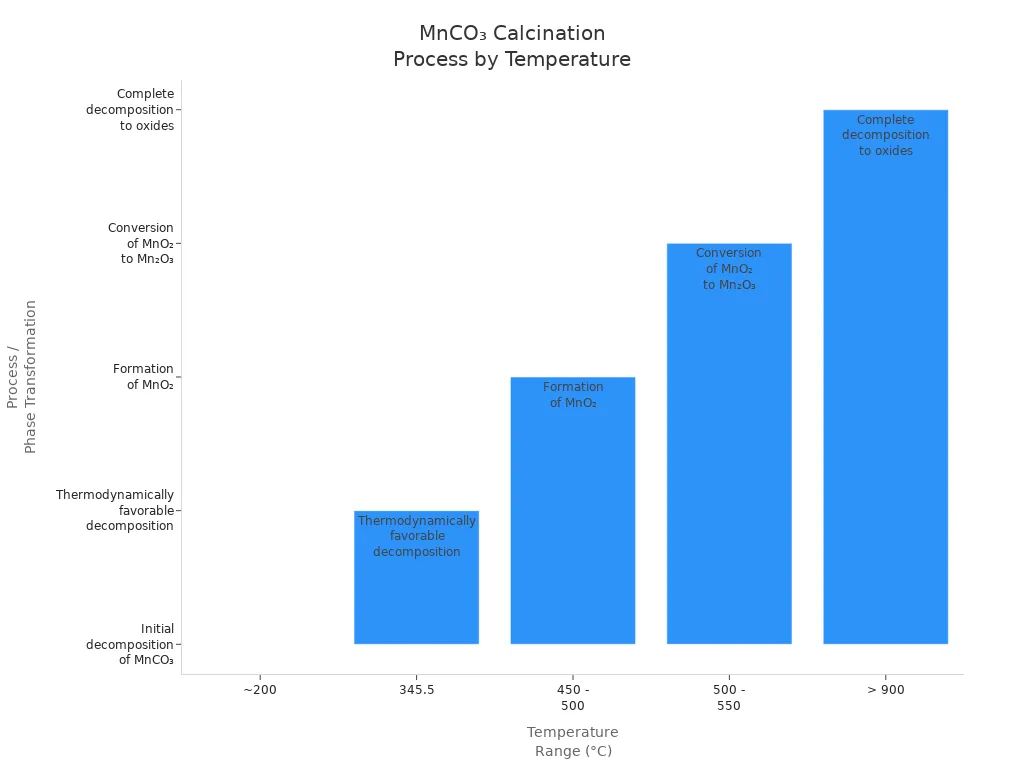
The table below shows the usual conditions for this change:
Temperature Range (°C) | Process / Phase Transformation | Notes |
|---|---|---|
~200 | Initial decomposition of MnCO₃ to MnO + CO₂ | Decomposition starts, forming MnO |
345.5 | Favorable decomposition begins | Significant mass loss observed |
450 – 500 | Formation of MnO₂ | Main industrial temperature for MnO₂ creation |
500 – 550 | Conversion of MnO₂ to Mn₂O₃ | Further oxidation stage |
> 900 | Complete conversion to oxides | Removes all carbonate phases |
You usually heat MnCO₃ between 450°C and 500°C in air. This temperature helps the oxidation reaction make manganese dioxide. The manganese oxidation precipitation step works best at this heat. You can see the changes in the chart below:
Efficiency and Purity
This two-step process removes manganese very well. First, you take out manganese as MnCO₃. Then, you use oxidation to get pure manganese dioxide. Each step helps you control how good the product is. You can remove a lot of manganese and get a product that meets strict rules.
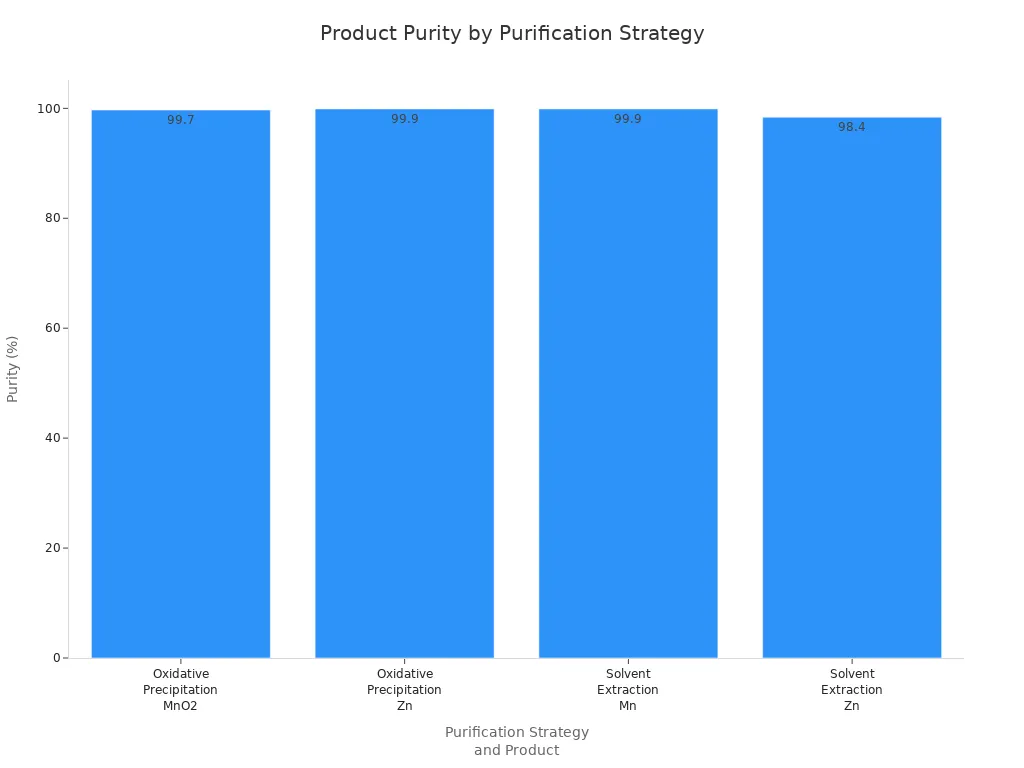
The oxidation in the second step takes away leftover impurities. This makes the manganese dioxide very pure. You can see how much better the purity and yield are in the table below:
Purification Strategy | Product Type | Purity (%) | Global Yield (%) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Oxidative Precipitation | MnO2 precipitate | 99.7 | 97.4 | High purity manganese precipitate |
Oxidative Precipitation | Zn solution | 99.9 | 94.8 | High purity zinc solution |
Solvent Extraction (Cyanex 302) | Mn solution | 99.9 | 96.3 | High purity manganese solution |
Solvent Extraction (Cyanex 302) | Zn solution | 98.4 | 100 | High purity zinc solution |
You can also see the purity improvements in this chart:
Tip: Try the two-step precipitation process for the best results. This method helps you follow tough rules and keeps your process working well.
By using this two-step process, you remove more manganese. You also get better efficiency and a cleaner product. The oxidation at each step helps you reach your goals and improve manganese dioxide quality.
Practical Considerations
Process Optimization
You can make manganese removal better by following some steps. First, keep the pH in the right range. Most manganese precipitation works best at pH 3 to 5. The best removal happens at pH 5. If the pH goes up to 7, you remove less manganese. Always check and change the pH during treatment.
You also need to watch how much reagent you use. Using the right amount of sodium carbonate or ammonium bicarbonate helps you remove more manganese. It also keeps costs low. Surfactants like CTAB, SDS, or PVP can change the shape and size of manganese carbonate particles. This helps make porous or round particles. These shapes help with removal and bioremediation. Hydrothermal synthesis with the right urea amount lets you control particle size and surface area. This makes microbially induced carbonate precipitation work better.
Tip: Use surfactant-assisted crystallization and heat together. This gives you better manganese oxide shapes and higher removal rates.
You can use reactors that control pH, filter, and dry to make pure manganese carbonate in large amounts. This helps you follow strict rules and clean up heavy metals.
Challenges and Solutions
You may have problems when removing manganese. Selectivity is a big challenge if other metals like zinc, calcium, or magnesium are in your solution. To separate manganese from zinc, control the pH carefully. Manganese comes out above pH 8. Zinc comes out between pH 6 and 8. If there is not much manganese, hydroxide precipitation does not work well. You should use microbially induced carbonate precipitation or oxidative precipitation for better results.
Solubility can also cause problems. At high pH, manganese forms Mn(OH)₂. This lets you take it out before removing zinc. But this needs more chemicals and can make byproducts like sodium sulfate. You can use oxidative precipitation with SO₂ and air at near-neutral pH. This gives better selectivity and faster removal. It also uses less base and works well for cleaning up heavy metals.
Sometimes, calcium and magnesium come out with manganese during carbonate precipitation. This means you use more chemicals and spend more money. To fix this, adjust your pH and how much reagent you use. Solvent extraction can help, but it costs more and may not separate manganese from calcium. Always watch your process and make changes to keep it safe and efficient.
Note: Microbially induced carbonate precipitation and mn bioremediation are strong ways to clean up heavy metals. But you must control your process to avoid problems.
You help stop heavy metal pollution by using MnO₂ and MnCO₃ for manganese precipitation. These compounds let you take out heavy metal from water and soil. This makes the environment much safer for everyone. If you know how MnO₂ and MnCO₃ work together, you can control heavy metal reactions. You also stop unwanted byproducts from forming. You make manganese products more pure this way. By watching pH and temperature, you can focus on heavy metal and lower manganese pollution. This method keeps the environment safe and helps make cleaner processes. It also lets you handle heavy metal in the environment better. By removing heavy metal and manganese from factory waste, you make things safer for people and nature.
FAQ
What is the main goal of manganese precipitation in industry?
Manganese precipitation helps lower manganese in water or waste. This keeps the water safer and follows safety rules. It also protects the environment from heavy metal pollution. The process makes products better and helps remove manganese faster.
How does manganese dioxide help with manganese removal?
Manganese dioxide works as an oxidant in the process. You add it to the solution to start a reaction. This reaction turns dissolved manganese into a solid. The solid is easier to take out. This makes manganese removal work better.
Can biological remediation methods work for manganese pollution?
Yes, you can use biological remediation for manganese removal. Microbially induced carbonate precipitation is one way to do this. Bacteria help change manganese in the environment. This helps clean up heavy metals in water or soil.
What factors affect the efficiency of manganese removal?
You can make manganese removal work better by controlling pH and temperature. The amount of chemicals you use is important too. The way the reaction works and the type of solution also matter. Good control of the process gives better results and higher removal.
Related Posts

I am Edward lee, founder of manganesesupply( btlnewmaterial) , with more than 15 years experience in manganese products R&D and international sales, I helped more than 50+ corporates and am devoted to providing solutions to clients business.





