If you’re deciding between electrolytic vs chemical manganese dioxide for strong batteries, choose electrolytic manganese dioxide. This type is much purer and performs better in demanding battery applications. On the other hand, if you’re looking to save money, chemical manganese dioxide is a more cost-effective option. Purity plays a crucial role in battery performance, and electrolytic manganese dioxide offers higher purity compared to chemical manganese dioxide. When making your choice, consider factors like purity, price, and overall effectiveness. Keep in mind how the difference between electrolytic vs chemical manganese dioxide can impact the way manganese functions in batteries and other uses.
Key Takeaways
- Electrolytic manganese dioxide (EMD) is more pure. It works better in batteries. EMD gives batteries longer life and more power.
- Chemical manganese dioxide (CMD) costs less money. CMD is good for things like ceramics and water treatment. It is also used in supercapacitors. These uses do not need high purity.
- Pick manganese dioxide based on what you need. Use high purity and stable types for electronics and batteries. Use cheaper types for simple jobs.
- Always check the purity before you buy. Look at the crystal structure and the supplier’s quality. This helps you avoid bad results and keeps you safe.
- Using the right manganese dioxide for your job saves money. It also makes things work better.
Quick Comparison
Key Differences
When you look at electrolytic vs chemical manganese dioxide, you notice some big differences. Electrolytic manganese dioxide is very pure. It has fewer things mixed in, so it works well in batteries that need to last a long time. Its crystal structure, called γ-MnO2, has lots of tiny tunnels and a big surface area. These help it store and give out energy really well. You will find this type in alkaline batteries and other strong battery systems.
Chemical manganese dioxide comes in different crystal shapes. Each shape has its own special features. For example, δ-MnO2 has layers, a big surface area, and many spots where oxygen is missing. This makes it good for supercapacitors and cleaning water. Chemical manganese dioxide usually costs less than electrolytic manganese dioxide. But it can have more things mixed in, which can make batteries work less well.
You should think about price too. Electrolytic manganese dioxide costs more because it is purer and works better. Chemical manganese dioxide is cheaper if you do not need high purity.
Tip: If you want manganese dioxide for batteries, pick electrolytic manganese dioxide for better purity and longer battery life. For jobs that are not as hard, chemical manganese dioxide can help you save money.
Comparison Table
Here is a simple table to help you see the differences between electrolytic vs chemical manganese dioxide:
| Feature | Electrolytic Manganese Dioxide (EMD) | Chemical Manganese Dioxide (CMD) |
|---|---|---|
| Purity | Very high (91-96% MnO2) | Moderate to high |
| Main Crystal Structure | γ-MnO2 (tunnel structure) | α-, β-, γ-, δ-, ε-MnO2 (varied) |
| Surface Area | Large | Varies by type |
| Particle Size | Small, uniform | Varies |
| Typical Uses | Batteries (alkaline, Li-ion), ceramics, water treatment | Ceramics, pigments, water treatment, supercapacitors |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
| Key Properties | High electrochemical activity, stable cycling | Depends on crystal form |
| Impurities | Very low (<0.01% Fe, Cu, Ni) | Higher than EMD |
| Cycle Life in Batteries | >400 cycles | Up to 230 cycles (optimized) |
You can see that electrolytic manganese dioxide is purer and works better in batteries. Chemical manganese dioxide is cheaper for uses that do not need high purity.
The chart below shows how much power batteries keep after many cycles when using manganese dioxide:
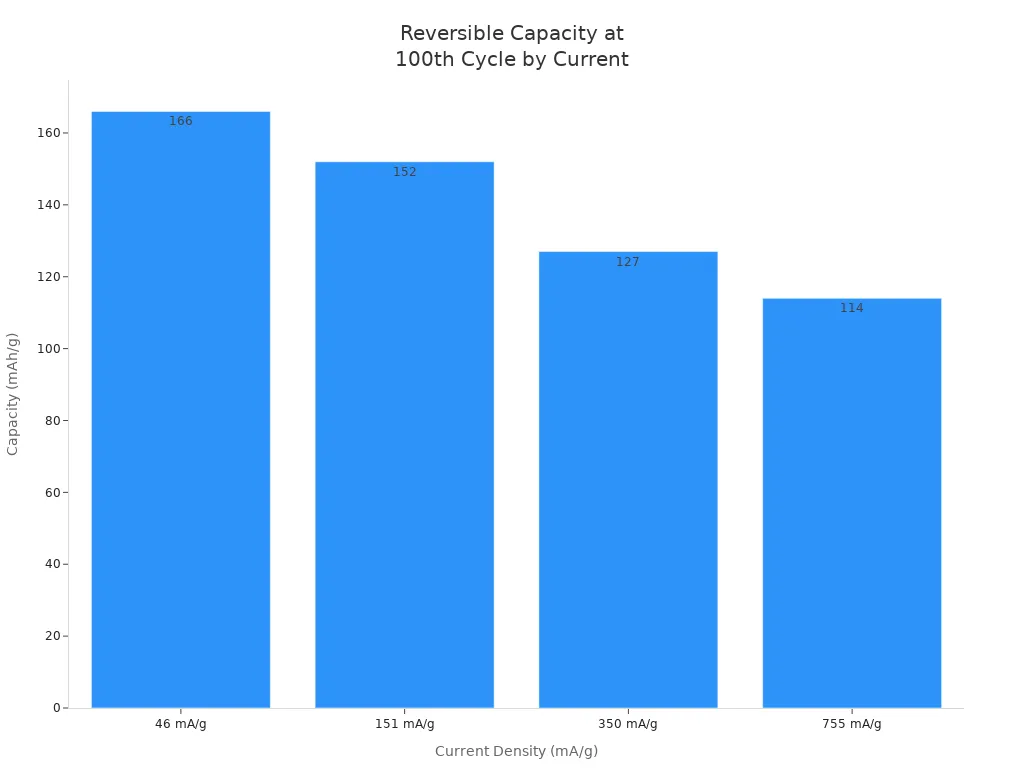
This chart shows that electrolytic manganese dioxide keeps its power even after many cycles. That is why it is the best for batteries that need to last a long time and give steady power.
Electrolytic vs Chemical Manganese Dioxide
Electrolytic Manganese Dioxide
Electrolytic manganese dioxide is made using electricity. First, people mine and crush manganese ores like pyrolusite. Next, the crushed ore is mixed with sulfuric acid. Then, the mixture goes through steps to remove iron, copper, nickel, and other unwanted things. These steps make impurity levels very low, less than 0.1%. High purity helps batteries last longer and work better.
During electrolysis, manganese dioxide forms on titanium anodes. The way electrolysis is done changes the final product. Things like current density, voltage, and temperature matter a lot. Here is a table that shows how these things affect quality:
Parameter | Typical Range | Effect on Product Quality |
|---|---|---|
Current Density | 100 – 200 A/m² | Changes deposit shape and surface area |
Voltage | 0.6 – 1.2 V | Lower voltage gives smooth, crack-free deposits |
Temperature | 94°C – 120°C | Alters crystal size and surface area |
Deposition Time | ~5 hours | Balances storage and porosity |
MnSO4 Concentration | ~0.9 mole/liter | Keeps manganese supply steady |
H2SO4 Concentration | ~0.5 mole/liter | Maintains acidic, stable electrolyte |
Titanium Doping | Added as TiOSO4 | Improves structure and electrochemical performance |
Electrolytic manganese dioxide usually has the γ-MnO2 crystal structure. This structure has many tunnels that help ions move fast. Because of this, batteries can store more energy and last longer. The high purity and special structure make electrolytic manganese dioxide great for strong batteries.
Chemical Manganese Dioxide
Chemical manganese dioxide is made by chemical reactions, not electricity. There are many ways to make it, like hydrothermal synthesis, sol–gel, reflux, microemulsion, coprecipitation, or chemical reduction. Each way changes how the final product turns out. For example, hydrothermal synthesis makes high-purity manganese dioxide with even particle size. Coprecipitation is easy and cheap but can make lower purity and uneven particles.
Here is a table that shows some common ways to make chemical manganese dioxide and what they do:
Production Process | Key Features and Effects on Properties |
|---|---|
Hydrothermal Synthesis | High purity, controlled size, better electrochemical properties |
Sol–Gel Approach | Phase control, improved properties, less common |
Reflux Method | Simple, large-scale, quality varies |
Microemulsion Approach | Small, uniform particles, high cycling performance |
Coprecipitation | Low cost, lower purity, poor homogeneity |
Chemical Reduction | Controlled size, better uniformity |
Chemical manganese dioxide can have different crystal forms, like δ-MnO2, α-MnO2, and β-MnO2. Each form has its own special features. For example, δ-MnO2 has layers and can hold more charge. γ-MnO2 has tunnels that help ions move. The way you make it and the crystal form change how well it works in batteries, water cleaning, or supercapacitors.
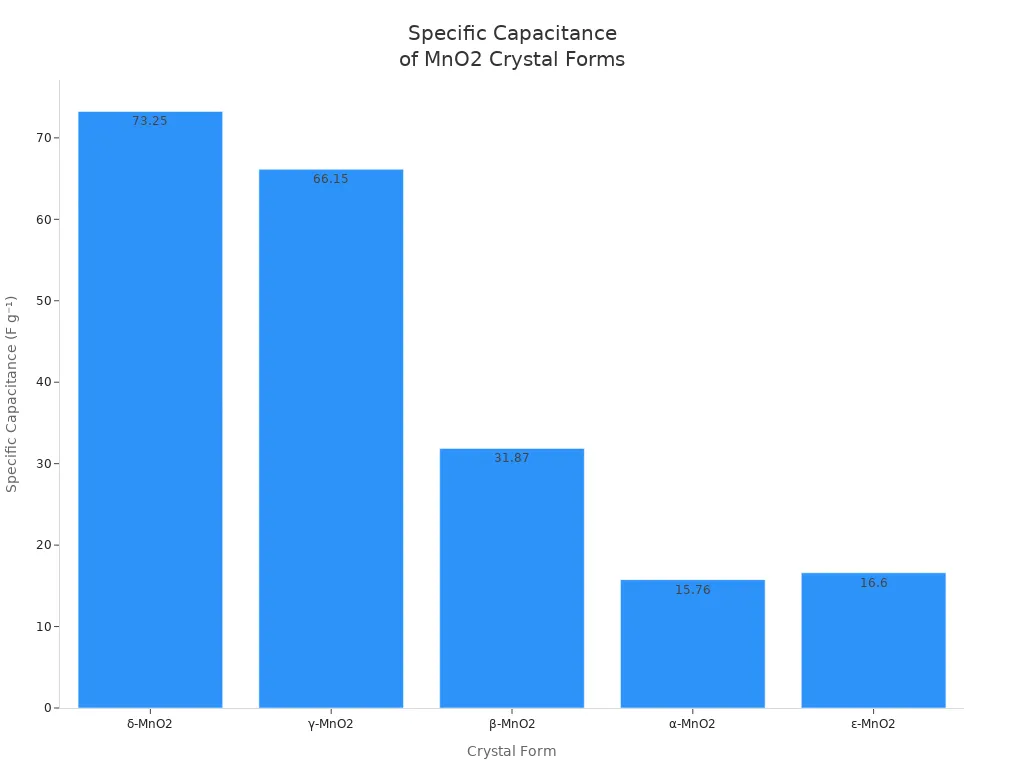
Note: The chart above shows that δ-MnO2 and γ-MnO2 have the best properties for storing energy, so they are good for energy storage.
When you compare electrolytic and chemical manganese dioxide, you see some big differences. Electrolytic manganese dioxide is purer and works better in batteries. Chemical manganese dioxide gives you more choices in structure and price, but its purity and performance can change.
Manganese Dioxide vs Oxide
Chemical Differences
When you look at manganese dioxide vs oxide, you notice they are different. Manganese dioxide (MnO₂) has a higher oxidation state, called Mn(IV). Other manganese oxides, like Mn₃O₄ and MnO, have lower or mixed oxidation states. This changes how each one reacts and what it can do. Manganese dioxide has a special crystal shape, like rutile or tunnel shapes. This makes it very stable and a strong oxidizer. Other oxides, such as Mn₃O₄, have spinel or hausmannite shapes and more impurities.
Here is a table that shows how manganese dioxide and other oxides are different in chemical ways:
Property/Aspect | Manganese Dioxide (MnO₂) | Other Manganese Oxides (e.g., Mn₃O₄) |
|---|---|---|
Oxidation State | Higher (Mn(IV)) | Mixed (Mn(II,III)) |
Crystal Structure | Rutile/tunnel | Spinel/hausmannite |
Oxygen Vacancies | Variable, affects catalysis | Different, changes reactivity |
Electrochemical Behavior | Stable, good for batteries | Varies, used in supercapacitors |
Surface Area | High, helps in catalysis | Lower, less active |
You can also see the differences in surface area and specific capacitance in the chart below:
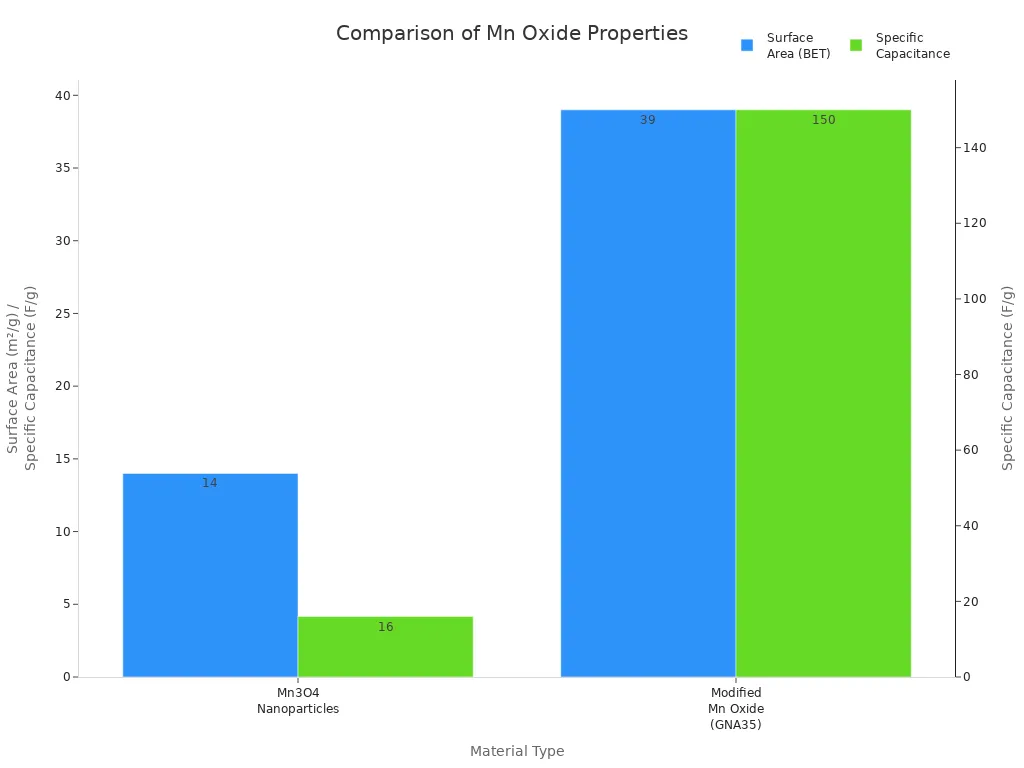
Manganese dioxide and other oxides have different chemical makeups and shapes. These differences change how well they work in energy storage and as catalysts.
Application Impact
The chemical differences between manganese dioxide and other oxides change how you use them. Manganese dioxide has a high oxidation state and a stable shape. It works best in batteries, especially as a cathode in alkaline and zinc-carbon batteries. Its strong oxidizing power and high surface energy make it great for catalysts and cleaning water.
Other manganese oxides, like Mn₃O₄ and MnO, have lower oxidation states and are less stable. You often find these in ceramics, pigments, and fertilizers. Their mixed oxidation states and different shapes make them less useful in batteries. But they are good for supercapacitors and as chemical catalysts.
Here is a table that shows how manganese dioxide and other oxides are used:
Feature | Manganese Dioxide (MnO₂) | Manganese(II) Oxide (MnO) | Manganese(II,III) Oxide (Mn₃O₄) |
|---|---|---|---|
Main Use | Batteries, catalysts, water treatment | Ceramics, fertilizers | Catalysts, pigments, ferrites |
Stability | High | Lower | Moderate |
Reactivity | Strong oxidizer | Less reactive | Moderate |
Note: When you pick manganese dioxide or another oxide, match its features to your job. This helps you get the best results and save money.
Uses
Batteries
Batteries are everywhere, like in remotes and cars. They use the most manganese dioxide, about 45% of the world’s supply. Electrolytic manganese dioxide is best for batteries. It is very pure and has a special structure. This helps batteries work better and last longer. You find it in lithium-ion and alkaline batteries. These are used in electric cars and portable gadgets. EMD lets batteries store more energy and stay strong. Chemical manganese dioxide is in some batteries too. But it is not as stable or powerful as EMD. As battery tech gets better, more companies pick EMD. They want batteries that are reliable and meet tough rules.
Note: EMD is chosen for top batteries because it is stable and holds a lot of energy.
Ceramics and Glass
Manganese dioxide is used in ceramics and glass for color and strength. Chemical manganese dioxide is the main type here. It often comes from recycled stuff, which is good for the planet. CMD makes glass-ceramics strong and hard. It also helps them resist damage. These things are used in tiles, dishes, and special ceramics. Electrolytic manganese dioxide is used less in this area. It is mostly for special products.
Aspect | EMD in Ceramics/Glass | Benefits of CMD | |
|---|---|---|---|
Raw Material | Recycled D-EMR | Minor use | Sustainability |
Mechanical Strength | High | Not specified | Durability |
Environmental Impact | Positive | Limited | Waste reduction |
Water Treatment
Manganese dioxide is also used to clean water. It helps take out iron, manganese, and other bad things. Pyrolusite, a natural kind, is used in big water plants. It acts like a helper and removes metals and gases. Lighter CMD types are good for small or cheap systems. You pick the type based on how big your system is and what you need to clean.
Role/Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
Main Roles | Removes iron, manganese, hydrogen sulfide, arsenic, and radium from water |
Common Media Types | Pyrolusite (large systems), CMD-coated media (smaller systems) |
Key Benefits | High loading rates, strong catalyst, smaller system footprint |
Other Applications
Manganese dioxide is used in many other ways. Supercapacitors use CMD because it has a big surface area and stores charge well. EMD is used to speed up chemical reactions and make colors and ceramics. Some farms use manganese dioxide to add nutrients to soil and animal food. It is also used in making special chemicals and in filters.
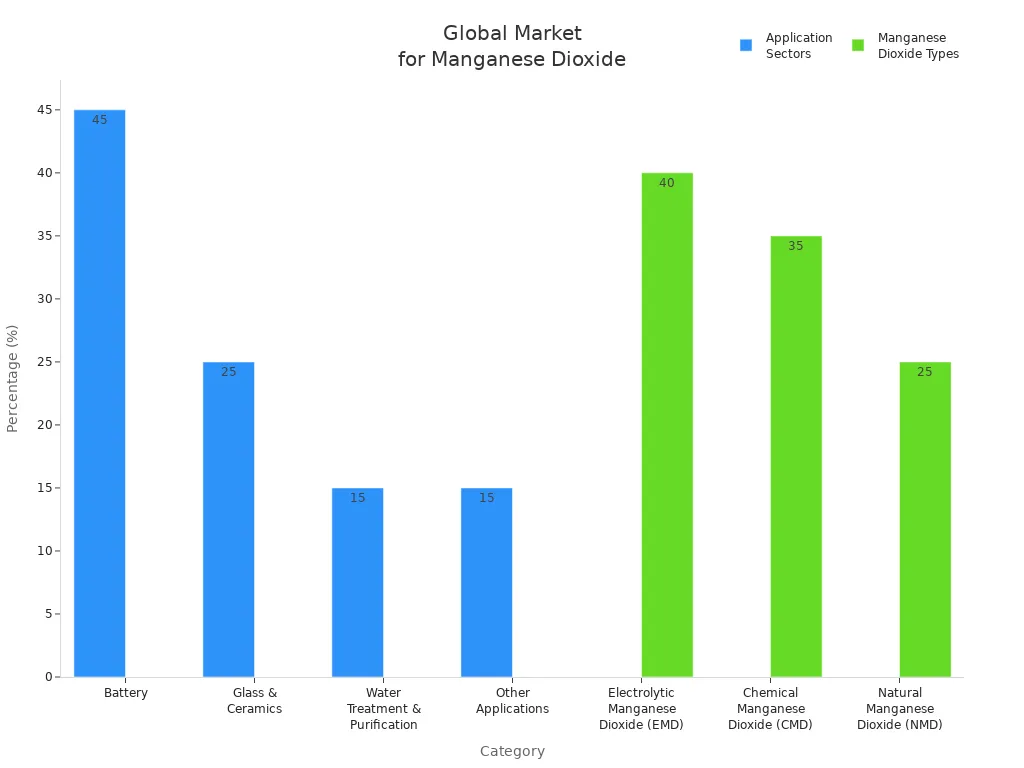
Tip: Pick manganese dioxide based on what your industry needs. Batteries need pure types. Ceramics and water cleaning care more about price and helping the environment.
How to Choose
Factors to Consider
When you pick the right type, think about a few things. Each type has special features that change how it works. The table below helps you compare them:
Key Factor | EMD Characteristics | CMD Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
Preparation Method | Commercial electrolytic process | Acid activation and chemical modification |
Acid-Base Properties | Residual dissociation in basic pH range | Similar acid-base properties to EMD |
Structural Defects | Less disordered, fewer defects | Highly disordered, may contain Mn2O3 or γ-MnO2 phases |
Manganese Oxide Phases | Mainly γ-MnO2 | Mn2O3 in first step; γ-MnO2 in second step |
Electrochemical Behavior | Standard voltammetric peaks | Similar peaks, higher current intensity |
You should also think about these points:
Purity: High-purity types are best for electronics or medical uses.
Storage needs: For long storage or high energy, pick a stable type with few defects.
Cost: Lower purity types cost less but may not work as well for fancy uses.
Surface finish: Some jobs need smooth material, others can use rougher kinds.
Modification: Surfactants can change how the material works. Triton X-100 helps storage and cycle life. SDBS can make performance worse.
Tip: Always match the material’s features to what you need. This way, you get the best results for your job.
Application Guide
A simple guide can help you pick the right type. Think about what matters most: storage, cost, or purity. Here are some common uses and what works best:
Water treatment: Lower purity types work well and save money. These are used in big systems where storage is not the main goal.
Agriculture: Lower purity types add nutrients to soil and animal feed. They are cheap and work for most needs.
Electronics and specialty chemicals: High-purity types are best. They give good storage and meet strict rules.
Batteries: High-purity types, especially electrolytic ones, give better storage and last longer.
Ceramics and glass: Lower purity types are fine. They add color and strength without costing a lot.
Supercapacitors: Types with high surface area and special crystal forms help storage and charge speed.
Industries try to balance cost, storage, and purity when picking a type. For example, steel and alloy makers use lower purity types because they are cheaper and still work. But electronics and specialty chemicals need high-purity types for better storage and performance.
Note: If you want high storage and long life, pick high-purity types. For easier jobs, lower purity types save money.
Common Mistakes
Many people make mistakes when picking the right type. You can avoid these problems by watching out for these things:
Ignoring purity: Using low-purity material for high-storage or sensitive jobs can cause bad results.
Overlooking structure: Not all types store energy the same. Pick the right crystal form for your job.
Focusing only on cost: Saving money is good, but the wrong type can cause bigger problems later.
Forgetting about modification: Some surfactants help storage and cycle life, but others can hurt performance.
Not matching finish to use: Some jobs need a smooth finish for better storage or making things. Others can use rougher types.
⚠️ Always check your storage, purity, and cost needs before you buy. This helps you avoid mistakes and get the best results for your job.
It is important to pick the right manganese dioxide for your job. Purity is very important for jobs that need strong performance. If you need very pure material, use electrolytic manganese dioxide. For easier jobs, chemical types with lower purity can help you save money. Always look at purity, shape, and if the supplier is good before you buy.
If you pick the wrong type or forget about purity, you might get bad results or even health problems.
Here are steps to follow before you buy:
Figure out how pure the manganese dioxide must be for your job.
Choose the best shape and how much you need.
Make sure the supplier is trusted and test some samples.
Look over all the product details and safety rules.
FAQ
What is the main difference between EMD and CMD?
EMD has higher purity and works better in batteries. CMD costs less and fits uses like ceramics or water treatment. You should pick EMD for high-performance batteries and CMD for cost-saving projects.
Can you use CMD in batteries?
You can use CMD in some batteries, but it does not last as long or store as much energy as EMD. For the best battery life and power, always choose EMD.
Is manganese dioxide safe to handle?
Manganese dioxide is safe if you use gloves and avoid breathing in dust. Always follow safety rules and check the CDC guidelines for handling manganese compounds.
How do you choose the right manganese dioxide for your project?
Check what your project needs. If you want high purity and strong performance, pick EMD. For lower cost and less strict needs, CMD works well. Always match the type to your application.
Related Posts

I am Edward lee, founder of manganesesupply( btlnewmaterial) , with more than 15 years experience in manganese products R&D and international sales, I helped more than 50+ corporates and am devoted to providing solutions to clients business.





