Manganese sand filter media is very important in water treatment. This material is made of small grains. It takes out bad things from water by catching and changing them. Many city and factory systems use it to fix water problems. It is used a lot for iron and manganese in water. These things can make water taste like metal. They can also leave stains and hurt machines. Manganese sand filter media can lower hydrogen sulfide too. Hydrogen sulfide makes water smell bad. Picking the right media helps clean water well. It also makes sure water treatment works for each need.
Manganese sand filter media takes out iron, manganese, and hydrogen sulfide. This helps water taste better and smell better. It also makes water safer to drink. The media changes dissolved metals into solids. Then, it catches and holds them in the filter bed. You need to backwash the filter often. You also need to use chemicals like potassium permanganate to keep it working well. This helps the filter last a long time. Picking the right filter size and flow rate is important. This makes sure the system cleans water well. It also stops clogging or damage. Manganese greensand is a popular coated media. It is simple to use and can be used for many years. The filter media is safe for drinking water. It helps lower bad metals to meet health rules. Operators should check water quality and how the filter works. This helps them know when to clean or change the media. Usually, this is every 5 to 10 years. For hard-to-remove things like arsenic, manganese sand filter media works best with other treatments.
Manganese sand filter media overview
What is manganese sand filter media
Manganese sand filter media is made of small grains. These grains are covered with manganese oxides, mostly birnessite. The manganese oxides have manganese in different forms, like Mn(III) and Mn(IV). The grains work as helpers called catalysts. They help take out dissolved manganese, iron, and other things from water. The media uses both chemical and biological ways to clean water. In older filters, chemical oxidation is the main process. Sometimes, special bacteria that use manganese also help. People often call manganese sand filter media “greensand.” It is a big part of greensand filters and manganese greensand filter media systems.
Note: Manganese oxides on the grains help remove manganese faster, especially when used with oxidants like chlorine.
Key properties
How well manganese sand filter media works depends on its physical and chemical features. The table below shows the main properties and how they affect filtration:
Property | Value/Range | Impact on Performance |
|---|---|---|
Black | Shows manganese oxide is present | |
Bulk Density | 1360 kg/m³ | Changes how the media packs and water moves |
Specific Gravity | 2.4 – 2.9 | Affects settling and cleaning |
Effective Particle Size | 0.30 – 0.35 mm | Impacts how well it filters and how water flows |
Uniformity Coefficient | 1.6 | Tells how even the grain sizes are, affects clogging |
Attrition Loss | 2% per year | Shows how strong the media is |
pH Range | 6.2 – 8.5 | Helps keep the media stable and working well |
Max Water Temperature | 26.7°C | Limits how active and stable the media can be |
Regeneration | 1.5 – 2.0 g KMnO₄/L | Brings back the media’s power to oxidize |
Max Fe or Mn in Raw Water | 15 ppm | Sets the most it can treat |
Max H₂S in Raw Water | 5 ppm | Changes how long the media lasts and works |
Manganese sand filter media has manganese dioxide. This helps change dissolved iron and manganese ions. The size and purity of the grains help water flow evenly and make reactions happen well. Over time, the media collects solids, which makes it harder for water to pass through. Cleaning the filter often helps it work better again.
Common uses in water treatment
Manganese sand filter media is used in many water treatment jobs. People use it in homes and businesses. Greensand filters use this media to take out iron, manganese, and hydrogen sulfide. These filters make water taste and look better. Manganese greensand is a special kind with a hard manganese oxide layer. It is very good at helping remove iron, manganese, and even arsenic.
Industrial water treatment
City water filters
Cleaning up water
Wastewater filters
Drinking water treatment
Pool, cooling, irrigation, and food and drink processing
Greensand filters and manganese greensand filter media are important in these systems. They help keep pipes safe, make water taste better, and stop stains. In city systems, manganese sand filter media usually lasts 5 to 10 years. How long it lasts depends on water quality and how well it is cared for.
How it works
Filtration process
Manganese sand filter media cleans water in a special way. It uses a few steps that work together. These steps help take out things we do not want in water. The main steps are oxidation, physical filtration, and regeneration.
Oxidation
Oxidation is the first step and is very important. When water goes through the filter, manganese dioxide acts as a helper. It changes dissolved iron and manganese into solid pieces. At first, these metals are clear and mixed in the water. The manganese dioxide makes the change happen faster. It turns them into ferric iron and manganese oxides. These new forms cannot dissolve in water.
People often add things like chlorine, ozone, or hydrogen peroxide before filtering. Chlorine is used a lot because it works well. It also stops germs from growing. Oxidation makes the water’s redox potential go up. This helps manganese dioxide turn metals into solids. The filter media does not get used up. It just helps the reaction go faster.
Note: Oxidation is needed because it changes iron and manganese into forms the filter can catch.
Physical filtration
After oxidation, the filter catches the solid pieces. Manganese sand grains have tiny spaces between them. Water moves through and these spaces trap the solid iron and manganese. This is called physical filtration. The filter also takes out other small bits in the water.
The filter bed acts like a wall. It keeps the solid pieces from going through. Over time, these pieces build up in the filter. People must clean the filter by backwashing. This step washes out the trapped solids. It helps the filter keep working well.
Here are the steps of the filtration process:
Oxidation: The media changes iron, manganese, and hydrogen sulfide into solids.
Filtration: The filter traps these solids in the media bed.
Regeneration: Potassium permanganate is used to make the media work again.
Removal mechanisms
Manganese sand filter media uses a few ways to take out bad things from water:
Catalytic oxidation: The manganese oxide on the media helps speed up the change of dissolved manganese and iron. Free chlorine in the water helps this and keeps the coating working.
Sorption: The media can pull and hold dissolved manganese ions on its surface. This helps remove them even before they turn into solids.
Physical removal: The filter traps solid pieces of iron, manganese, and other things after oxidation. These stay in the filter until backwashing takes them out.
Microbial action: Sometimes, special bacteria grow on the media. These bacteria help make a manganese oxide coating. This coating helps the filter remove manganese and other bad things even better.
Tip: Keeping a little free chlorine in the water helps the filter work better and last longer.
All these ways together make manganese sand filter media very good for cleaning water. The filter takes out iron and manganese. It also helps with hydrogen sulfide and other things we do not want.
Contaminants removed
Iron
Manganese sand filter media helps take iron out of water. Iron is often found in groundwater as clear ions. When water goes through the filter, the manganese dioxide coating changes the iron into solid bits. These bits get stuck in the filter bed. This makes the water clear and safe to use.
How well the filter removes iron depends on the method and conditions. The table below shows how much iron and manganese the filter can remove in different ways and seasons:
Treatment Module / Condition | Iron Removal Efficiency (%) | Manganese Removal Efficiency (%) |
|---|---|---|
Module #1 (chlorine oxidizer) | 67.7 | 58 |
Module #2 (aeration only, no chemicals) | 57 | 48.7 |
Module #4 (no oxidizer) | 42.6 | 38.9 |
Warm Season Average | 61.7 – 69.7 | 48.2 – 56.8 |
Other Modules / Cold Season | 42.6 – 57 | 38.9 – 48.7 |
The data shows the filter can remove iron with about 57% to 70% efficiency. The best results happen in warm weather and when using chlorine. Aeration also helps the filter remove iron and manganese.
A study found the filter works best when iron in the water is about 1.5 mg/L. In real plants, iron levels between 0.5 and 1.5 mg/L let the filter work well. These systems can lower iron in treated water to less than 0.1 mg/L, sometimes as low as 0.05 mg/L. This meets safe drinking water standards.
Manganese
Manganese sand filter media is made to take manganese out of water. Manganese is often found with iron in groundwater. Like iron, manganese starts as a dissolved ion. The manganese dioxide coating acts as a helper. It changes dissolved manganese into solid manganese oxides. These solids get caught in the filter bed.
Taking out manganese is important because it can make black stains on sinks and laundry. It can also make water taste bitter. The filter can remove manganese and iron at the same time. The filter usually removes about 48% to 58% of manganese, depending on the method and water temperature.
Operators should keep the water pH between 6.2 and 8.5 for best results. The filter works best if manganese in the water is not more than 15 ppm. Cleaning and regenerating the filter often helps it keep working well for both iron and manganese.
Hydrogen sulfide
Manganese sand filter media also helps take out hydrogen sulfide from water. Hydrogen sulfide makes water smell like rotten eggs and can damage pipes. The manganese dioxide in the filter reacts with hydrogen sulfide and turns it into solid sulfur. The filter bed then traps the sulfur.
Homes use manganese greensand filters to remove hydrogen sulfide. The size of the filter and how fast water flows through it affect how well it works. The table below shows common tank sizes and flow rates for removing hydrogen sulfide in homes:
Tank Size (inches) | Manganese Greensand Volume (ft³) | Recommended Service Flow Rate (GPM) | Maximum Recommended Flow Rate (GPM) |
|---|---|---|---|
8 x 44 | 0.75 | 1.7 | 3.5 |
9 x 48 | 1.0 | 2.2 | 4.4 |
10 x 54 | 1.5 | 2.7 | 5.5 |
12 x 52 | 2.0 | 3.9 | 7.9 |
13 x 54 | 2.5 | 4.6 | 9.2 |
14 x 65 | 3.5 | 5.3 | 10.7 |
16 x 65 | 4.5 | 7.0 | 14.0 |
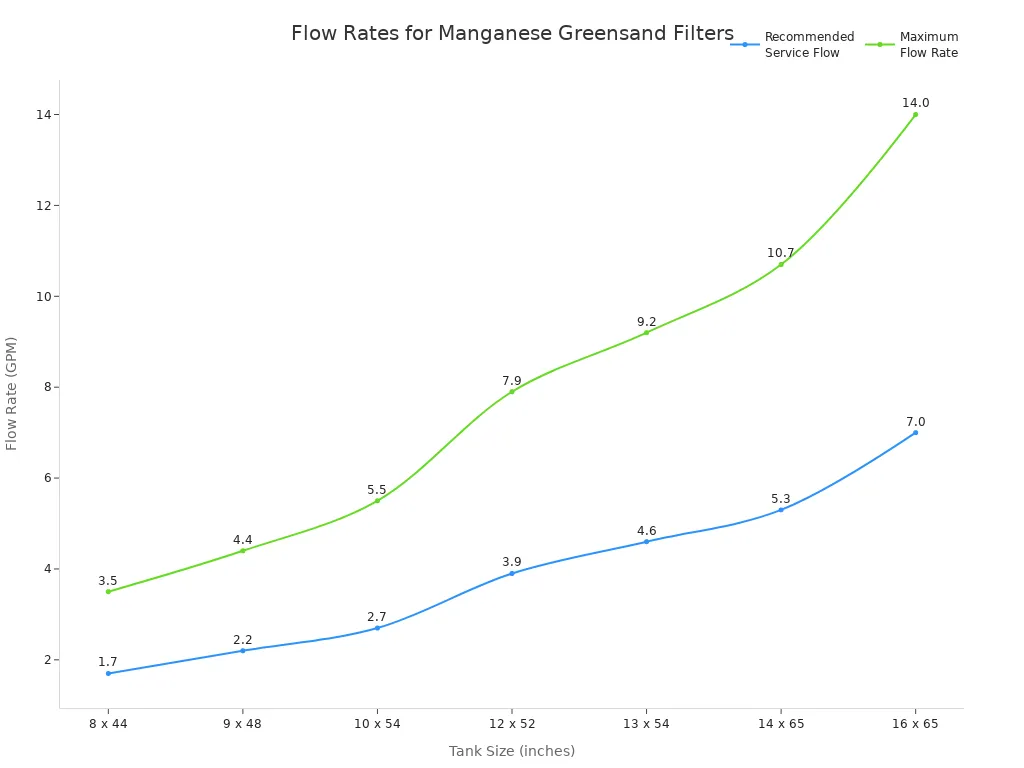
Most home systems work at flow rates between 1.7 and 7.0 gallons per minute, depending on tank size. This helps the filter remove hydrogen sulfide well and gives clean, odor-free water for daily use.
Arsenic and radium
Manganese sand filter media helps take out some harmful things from groundwater. Many water treatment systems use this media to remove metals like manganese and radium. The filter media has a layer of manganese dioxide. This layer acts as a helper called a catalyst. The catalyst helps change dissolved manganese and radium into forms the filter can catch. When water moves through the filter bed, the manganese dioxide layer grabs Mn2+ ions and changes them. This also works for radium, which is often found with manganese in groundwater.
Operators often pick manganese dioxide coated filter media, like GreensandPlus™, because it removes manganese and radium well. These filters need to be cleaned often with oxidants like chlorine. Cleaning keeps the manganese dioxide layer working and ready to remove more bad things. How well the filter works depends on water quality and how often it is cleaned. If there is a lot of manganese or radium in the water, the filter needs cleaning more often.
Radium removal works well because radium sticks to the manganese dioxide layer. This is called adsorption. The filter holds onto radium ions and lowers their amount in the water. Many city water systems use this method to meet safe drinking water rules for radium. The filter media can last for years if operators clean and take care of it the right way.
Arsenic is harder to remove. Studies show manganese sand filter media alone does not take out arsenic well. Some systems use electrocoagulation (EC) with oxidative media filtration to remove arsenic. In these systems, EC does most of the work for arsenic, while the manganese sand filter media helps with manganese and radium. The filter media by itself cannot make sure arsenic is at a safe level.
Note: Manganese sand filter media works best for manganese and radium. For arsenic, water treatment systems should use other methods like electrocoagulation.
Operators need to know what manganese sand filter media can and cannot do. The filter needs regular cleaning and careful watching. Water quality, especially iron, manganese, and radium, changes how well the filter works. For arsenic, using only manganese sand filter media may not make water safe. Using more than one treatment method works better for tough water problems.
Types of manganese-based filter media
Manganese greensand filter media
Manganese greensand is a very common filter media. It has a quartz sand core with a manganese dioxide coating. The coating helps remove iron, manganese, and hydrogen sulfide. Both city and home water systems use this media. People pick manganese greensand because it works in many water types. It can be cleaned and used again with potassium permanganate.
Greensand media can be made in different ways. Some types have a coating stuck onto the quartz. Others have the coating melted into the surface. The table below shows how these types are different:
Media Sample | Composition Characteristics | Physical Properties | Performance Characteristics |
|---|---|---|---|
GS1 | MnO2 coating on quartz; physically coated | 250–1000 µm particle size | Moderate Mn(II) removal; depends on activation |
GS2 | MnO2 fused into quartz surface | 2.0–4.0 mm particle size | Lower surface area; performance affected by iron |
GS3–GS5 | Lower silica; mix of metal oxides (hematite, MnO2, quartz) | GS5: 0.25–2.0 mm, high surface area | Higher Mn(II) removal, especially GS5; best with permanganate activation |
Operators use potassium permanganate to make greensand work better. With good care, greensand filters can last for a long time.
Pro-OX and Pyrolox
Pro-OX and Pyrolox are newer manganese filter media. Both use manganese dioxide to clean water. Pro-OX has over 80% manganese dioxide. Pyrolox Advantage has about 12.5%. Pro-OX’s higher amount means it can remove more iron, manganese, and hydrogen sulfide.
Both types use oxidation and filtration. Pyrolox needs a chlorine tank to be cleaned. It works best when water pH is between 6.5 and 8.5. It can handle water flow from 2 to 12 gallons per minute per square foot. Pro-OX is heavier and needs a stronger backwash. Because Pro-OX has more manganese dioxide, it may clean water better. But it is also heavier and harder to move.
Parameter | Pyrolox Advantage | Pro-OX |
|---|---|---|
Manganese Dioxide Content | 12.5% | Over 80% |
Contaminant Removal | Iron, manganese, hydrogen sulfide, arsenic | Iron, manganese, hydrogen sulfide |
Regeneration Method | Chlorine or ozone | Strong backwash required |
Media Weight (lbs/cf) | 84 | Heavier than Pyrolox |
pH Operating Range | 6.5 – 8.5 | Not specified |
Pro-OX and Pyrolox are good choices instead of regular greensand. They work well when water has more bad stuff or is harder to treat.
Coated vs. uncoated media
Some filter media have a coating, and some do not. Coated media, like manganese greensand, have a layer of manganese oxide on sand or carbon. This gives them more surface area and helps them grab metals like iron and manganese. Coated media are easy to use and cost less for most water systems.
Uncoated manganese media are often very tiny, like nanoparticles. They have a lot of surface area but are hard to separate from water. These types can work well in labs but are not easy to use in real water plants. They may need special and expensive machines.
Aspect | Coated Manganese Filter Media | Uncoated Manganese Filter Media |
|---|---|---|
Surface Area | High, due to coating | Very high (colloidal/nano form) |
Adsorption Capacity | Enhanced, attracts metal ions | High, but separation is difficult |
Cost and Handling | Cost-effective, easy to use | Expensive, hard to separate |
Operational Efficiency | Good, easy to operate | Low, not practical for most filters |
Limitations | Needs longer contact time sometimes | Not suitable for most water systems |
Tip: Most water plants use coated manganese filter media. They are easier to use and give good results.
Greensand filters, especially those with manganese greensand or new types like Pro-OX and Pyrolox, are the best for removing iron, manganese, and hydrogen sulfide. Operators should pick the right greensand media for their water, system size, and how much care it needs.
Installation and operation
System setup
Setting up the system the right way helps manganese sand filter media work well. Operators follow some important steps to make sure the filter does its job.
First, they change dissolved manganese into solid pieces. They often use chlorination or ozonation for this. The filter can then catch these solid pieces.
Next, they pick a filter tank size that fits the water flow needed. Bigger tanks can handle more water at once.
Operators plan regular backwashing. They follow the maker’s advice for how fast and how long to do it. This stops the filter from getting clogged.
They check if the wastewater system can take the extra water from backwashing. This keeps septic or city systems from getting too full.
Operators always follow the maker’s rules for putting in, running, and cleaning the filter. This helps the filter last longer and work better.
They test both untreated and treated water in certified labs after setting up the system. They also test at least once every year. This makes sure the filter is removing bad stuff as it should.
Operators keep good records of water tests, repairs, and filter care. These notes help them see how the system is doing and plan for the future.
They look at local rules about water use and backwashing. If they are not sure, they ask the local health department.
Tip: Good planning and regular checks help the filter system work well and give safe water.
Sizing and flow rate
Picking the right filter size and flow rate is very important. The tank size and type of filter media decide how much water the system can clean. Operators use gallons per minute for each square foot of filter area to figure out the size. For manganese greensand, about 3 gallons per minute per square foot is best. The highest flow rate can be 5 gallons per minute per square foot. Backwashing needs more water, usually 8 to 10 gallons per minute per square foot.
The table below shows common flow rates for different tank sizes:
Tank Diameter (inches) | Service Flow Rate (GPM) | Backwash Flow Rate (GPM) |
|---|---|---|
6 | 0.7 | 2.6 |
8 | 1.2 | 4.7 |
10 | 1.9 | 7.4 |
12 | 2.7 | 10.6 |
14 | 3.7 | 14.4 |
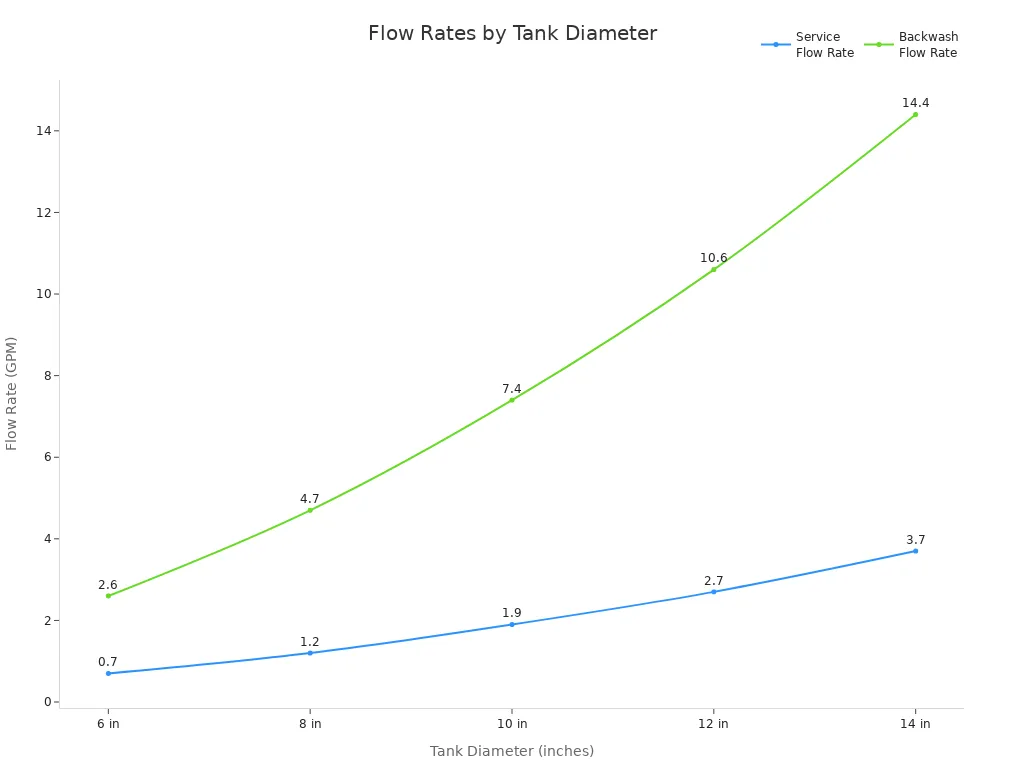
Operators often use a calculator to match tank size, filter media, and water flow. Picking the right size helps the filter system work well and remove bad things from water.
Integration with water treatment systems
Manganese sand filter media often works with other water treatment methods to get better results. Operators use both chemical and biological ways to take out manganese. The manganese oxides on the filter help with chemical changes. Tiny living things can also grow on the filter media. These help remove manganese faster, but they need two to three months to start working.
Adding chemicals like potassium permanganate makes a strong manganese oxide layer on the sand. This helps remove more manganese, iron, and ammonia. Aeration adds oxygen, which helps change iron and manganese and takes out gases like hydrogen sulfide and carbon dioxide. Sometimes, operators mix manganese greensand with other filter media. This helps remove more than one bad thing at the same time.
Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
Aeration | Adds oxygen, removes gases, and makes water taste better. |
Filtration Rate | Works best at 300 L/hr; higher rates do not clean as well. |
Chemical Processes | Changes iron and manganese, grabs arsenic, and makes solids for the filter to catch. |
Filter Media Integration | Mixes manganese greensand with other media to remove many bad things at once. |
Media Properties | Has an even coating, can be cleaned, and stays strong during backwashing. |
Particle Sizes/Volumes | The right sizes and amounts help the filter work with other parts of the system. |
Operators design water filter systems using these good ideas. This helps the system remove bad things from water and last a long time.
Maintenance and regeneration
Routine maintenance
Routine maintenance helps manganese sand filter media work well. Over time, things like biofilms, calcium scale, iron, manganese, and algae can build up. These things make the filter work less well. Backwashing does not get rid of all the buildup. Chemical cleaners break down tough layers and clean underdrains. This brings back the filter’s power and saves water, time, and energy. Operators should use pre-filters to catch big particles before they reach the filter. Sediment filters help stop clogging. Tools like chlorinators and carbon backwash filters help keep water clean. Regular care means changing filters on time, cleaning the system, and washing the filter bed. These steps help the system give clean water and work well.
Maintenance Task | Purpose | Frequency |
|---|---|---|
Backwashing | Removes trapped solids and prevents clogging | Weekly or as needed |
Chemical Cleaning | Dissolves scale and biofilm | Every 6-12 months |
Pre-filter Replacement | Stops large particles from entering system | Monthly |
System Sanitization | Prevents bacteria growth | Quarterly |
Water Quality Monitoring | Ensures filter effectiveness | Ongoing |
Tip: If water looks cloudy, smells bad, or flows slowly, the filter needs care or a new part.
Regeneration methods
Manganese sand filter media needs regular regeneration to keep working. There are two main ways to do this: backwashing and chemical regeneration.
Backwashing
Backwashing pushes water backward through the filter bed. This washes out dirt and trapped solids. Operators use a strong flow to lift and clean the media. Backwashing should be done every week or when pressure goes up. Good backwashing stops channels from forming and keeps the filter working.
Chemical regeneration
Chemical regeneration uses oxidizers like potassium permanganate or chlorine. Operators add these to bring back the manganese oxide coating. There are two main ways to do this:
Continuous Regeneration (CR): Operators add an oxidizer before filtering. This works best for iron and lets the filter regenerate quickly, sometimes in 15 minutes.
Intermittent Regeneration (IR): The media works until it is full. Then operators regenerate and backwash, which takes about 75 minutes.
Operators must soak new greensand media in potassium permanganate before first use. Keeping enough oxidizer in the system helps the media work well.
Note: How often you regenerate depends on how much iron or manganese is in the water and how fast water flows. More iron or manganese means more regeneration.
Troubleshooting
Operators should look for signs the media is worn out or not working. Signs include bad water, shorter filter runs, using more chemicals, channels in the filter bed, and bad smells. If these happen, operators should:
Regenerate before the media is used up.
Keep flow rates right and backwash well to stop channels.
Use chemical cleaning to remove buildup and help the filter work again.
Doing regular regeneration and care helps the filter keep removing iron, manganese, and hydrogen sulfide. If problems do not go away after cleaning and regenerating, the media may need to be replaced.
Effectiveness and safety
Performance in water treatment
Manganese sand filter media works well to clean water. Many water plants use this media because it removes bad things. Operators see good results for iron, manganese, and hydrogen sulfide. The table below shows how well the filter works in real systems:
Parameter | Removal Efficiency (%) | Notes |
|---|---|---|
Iron | 85-92 | Full-scale biological trickling filter in New Vouprasio, Greece |
Manganese | 69 | Same full-scale filter; manganese removal is rate-limiting due to oxidation difficulty |
Hydrogen Sulfide | 100 | Complete elimination via aeration in the trickling filter |
Manganese (with chlorine dioxide preoxidation + manganese sand filtration) | >95 | Coupling method studied by Chen et al. (2016) for deep manganese removal |
Iron removal can reach up to 92% with this filter. Manganese removal can be 95% if preoxidation is used. Hydrogen sulfide is often removed completely. These results show the filter works well even with hard water problems. Operators check the system often to keep water clean and the filter working.
Safety for drinking water
Manganese sand filter media is safe for cleaning drinking water. The media does not add anything harmful to the water. It helps lower manganese and iron, which can be bad for health. Manganese greensand filters use potassium permanganate to help remove metals. This process does not leave anything dangerous in the water.
Note: Health experts say too much manganese in water can hurt kids. Manganese sand filter media helps by lowering manganese to safe amounts.
Operators trust this filter because it makes water better and meets safety rules. The filter helps with taste and health, so it is a good choice for homes and towns.
When to replace media
Operators need to know when to change the manganese sand filter media. Over time, the media stops working as well. Signs to change the media include:
The filter does not remove as much iron, manganese, or hydrogen sulfide
The filter needs backwashing more often
The pressure in the filter goes up
Water still tastes or smells bad
Most filters need new media every 5 to 10 years. This depends on how dirty the water is and how well the filter is cared for. Operators test and watch the filter to know when to change it. Changing the media on time keeps water clean and safe for everyone.
Manganese sand filter media works well to take out iron, manganese, and hydrogen sulfide from water. New improvements help the filter clean water faster and last longer. This makes it a smart and money-saving choice. People should pick the right media for their water and system. They need to backwash and regenerate the filter often. It is important to check water quality regularly. If water problems are hard to fix, asking an expert can help the filter work its best and last a long time.
FAQ
What does manganese sand filter media remove from water?
Manganese sand filter media takes out iron, manganese, and hydrogen sulfide. It can also help lower radium and some other metals. This media makes water taste, smell, and look better.
How often should operators backwash the filter?
Operators should backwash the filter every week or when water slows down. Doing this often keeps the filter working well and stops it from clogging.
Is manganese sand filter media safe for drinking water?
Yes. Manganese sand filter media does not put anything harmful in water. It helps meet safe drinking water rules by taking out metals and bad smells.
How long does manganese sand filter media last?
Most manganese sand filter media lasts between 5 and 10 years. How long it lasts depends on water quality and how well the system is cared for.
Can manganese sand filter media remove arsenic?
Manganese sand filter media alone does not take out arsenic well. Operators often use other ways, like electrocoagulation, to remove arsenic better.
What is the best pH range for manganese sand filters?
The best pH range is from 6.2 to 8.5. This range helps the filter take out iron and manganese and keeps the media working well.
Do operators need to use chemicals with manganese sand filters?
Yes. Operators often use chemicals like chlorine or potassium permanganate. These help bring back the filter media and make it better at removing metals.
What signs show the filter media needs replacement?
Operators should watch for cloudy water, bad smells, or less iron and manganese being removed. Needing to backwash a lot or high pressure also means the media may need to be changed.
Related Posts

I am Edward lee, founder of manganesesupply( btlnewmaterial) , with more than 15 years experience in manganese products R&D and international sales, I helped more than 50+ corporates and am devoted to providing solutions to clients business.





