Nanostructured manganese dioxide brings new chances for better batteries. It helps store more energy, makes batteries last longer, and is better for the environment. Recent studies show manganese dioxide nanostructures help batteries keep working well over time. This is good for electric cars and big energy storage. The need for manganese-based battery materials is growing fast. This is because more people want electric cars, portable gadgets, and home energy storage. The table below shows how fast the market for manganese dioxide in batteries is growing:
| Market Segment | 2024 Market Value (USD Billion) | 2033 Forecast Value (USD Billion) | CAGR (2026–2033) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manganese Dioxide for Battery | 1.5 | 2.8 | 8.5% |
| Manganese Oxide Cathode Battery | 1.5 | 3.2 | 9.2% |
New ways to shape manganese dioxide make it stronger and better at carrying electricity. This helps make better batteries and supports clean energy solutions.
- Nanostructured manganese dioxide helps batteries last longer. It lets ions move faster and makes batteries stronger.
- This material helps lithium-ion, zinc-ion, and zinc-air batteries work better. These batteries are good for electric cars and clean energy storage.
- There are problems like losing capacity and not conducting well. Nanostructures and adding chromium or bismuth can fix these problems.
- Green synthesis uses plant extracts to make safe manganese dioxide nanoparticles. This helps make batteries in a way that is good for the environment.
- The manganese dioxide battery market is growing quickly. More people want electric cars and renewable energy. This gives good chances for people to invest.
Nanostructured Manganese Dioxide in Batteries
Nanostructured manganese dioxide helps batteries work better than older forms. It is used as a cathode material in advanced batteries. This lets batteries store more energy and last longer. Scientists found that making a smooth, porous nanostructured film on cathodes helps the battery parts stay strong. It also helps electricity move faster. This means batteries can keep working well for many cycles. This is important for electric cars and big energy storage.
Nanostructured manganese dioxide has special features. It has tiny crystal particles and a large surface area. These help ions move quickly and let electricity flow easily at the electrode. For example, γ-MnO2 nanoflakes made at room temperature have high capacitance and steady discharge. These cathodes work better than regular manganese dioxide. They are great for batteries that need high performance.
Nanostructured manganese dioxide, like λ-MnO2, can hold more charge than regular forms. This happens because it helps charge move better between the electrode and the electrolyte. The nanostructure also stops unwanted layers from forming. This keeps the battery strong and helps it last longer.
The table below shows how different types and treatments of manganese dioxide change battery charge and discharge rates:
MnO2 Form / Treatment | Key Experimental Findings | Effect on Charge/Discharge Rates |
|---|---|---|
Stabilized α/β-MnO2 | Starts with about 230 mAh/g; keeps about 150 mAh/g after 20 cycles | Higher discharge and good recharge because of stable structure |
Ramsdellite (R-MnO2) and Pyrolusite (β-MnO2) | Highest discharge; flat curves | Great capacity but not good for deep recharge because of changes |
α-MnO2 nanorods (~20 nm diameter) | 189 mAh/g at 50 mA/g current | Better rate because ions move faster in the nanostructure |
Bi-doped MnO2 | Bi3+ ions help keep the structure strong | Better stability and electricity flow, so charge/discharge is improved |
Alkali ion doping (e.g., K+, Li+) | Alkali ions make tunnels stable and help ions move | Faster charge and discharge because ions and electricity move better |
Scientists also saw that nanostructured manganese dioxide cathodes, like nanorods and nanofibers, help lithium ions move faster. These cathodes make the path for ions shorter. This lets batteries charge and discharge quickly. Adding elements like Bi, Ag, or alkali ions makes the battery even stronger and helps electricity move better. These new ideas help make batteries for electric cars and energy storage work better.
Tip: Nanostructured manganese dioxide cathodes help batteries work well by giving more surface area, helping ions move, and keeping the structure strong during many uses.
Role in Zinc-Ion and Zinc-Air Batteries
Aqueous zinc ion batteries get a big boost from nanostructured manganese dioxide. These batteries use manganese dioxide cathodes shaped into hollow rods, dots, or flowers. These shapes help ions move and make the battery work faster and last longer. Adding metals or mixing with carbon materials like nanotubes or graphene makes the battery even better. These changes help electricity flow and keep the battery strong.
New studies show that mixing manganese dioxide with carbon nanofibers or graphite flakes makes cathodes with high capacity and fast charging. For example, δ-MnO2 nanoflowers on graphite flakes help electricity move and give more power at first. Graphene scrolls on α-MnO2 cathodes stop the material from breaking down and help store more energy. This makes them good for batteries that need to work very well.
The table below shows how changing manganese dioxide cathodes helps zinc ion batteries work better:
Modification Type | Description | Effect on Zinc-Ion Battery Performance |
|---|---|---|
Nanostructure engineering | Making hollow rods, dots, and flowers from MnO2 | Helps ions move and makes the battery work faster and last longer |
Metal doping | Adding metal ions to MnO2 | Makes electricity flow better and keeps the battery strong |
Composite formation | Mixing MnO2 with carbon materials | Helps electricity flow, stops breakdown, and helps ions move back and forth |
Zinc ion batteries with nanostructured manganese dioxide cathodes work well for a long time. For example, MnO2 with carbon nanofibers keeps its power for over 1,000 cycles. These cathodes also let H⁺ and Zn²⁺ ions move back and forth, which helps the battery work better and store more energy.
In zinc-air batteries, nanostructured manganese dioxide is also important. Scientists use β-MnO2 nanorods as cathodes in rechargeable zinc-manganese dioxide batteries. These cathodes can hold up to 225 mAh/g and keep 94% of their power after 2,000 cycles. Using a mild acid electrolyte stops manganese from breaking down and helps the battery stay strong. The change from tunnel-shaped MnO2 to layered zinc-buserite lets Zn2+ ions move in and out. The nanostructure keeps ions moving and the battery strong.
These new ideas for manganese dioxide cathodes help zinc batteries store more energy and last longer. The better performance and storage make these batteries good for electric cars, grid storage, and other uses where strong batteries are needed.
Battery Performance Challenges
Capacity Fading
Capacity fading is a big problem for manganese dioxide batteries. Scientists at Argonne National Laboratory studied this issue. They found manganese ions leave the LiMn2O4 cathode. These ions travel to the anode and get stuck in the solid-electrolyte interphase. This traps lithium ions and lowers how much energy the battery can hold. When manganese dissolves, the battery loses active material. The anode also becomes harder for electricity to pass through. Over time, the cathode gets damaged and changes shape. High heat makes manganese dissolve faster and causes more capacity loss. All these problems make fewer lithium ions available and hurt battery performance.
Note: Capacity fading happens because of chemical changes and weak structure in the cathode. This problem makes batteries not last as long in electric cars and energy storage.
Conductivity Issues
Manganese dioxide in battery electrodes does not conduct electricity well. This makes batteries work less well and less stable. Poor conductivity makes it hard for the electrode to work during charging and discharging. In zinc-manganese dioxide batteries, this means the battery cannot be used as many times. The battery also works worse. Scientists fixed this by adding surfactants to the electrolyte. Surfactants help make better crystal shapes. This lets ions move easier and stops bad reactions.
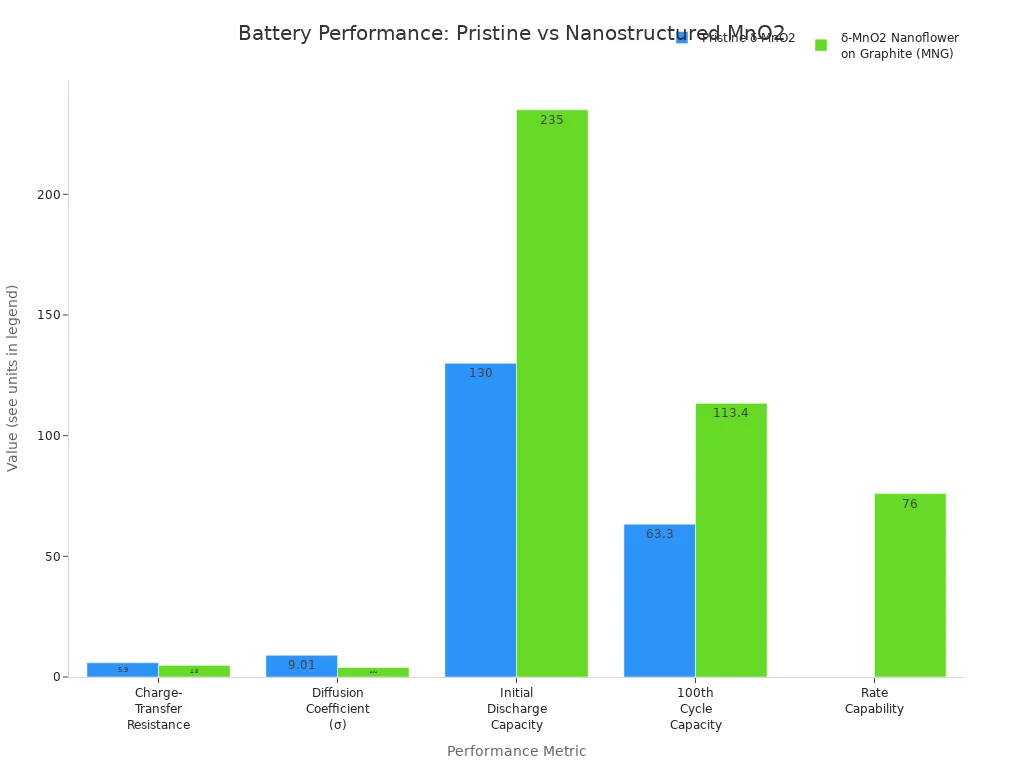
The table below shows how regular and nanostructured manganese dioxide compare in batteries:
Property / Metric | Pristine δ-MnO2 | δ-MnO2 Nanoflower on Graphite (MNG) |
|---|---|---|
Electrical Conductivity | Lower (poor intrinsic conductivity) | Significantly improved due to graphite support |
Charge-Transfer Resistance (Rct) | 5.9 Ω | 4.8 Ω |
Diffusion Coefficient of Zn2+ ions | Lower (σ = 9.01) | Higher (σ = 3.94) |
Initial Discharge Capacity at 200 mA/g | 130 mAh/g | 235 mAh/g |
Discharge Capacity at 100th cycle (400 mA/g) | 63.3 mAh/g | 113.4 mAh/g |
Rate Capability (at 1600 mA/g) | Lower | Higher (discharge capacity 76 mAh/g) |
Cycling Stability and Coulombic Efficiency | Lower capacity retention | Higher capacity retention and ~100% coulombic efficiency |
Material Degradation
Material degradation makes batteries weaker and not last as long. Many things cause this problem:
The structure breaks down when β-MnO2 turns into orthorhombic LixMnO2 in the first cycle. Later, it partly changes into spinel-like LiMn2O4, which lowers capacity.
Manganese dissolves more when ethylene carbonate is in the electrolyte, especially at high voltages.
Layered manganese-based oxides change shape, making the structure weaker.
Jahn-Teller distortions make the battery even less stable and lower performance.
The kind of electrolyte affects how long the battery lasts. More ethylene carbonate means more manganese loss and faster capacity fading.
Scientists learned that making manganese dioxide into tiny shapes helps stop material degradation. Flower-like shapes and small particles help the battery keep its power and let lithium move better. Heating the material makes stable pyrolusite domains. Ball-milling helps the active material touch the conductive parts better. These changes keep the crystal structure strong and help ions move, so the battery works better.
Tip: Fixing material degradation is very important for making batteries work better and last longer.
Solutions with Nanostructured Manganese Dioxide
Enhanced Ion Transport
Nanostructured manganese dioxide helps batteries work better by moving ions faster. Scientists found that mixing α-MnO2 with carbon nanostructures makes electrons move easier than regular manganese dioxide. The place where the nanostructure and carbon meet lets electrons travel quickly. This helps cathodes work better in batteries. Computer tests show this mix can reach a current of 90.0 μA at 3.0 V, which is much higher than regular materials. Quantum capacitance checks also show these cathodes can store lots of energy, so they are great for strong batteries.
Different shapes of manganese dioxide help ions move inside batteries. α-MnO2 nanorods and δ-MnO2 nanoflakes are important for this. δ-MnO2 has wide layers that let Zn2+ ions move fast, which helps zinc ion batteries. α-MnO2 nanorods have tunnels that give Li-ions more ways to travel. When scientists put these nanostructures on carbon nanotubes, ions and electrons move even better. This means batteries have more power and last longer.
Tests show MnO2 cathodes work better than Mn2O3 in zinc-ion batteries. MnO2 has more surface area and better conductivity, so Zn2+ ions move easier. This gives batteries more power and better performance. Growing MnO2 nanoflakes on carbon nanotubes makes a strong bond. This keeps the nanoflakes in place and helps electrons move. Batteries made this way can be used many times and keep working well, which is good for storing energy.
Note: Picking the right nanostructure and support helps manganese dioxide cathodes work better in zinc ion batteries. This makes batteries stronger and last longer.
Structural Stability
Structural stability helps batteries last a long time. Nanostructured manganese dioxide with tiny pores and crystals can handle changes during battery use. Hollow shells made with surfactants keep their shape when lithium ions move in and out. This stops big particles from breaking down and helps batteries keep their power for many cycles.
Adding chromium to δ-MnO2 makes the cathode stronger. Studies show chromium helps the structure stay stable and tough in zinc ion batteries. This means the cathodes keep working well for a long time.
Scientists also found δ-MnO2 nanoflowers grown on carbon from coal gas slag stay stable. The special flower shape and oxygen spaces from the carbon help the cathode keep its shape and react faster. This makes batteries work better and last longer.
The shape of manganese dioxide matters too. α-MnO2 nanorods have tunnels that stop them from breaking down. These tunnels have spots that hold K+ ions without hurting the structure. The tunnel shape makes it easier for ions to move fast. This helps batteries keep their power and work well for a long time.
Tip: Using the right nanostructure and adding things like chromium makes manganese dioxide cathodes stronger. This is important for batteries that need to last and work well.
Green Synthesis Methods
Green synthesis methods for nanostructured manganese dioxide are good for the environment and save money. Scientists use safe ways to make MnO2 nanoparticles:
Chemical reduction, sol–gel, hydrothermal, and electrochemical methods are all green choices.
Oxidation of Mn(II) in basic solutions or reducing permanganate are common ways.
Plant extracts from Yucca gloriosa, acerola, olive leaves, and Gmelina arborea help make and stabilize nanoparticles.
Chemicals in these plants, like phenolics and flavonoids, control the size and shape of the nanoparticles.
These methods do not use harmful chemicals and work in gentle conditions, so they are safe and cheap.
Hydrothermal synthesis with green materials helps control the phase and purity.
Things like pH, temperature, and how much starting material is used change the final product.
Green synthesis is good because it does not hurt the environment and can be used for big projects. Using plant extracts cuts down on toxic waste and saves energy. Plants can be grown again and have antioxidants and sugars that help make nanoparticles. These methods work at room temperature, which saves energy and helps the planet. The process is easy and can be made bigger for factories, so it is good for making lots of batteries.
One study used olive leaf extract to make MnO2 nanoparticles about 15 nm wide. These particles had lots of surface area and were good for battery cathodes. Another study used lemon extract and turmeric curcumin to make nanoparticles with strong germ-fighting power and energy storage uses.
???? Green synthesis methods help the environment and make strong manganese dioxide cathodes for zinc ion batteries and other energy storage systems.
Manganese Dioxide Market Trends
Battery Applications
The manganese dioxide market is getting bigger as more people want better batteries. Battery-grade manganese dioxide is very important for storing energy. It helps many things work, like alkaline and zinc-carbon batteries, lithium-ion batteries, and special batteries for small electronics, medical tools, and machines. This kind of manganese dioxide helps batteries last longer and work well. It is needed for things like phones and electric cars.
Most of the manganese dioxide sold is used in batteries, especially lithium-ion and alkaline ones. These batteries are used in electric cars, storing energy from wind and solar, and backup power. The market is growing because people want cleaner energy and need good batteries in many places. Asia Pacific is the top area for manganese dioxide batteries. North America and Europe are next because they use new technology and have rules that help.
Battery Application Sector | Role of Manganese Dioxide (EMD) | Key Characteristics and Drivers |
|---|---|---|
Alkaline and Zinc-Carbon Batteries | Cathode material with high purity and strong electrochemical properties | Provides steady, long-lasting battery performance; widely used in dry-cell batteries |
Lithium-ion Batteries | Cathode component improving performance and durability | Enhances battery life and efficiency, important for portable electronics and electric vehicles |
Portable Electronics | Power source for cell phones, laptops, and other devices | Demand driven by lightweight, efficient energy storage needs |
Electric Vehicles (EVs) | Battery component critical for energy storage | Growth fueled by shift to sustainable energy and electric mobility |
Renewable Energy Storage Systems | Energy storage solutions for wind, solar, and off-grid systems | Increasing demand due to clean energy initiatives and need for reliable backup power |
Consumer Electronics | Batteries for hearing aids, watches, remote controls | Growth linked to miniaturization and IoT expansion |
Medical Devices | Implantable devices and diagnostics | Requires reliable, long-lasting power sources |
Industrial Applications | Sensors and instrumentation | Demand driven by durability and safety requirements |
The manganese dioxide battery market is helped by smaller batteries, safer designs, and longer life. More people want batteries for clean energy and electric cars, so the market keeps growing. Battery-grade manganese dioxide is still the best choice for companies that want strong and earth-friendly batteries.
Investment Opportunities
There are good chances to invest in manganese dioxide as more electric cars and energy storage are needed. Investors like battery-grade manganese dioxide because it is key for electric cars, clean energy, and small electronics. The market for these batteries is expected to grow over 7% each year until 2028, with battery-grade manganese dioxide leading the way.
Where people invest changes the manganese dioxide market. Asia Pacific is growing the fastest because of government help, more factories, and cheaper production. North America and Europe focus on new ideas, green energy, and rules that help battery use. New markets in Latin America, the Middle East, and Africa are getting more money and building more, which gives new chances for manganese dioxide batteries.
Region | Market Characteristics and Investment Impact |
|---|---|
North America | Mature market with high technology adoption, strong consumer demand, and supportive regulatory frameworks. |
Europe | Innovation and sustainability focus, driven by strict regulatory standards and government investments. |
Asia-Pacific | Fastest-growing region, propelled by urbanization, industrial expansion, and rising demand for battery applications. |
Latin America, MEA | Untapped opportunities with growing foreign investments and infrastructure development. |
The manganese dioxide market is growing because more people use electric cars, want clean energy, and governments support green batteries. Companies spend money on new ideas, recycling, and making sure they have enough materials. The battery market for manganese dioxide keeps getting bigger as companies make more and try new things to be leaders in energy storage.
Innovations in Manganese Dioxide for Battery Market
Nanocomposites and Doping
New ideas in nanocomposites and doping are changing the manganese dioxide battery market. Scientists mix manganese with other elements like nickel, chromium, neodymium, cobalt, copper, titanium, and vanadium. These elements change the crystal structure and make batteries work better. Nickel-doped ZnMn2O4/Mn2O3 nanocomposites use a special method to control the Mn3+/Mn4+ ratio. This gives batteries high discharge capacity and helps them last longer. Chromium-doped Mn2O3 has a cauliflower-like shape and works better than materials without chromium. Adding nitrogen and sulfur makes more oxygen spaces, which helps electricity and ions move faster. These changes help cathodes work well and make batteries last longer.
Dopant(s) | Material/System | Synthesis Method | Structural/Compositional Changes | Electrochemical Performance Improvements |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Ni | Pulse potential electrodeposition | Regulated Mn3+/Mn4+ ratio, reduced potential gap | High discharge capacity (114.67 mAh/g after 3000 cycles at 2 A/g) | |
Cr | Cr-doped Mn2O3 with cauliflower-like nanostructure | Constant-current cathodic electrodeposition | Reduced crystallinity, improved morphology | Superior performance vs undoped Mn2O3 |
Nd (5%) | Nd-doped α-Mn2O3 microspheres | Hydrothermal method | Increased oxygen vacancies, uniform morphology | Enhanced capacity, ion mobility, cycle stability |
Co | Co-doped Mn3O4 | Not specified | Co2+ acts as structural pillar, Co4+ enhances conductivity, alleviates Jahn-Teller distortion | Maintains 292.6 mAh/g after 250 cycles, 90% retention |
Cu | Cu-doped Mn3O4 | Not specified | Cu2+ substitutes Mn3+, porous micro/nanostructure | Improved conductivity and Zn2+ diffusivity, 250 mAh/g discharge capacity |
Ti | Ti-doped α-MnO2 nanowires | Atomic layer deposition (ALD) | Ti doping supplies electrons, creates oxygen vacancies | Improved ion diffusion kinetics and electrochemical performance |
V | V-doped MnO2 | Increased specific surface area |
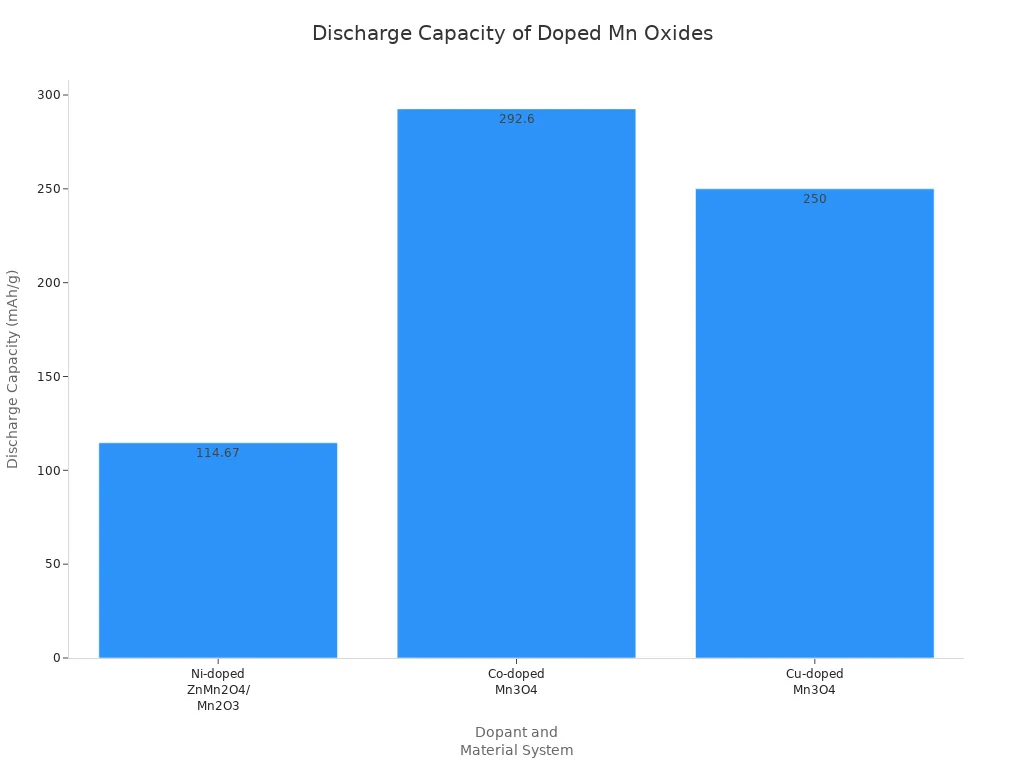
Other elements like lithium, ammonium, cobalt, iron, tungsten, and vanadium also help cathodes work better. These changes make batteries charge and discharge more easily. This helps batteries reach high performance in the manganese dioxide battery market.
Synthesis Techniques
New ways to make manganese dioxide help batteries work better and can be used in many places. Hydrothermal methods let scientists control the shape and size, making nanorods and flat pieces with lots of surface area. Sol–gel and template methods help make even cathodes for batteries. Electrochemical synthesis lets manganese dioxide grow right on electrodes, which helps batteries work well in zinc ion batteries. Microemulsion and coprecipitation methods make tiny particles with the right size and crystal shape. Supercritical CO2 synthesis and heating special materials make new shapes for batteries that work well.
Synthesis Technique | Description & Advances | Impact on MnO2 Nanostructures and Applications |
|---|---|---|
Hydrothermal | Chemical reactions in water at high temperature and pressure; morphology controlled by temperature/pressure | Enables diverse morphologies; widely used for tailored nanostructures |
Sol–gel | Chemical solution process forming gels that convert to MnO2 nanomaterials | Controls particle size and crystallinity |
Template | Uses templates to direct nanostructure formation | Produces specific shapes like nanowires, porous, or hollow structures |
Electrochemical | Electrosynthesis methods including cathodic electrosynthesis | Allows direct growth on electrodes; precise control of nanostructure formation |
Coprecipitation | Simultaneous precipitation of Mn compounds | Influences particle size distribution and crystal transformation |
Microemulsion | Self-reacting microemulsion methods for nanosized hydrous MnO2 | Produces uniform nanoparticles with controlled size and electrochemical properties |
Supercritical CO2 Synthesis | Synthesis in supercritical carbon dioxide environment | Novel method for electrocatalysts with unique morphologies |
Heat Annealing of Precursors | Thermal treatment of manganese hydroxide precursors to form hexagonal nanosheets | Achieves specific nanostructures with enhanced electrochemical performance |
Hydrothermal synthesis is great for making cathodes with lots of surface area and good catalytic ability. This method is cheap and can make lots of material, so it is good for electric cars and energy storage.
Future Research Directions
Experts think there are many good ideas for the manganese dioxide battery market. Scientists want to make cathodes better for new batteries, like magnesium and lithium ones. They try to control the structure of manganese dioxide, especially the spinel phase, to get high performance and one-electron transfer. Learning about how reactions work, like intercalation and conversion, will help batteries hold more energy and keep voltage steady. These plans help make cathodes for zinc ion batteries and other advanced uses.
Note: Future research will help the manganese dioxide battery market get higher energy, longer life, and better stability.
Right now, more people want strong batteries for electric cars, portable gadgets, and factories. New ways to make manganese dioxide and bigger production help companies sell more batteries. The market gets better cycling stability, lower costs, and helps the environment. Battery grade electrolytic manganese dioxide keeps growing because of electric cars and clean energy storage. The manganese dioxide battery market has problems like changing prices and other technologies, but new research will bring better cathodes for high performance.
Nanostructured manganese dioxide helps fix big battery problems. These cathodes make batteries work better and store more energy. They help batteries in many different areas. The market for manganese dioxide keeps getting bigger as new ideas come out. New ways to make cathodes help batteries last longer and work better. More people want electric cars, so the market grows even more. Companies spend money on research to make strong cathodes and be leaders. The future looks good for energy storage and green batteries with manganese dioxide.
FAQ
What makes nanostructured manganese dioxide important for next-gen batteries?
Nanostructured manganese dioxide helps batteries work better. It lets batteries store more energy and stay strong longer. Companies use it because more people want good batteries. This material helps electric cars and energy storage systems last longer and work better.
How does the manganese dioxide market support clean energy growth?
The manganese dioxide market grows as more people use electric cars and clean energy. Battery makers pick this material because it is reliable and good for the planet. The market also gets better with new recycling and green ways to make manganese dioxide.
Are there challenges in scaling up nanostructured manganese dioxide for the market?
Making more nanostructured manganese dioxide can be hard. Factories must keep the quality high and costs low. The market needs a steady supply and better ways to make the material. Companies spend money on research to fix these problems and meet the need for battery materials.
What role does recycling play in the manganese dioxide battery market?
Recycling helps by cutting down waste and saving resources. Companies take manganese dioxide from old batteries and use it again. This helps the planet and makes batteries cheaper to make. The market gets better with green rules and eco-friendly actions.
How do innovations in manganese dioxide affect the global battery market?
New ideas in nanostructured manganese dioxide help the battery market grow. Better ways to make and change the material help batteries last longer and work better. These changes help companies keep up and give people the batteries they need for energy storage.
Related Posts

I am Edward lee, founder of manganesesupply( btlnewmaterial) , with more than 15 years experience in manganese products R&D and international sales, I helped more than 50+ corporates and am devoted to providing solutions to clients business.