Manganese sulfate fertilizer is important in farming today. Farmers add it to fertilizer mixes to help crops grow well and produce more. Manganese helps plants make food, use enzymes, and fight diseases. Many crops like wheat, cereals, and soybeans do not get enough manganese. These crops may have pale leaves or not grow tall. Manganese sulfate fixes these problems fast. It makes plants stronger and gives better harvests. Farmers everywhere use more manganese sulfate now. They know it helps crops stay healthy and makes food better.
Manganese sulfate fertilizer gives plants an important nutrient. It helps plants grow strong. It helps plants make food. It helps plants fight diseases. This fertilizer works quickly. It dissolves easily in water. Plants can take in manganese fast. They absorb it through roots and leaves. Manganese helps plants make chlorophyll. It turns on enzymes in plants. It helps build strong cell walls. Strong cell walls help plants handle stress. They also help plants fight disease. Farmers should test soil and leaves. This helps find if plants lack manganese. Lack of manganese shows as yellow leaves. Young leaves turn yellow first. Plants also grow slowly. Farmers should use manganese sulfate the right way. They can put it in soil. They can spray it on leaves. They can add it to water for irrigation. Using manganese sulfate helps crops grow better. It makes crops higher quality. It also makes food safer.
Manganese Sulfate Fertilizer in Blends
Key Micronutrient
Manganese sulfate fertilizer is very important for farming today. It gives plants a key micronutrient they need to grow well. Manganese helps many plant enzymes work. These enzymes help plants make food and build strong parts. Plants also use manganese to stay healthy and fight off sickness. Manganese sulphate monohydrate gives plants this nutrient in a way they can use fast. Crops like potatoes, onions, and spinach need enough manganese. If they do not get it, they may not grow tall or their leaves may look pale. Wheat, maize, and citrus also need manganese sulfate fertilizer to grow strong.
Studies show that not enough manganese causes yellow leaves and weak roots. It also means plants do not make as much food. If farmers find this problem early, they can fix it with manganese sulfate fertilizer. This helps plants get healthy again and grow more food. Manganese sulphate monohydrate helps plants use sunlight to make energy. It keeps the plant cells working right and helps crops make energy well.
Note: Manganese sulphate monohydrate gives plants manganese and makes their tissues stronger. This helps crops handle stress better.
Vegetables like lettuce, peas, and cucumbers grow better with manganese fertilizer. Tests show that wheat grows taller and makes more grain with manganese sulfate. All these crops need enough manganese, especially if the soil does not have much.
Fast-Acting Source
Manganese sulfate fertilizer works fast and is easy to use. Manganese sulphate monohydrate mixes well with water. This makes it the best choice for giving plants manganese. Because it dissolves so well, plants can use it right away. Other types of manganese fertilizer do not dissolve as well. They need to be used in bigger amounts and do not work as quickly as manganese sulfate.
Manganese sulfate fertilizer mixes fully with water.
Plants take in manganese sulphate monohydrate fast through roots and leaves.
Spraying manganese sulfate on leaves fixes problems in just a few days.
Soils with high pH or too much lime can make it hard for plants to get manganese. In these cases, putting manganese sulphate monohydrate near the roots or spraying it on leaves helps crops get what they need. Experts say to use manganese sulfate fertilizer for both soil and leaf sprays because it works so well.
Vegetables like snap beans, table beets, and sweet corn grow better after using manganese sulfate. Manganese sulphate monohydrate also helps keep crops like wheat from taking in too much heavy metal. This makes food safer to eat. Using manganese sulfate fertilizer often helps keep soil healthy and crops growing well.
Tip: Always check soil and plant leaves to see if they need more manganese. Change how much manganese sulphate monohydrate you use based on what your crops and soil need.
Role of Manganese in Plants

Photosynthesis and Chlorophyll
Manganese is important for photosynthesis in plants. It is needed to make chlorophyll, which is the green part that lets plants use sunlight. If plants do not get enough manganese, they cannot make enough chlorophyll. This causes leaves to look pale and plants to grow weak. Manganese also helps break water apart during photosynthesis. This step lets plants give off oxygen and use sunlight to make food. When plants do not get enough manganese, photosynthesis slows down. Crops then do not grow well and make less food. Manganese also helps plants take in other nutrients. This keeps plants healthy and helps them grow strong.
Manganese helps plants make chlorophyll.
It lets plants break water and release oxygen.
Plants need manganese for good photosynthesis and energy.
Enzyme Activation
Plants need manganese to turn on many enzymes. These enzymes help plants grow, make energy, and stay safe from harm. Manganese works with enzymes like superoxide dismutase and catalase. These enzymes protect plants from bad molecules. If plants do not get enough manganese, their leaves turn yellow, wilt, and get brown spots. Manganese helps keep plant cells working right. It also helps plants use nutrients and build strong parts. Without manganese, plants cannot grow or protect themselves well.
Manganese turns on enzymes for photosynthesis and breathing.
It helps plants handle stress and use nutrients.
Disease Resistance
Manganese helps plants fight diseases in many crops. It helps plants build strong cell walls by making lignin. Strong cell walls stop diseases from getting inside. Studies show rice, tomato, potato, and bent grass fight diseases better with enough manganese. For example, rice with more manganese has less blast disease. Potato plants with manganese get less common scab. Manganese also helps plants make special compounds that block germs.
Plant Species | Disease | Pathogen | Effect of Manganese |
|---|---|---|---|
Rice | Blast | Pyricularia oryzae | Less blast symptoms |
Tomato | Black leaf mold | Pseudocercospora fuligena | Helps control disease |
Potato | Common scab | Streptomyces scabies | Less disease |
Bent grass | Take-all disease | Gaeumannomyces graminis var. avenae | More resistance |
Plants need enough manganese to stay healthy and fight sickness. Giving plants what they need helps them grow strong and make more food.
Manganese Availability and Deficiency
Causes of Deficiency
How much manganese is in soil depends on many things. If soil pH is high, above 6.5, plants get less manganese. The best pH for crops is between 5.0 and 7.0. When pH goes over 7.0, plants cannot get enough manganese. This can cause manganese deficiency. Soils with lots of organic matter can also have less manganese. In sandy soils, manganese washes away fast. This makes plants not get enough manganese. Dry weather makes it harder for plants to get manganese. Cool and wet soils slow down how fast manganese comes out. Farmers often see manganese problems in low spots in fields.
Soils with high pH (above 6.5) make less manganese.
Sandy soils lose manganese because it washes away.
Lots of organic matter can trap manganese and lower it.
Dry or cool, wet weather makes less manganese for plants.
These soil types often have more manganese problems.
Symptoms in Crops
Manganese deficiency shows up first on new leaves. This is because manganese does not move inside plants. The main sign is yellowing, called chlorosis, on young leaves. Plants may also grow slowly or have strange leaf shapes. In wheat, maize, and citrus, yellow starts at the edges or between veins. Plants with low manganese do not grow well or make as much food. Sometimes, manganese problems look like other issues. But yellow on new leaves helps farmers know it is manganese.
Tip: Look for yellow on new leaves and slow growth. These signs often mean plants need more manganese.
Soil and Tissue Testing
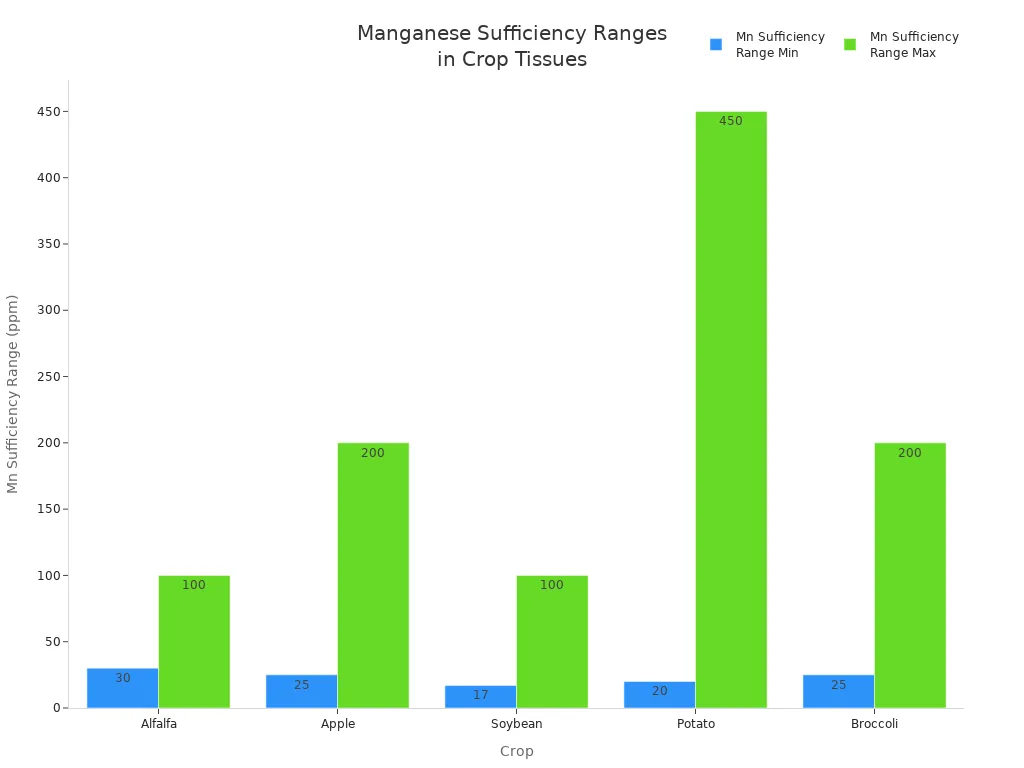
Testing helps farmers know if plants need more manganese. Soil tests using the DTPA method check how much manganese is there. But results can change with soil type and weather. Tissue tests show how much manganese is in the plant right now. Farmers should test the newest leaves because manganese does not move inside plants. If tissue manganese is under 20 ppm, plants likely need more. Using both soil and tissue tests with field history gives the best answer.
Crop | Plant Part | Sampling Time | Mn Sufficiency Range (ppm) |
|---|---|---|---|
Alfalfa | Top 6 inches | Bud | 30-100 |
Apple | Mature leaves from new growth | Summer | 25-200 |
Soybean | Most recently matured trifoliate | Early flowering | 17-100 |
Potato | Fully developed leaves and petiole | 40-50 days after emergence | 20-450 |
Broccoli | Mature leaves from new growth | Heading | 25-200 |
Looking at soil pH, manganese levels, and leaf color helps find manganese problems. Farmers should not use too much manganese to avoid harm. Spraying chelated manganese on leaves works well when tests show plants need more.
Benefits of Manganese Sulphate Monohydrate
Yield Improvement
Manganese sulphate monohydrate helps farmers grow more crops. This fertilizer gives plants the manganese they need to grow strong. When plants get enough manganese sulphate monohydrate, they make more food from sunlight. Their roots and stems also get stronger. Wheat treated with manganese sulphate monohydrate grows more grain and has stronger young plants. Grapes sprayed with manganese sulphate monohydrate have bigger berries and more sugar. These changes help farmers get better harvests and healthier plants.
Spraying manganese sulphate monohydrate on leaves puts more manganese in grains and straw.
Plants use sunlight better and have more energy.
Crops make more pollen and set more seeds.
Wheat grains have more nutrients and handle stress better.
Grapes get more color and taste better.
Farmers notice that manganese sulphate monohydrate keeps plants healthy and helps them handle stress.
Sulfur Contribution
Manganese sulphate monohydrate also gives plants sulfur, which is important for growth. Sulfur helps plants make proteins and use nitrogen well. This makes crops stronger and healthier.
Sulfur in manganese sulphate monohydrate helps plants make protein.
Plants use nitrogen better.
Crops grow faster and look greener.
Sulfur helps plants stay strong and healthy.
Plants that get enough sulfur from manganese sulphate monohydrate grow better and have stronger leaves.
Heavy Metal Reduction
Manganese sulphate monohydrate can help crops take up less heavy metal from the soil. This makes food safer for people to eat. When farmers use manganese sulphate monohydrate, crops absorb fewer harmful metals. This keeps both plants and people safer.
Note: Manganese sulphate monohydrate helps crops grow and also keeps food safe by lowering heavy metal levels.
Apply Manganese Sulphate
Application Methods
Farmers have different ways to use manganese sulphate monohydrate. The main ways are broadcast, sidedress, fertigation, and foliar spray. Each way works best for certain crops or soils.
Broadcast: Farmers spread manganese sulphate monohydrate over the soil before planting. This is good for big fields like wheat or maize. It helps put manganese near the roots.
Sidedress: They put the fertilizer next to growing plants. This helps roots get manganese and works well for potatoes and sugarcane.
Fertigation: Farmers mix manganese sulphate monohydrate into irrigation water. This gives crops a steady supply as they grow.
Foliar Spray: They spray manganese sulphate monohydrate on plant leaves. This works fast and fixes problems quickly, especially for citrus, soybeans, and vegetables.
Using manganese sulphate monohydrate in wheat fields can lower bad metals in grains. If farmers use it when planting, it can cut cadmium in wheat by up to 63%. This also puts more manganese in the soil and plants without hurting growth.
Tip: Foliar sprays help most when crops have yellow leaves or grow slow. Always spray young, healthy leaves for best results.
Rates and Timing
The right amount and time help crops get the most from manganese sulphate monohydrate. Farmers should check what crops need and test soil before using it.
Crop | Application Method | Rate (lb Mn per acre) | Timing / Conditions | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Citrus (acidic soils) | Soil application | 7–10 | When young leaves show deficiency | Use only on acidic soils |
Citrus (calcareous soils) | Foliar application | 3–5 | On two-thirds to fully expanded leaves | Add low biuret urea for better uptake |
Soybean | Foliar application | When deficiency appears | Soil application is less effective | |
Wheat | Soil application | 0.05–0.2% MnSO4 | At seeding stage | Reduces cadmium in grains |
Farmers should not use too much manganese sulphate monohydrate. Too much can hurt plants. They should only use it if tests show crops need it. Foliar sprays work best on young leaves. For soybeans, foliar sprays work better than soil use.
Always follow the label for how much to use.
Do not mix manganese sulphate with glyphosate unless it is chelated.
When mixing, add water first, then ammonium sulfate, then glyphosate, and last manganese EDTA.
Note: Farmers should check for deficiency before using manganese sulphate monohydrate. Using too much can hurt plants and lower yields.
Compatibility
Farmers often mix manganese sulphate monohydrate with other fertilizers or pesticides. Most pesticides, urea ammonium nitrate, and active copper or iron fertilizers mix well with manganese sulphate monohydrate. But some products do not mix safely.
Product Type | Compatibility Status | Notes |
|---|---|---|
Most pesticides | Compatible | Safe to mix manganese sulphate |
Urea ammonium nitrate | Compatible | No issues |
Ammonium thiosulfate | Not compatible | Do not mix manganese sulphate |
Potassium thiosulfate | Caution advised | Do not leave mixture overnight |
Ammonium poly phosphate | Not compatible | Avoid mixing |
Active Boron fertilizer | Not compatible | Avoid mixing |
Active Copper fertilizer | Compatible | Safe to mix manganese sulphate |
Active Iron fertilizer | Compatible | Safe to mix manganese sulphate |
A study showed that mixing manganese sulphate with some insecticides does not make them weaker. Manganese sulphate can make spray solutions thicker, but it does not stop pesticides from working. Adding adjuvants can help manganese sulphate get into leaves better. Farmers should always test new mixes before using them on big fields.
Callout: Always do a jar test before mixing manganese sulphate monohydrate with new products. Water quality and other things can change how products mix.
Farmers should use manganese sulphate monohydrate safely and follow good rules. They should wear gloves and eye protection when handling it. They should keep it dry and away from kids and animals.
Manganese sulfate is very important for plant health and crop yield. It helps plants use sunlight, enzymes, and nitrogen. This makes crops grow strong and healthy. Growers can do a few things to help their crops:
Look for yellow leaves on young plants and slow growth.
Use manganese sulfate on the soil, spray it on leaves, or add it to water if needed.
If growers follow these steps and change fertilizer plans after testing, they can grow more crops and help the environment.
FAQ
What is the role of manganese in fertilizer blends?
Manganese is a key nutrient in fertilizer blends. It helps plants grow and lets enzymes do their jobs. Plants take in more nutrients when they get enough manganese. Manganese sulfate fertilizer gives this nutrient to plants very fast. This makes plants healthier and helps farmers get more crops.
How can farmers identify manganese deficiency in crops?
Farmers may see yellow areas between veins on young leaves. Plants with not enough manganese grow slowly and have weak stems. To be sure, farmers test the soil and plant tissue. These tests show if plants need more manganese sulphate to fix the problem.
Why do vegetable crops need manganese sulfate fertilizer?
Vegetable crops need manganese sulfate fertilizer for strong growth. Sometimes, soil does not have enough manganese, especially if it is sandy or has high pH. Using manganese fertilizer helps vegetables grow better and gives bigger harvests.
Can farmers mix manganese sulphate with other fertilizers?
Farmers can mix manganese sulphate monohydrate with many fertilizers and pesticides. They should always check if products are safe to mix. Some things, like ammonium thiosulfate, do not mix well. Doing a jar test first helps farmers avoid mixing problems.
How does manganese sulphate monohydrate improve crop yield?
Manganese sulphate monohydrate helps plants take in more nutrients. It lets crops use sunlight better and makes cell walls stronger. It also helps plants take up less heavy metal. These things help crops grow better and give farmers more food.
Related Posts

I am Edward lee, founder of manganesesupply( btlnewmaterial) , with more than 15 years experience in manganese products R&D and international sales, I helped more than 50+ corporates and am devoted to providing solutions to clients business.





