You need to select the right mesh size for mno₂powder by first understanding your specific application. Mesh size for mno₂powder controls how fine or coarse the powder is. This choice affects how mno2 performs in your process. Finer mesh increases surface area, which boosts reactivity. Coarser mesh improves flow and handling. Always match the mesh size to your technical needs for best results.
Key Takeaways
- Mesh size tells you how many holes are in one inch of a screen. It controls how big or small the powder pieces are. Finer mesh has smaller particles. This gives more surface area. It can help batteries or catalysts work better. Coarser mesh lets powder flow and move more easily. But it might lower how well it reacts or stores energy. Pick the mesh size that matches what you need. Think about your tools and rules like ASTM or ISO. Always test a small amount of powder first. Make sure the mesh size works for your process and gives good results.
Mesh Size for MnO₂Powder
What Is Mesh Size
Mesh size tells you how many openings exist in one linear inch of a screen. You use this number to classify powders by particle size. For example, a 100 mesh screen has 100 openings per inch. If you see “-325 mesh,” it means all particles pass through a 325 mesh screen, so they are smaller than 44 microns. This system helps you control the particle size distribution during manufacturing.
You can measure mesh size for mno₂powder using several methods:
- Sieving with test sieves is the most common. It works well for coarse and medium particles.
- Laser diffraction measures how light scatters through the powder. It works for particles from 10 microns up to 2 millimeters.
- Sedimentation checks how fast particles settle in a liquid.
- Image analysis uses cameras or microscopes for particles as small as 5 microns.
These methods help you get accurate results, especially when you need to classify fine powders.
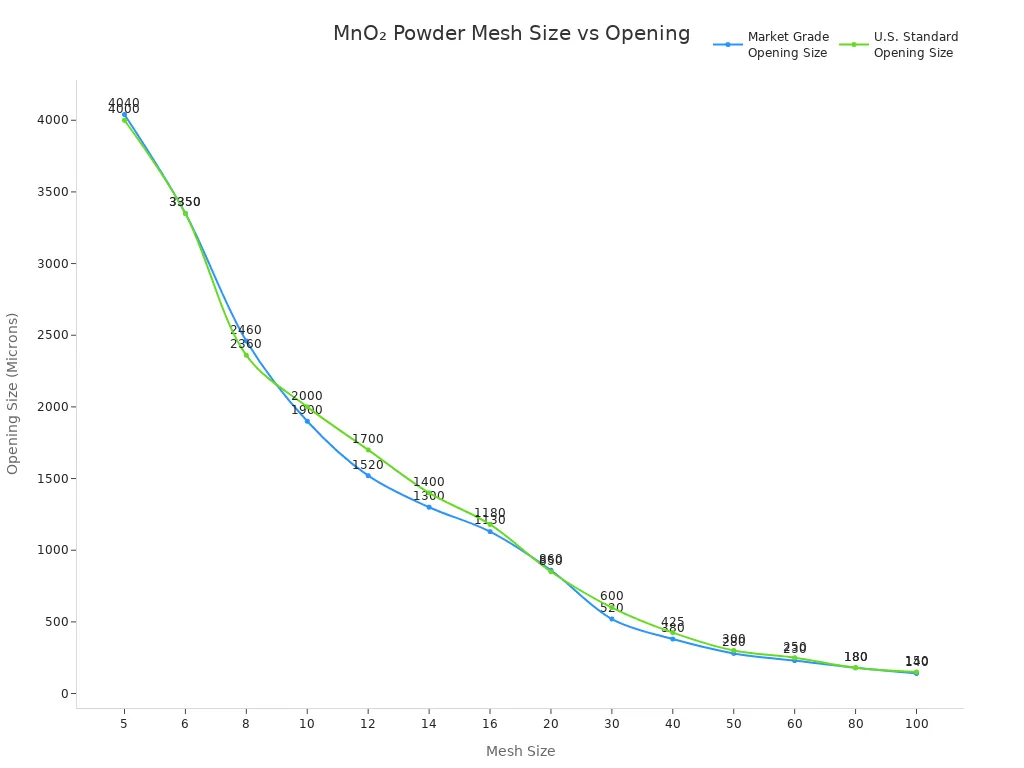
Here is a table showing standard mesh sizes for MnO₂ powder:
| Mesh Size (Market Grade) | Opening Size (Microns) | Mesh Size (U.S. Standard) | Opening Size (Microns) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | ~4040 | 5 | ~4000 |
| 6 | ~3350 | 6 | ~3350 |
| 8 | ~2460 | 8 | ~2360 |
| 10 | ~1900 | 10 | ~2000 |
| 12 | ~1520 | 12 | ~1700 |
| 14 | ~1300 | 14 | ~1400 |
| 16 | ~1130 | 16 | ~1180 |
| 20 | ~860 | 20 | ~850 |
| 30 | ~520 | 30 | ~600 |
| 40 | ~380 | 40 | ~425 |
| 50 | ~280 | 50 | ~300 |
| 60 | ~230 | 60 | ~250 |
| 80 | ~180 | 80 | ~180 |
| 100 | ~140 | 100 | ~150 |
Why Mesh Size Matters
Mesh size for mno₂powder affects how you use the powder in your process. If you choose a finer mesh, you get smaller particles. This increases the surface area, which can boost reactivity. For example, in battery production, you want high reactivity, so you pick a fine mesh. If you need better flow or easier handling, a coarser mesh works better.
You also need to match mesh size to your equipment and process. Some machines work best with certain particle sizes. Using the wrong mesh size can slow down production or cause blockages.
Note: Standard mesh sizes follow ASTM E11 and ISO 565. These standards help you get consistent results and quality control in your MnO₂ powder applications. You can find more about these standards at NIST.gov.
Selection Steps
Identify Application Needs
Start by knowing what you need for your application before picking mesh size for mno₂powder. Different industries want different particle sizes, flow, and ways to process the powder. For example, battery makers use fine powders to get more surface area and make batteries work better. In sodium-ion batteries, the right mesh size helps the battery work well and last longer.
Think about these things when you decide what you need:
- Good product quality and evenness come from the right particle size.
- How fast you want to make things changes the sieve size and how much it can hold, which can make production faster or slower.
- The powder’s moisture and how it flows matter, so you don’t get clogs and everything runs smoothly.
- Your machines and sieves must fit the mesh size you pick.
- Some rules or industry standards might say you need a certain mesh size or particle size.
Always choose mesh size for mno₂powder that fits your technical needs and any rules you must follow. For example, in medicine and pigments, people often say the mesh size is the finest sieve all the powder goes through. In batteries and electrochemical uses, you want to get the most active surface area for better results.
Particle Size and Mesh Conversion
It is important to know how mesh size and particle size are connected. Mesh size means how many holes are in one inch of a screen. A bigger mesh number means smaller holes and smaller powder pieces. For example, a 200 mesh screen only lets powder smaller than about 75 microns go through. This is very important for sodium-ion batteries, because small powder pieces help the battery work better.
You can guess the particle size with this formula:
Particle size (μm) ≈ 15000 / mesh number
For example, a 100 mesh screen is about 150 μm, and a 400 mesh screen is about 38 μm. This formula helps you turn mesh size into particle size, so you can control the powder for batteries and other uses.
| Powder Category | Sieve Aperture Size (microns) | Mesh Number (Approx.) | Description/Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Coarse powder | 1,700 | No. 10 | All-purpose powder; fine powders pass this sieve but limited passing through finer sieves |
| Moderately coarse | 710 | No. 60 | Powder passes sieve with aperture ≤ 250 microns |
| Moderately fine | 355 | No. 44 | Also passes 180 microns (No. 85 sieve) |
| Fine powder | 180 | No. 85 | Considered fine powder |
| Very fine powder | 125 | No. 120 | Considered very fine powder |
Tip: Always check the particle size distribution (D10, D50, D90) to make sure your powder is right for battery performance and capacity.
Match Mesh to Use
Pick the mesh size that fits how you will use the powder. In sodium-ion batteries, smaller mesh sizes give more surface area, which helps reactions and makes batteries stronger. For electrochemical catalysts, you need to balance between how well it reacts and how easy it is to handle. Bigger powder pieces flow better but might not work as well in reactions.
Follow these steps to pick the best mesh size:
- Decide what you will use the powder for (battery, catalyst, pigment, etc.).
- Figure out what electrochemical properties and results you want.
- Use the mesh and particle size formula to find the right mesh size.
- Make sure your machines and process can use that mesh size.
- Test small amounts first to see if it works before making a lot.
Different industries use mesh size to show how fine the powder is. For example, a supplier might sell MnO₂ powder as -200 mesh for batteries and pigments. This means all the powder is smaller than 75 microns, which is good for battery performance.

Note: Always follow industry rules like ASTM E11 or ISO 565. These rules help make sure your powder is always good and works well in batteries and other uses. For more information, visit NIST.gov.
Performance Factors
Reactivity and Flow
When you pick mesh size for MnO₂ powder, think about reactivity and flow. Mesh size changes how the powder works in reactions. Finer mesh means smaller particles. These small particles give more surface area. This helps the powder work better in batteries. You get more power and better battery results. This is very important for sodium-ion batteries. You want the battery to hold more energy and work well.
Small particles also help you separate them better. Finer mesh lets you sort particles more exactly. This makes your work faster and your product better. Vibrating sieves work best if you use the right mesh size. Picking the right mesh size cuts down on waste and helps you make more. In battery making, you want powder that flows well and fills the molds evenly. Coarser mesh helps powder flow better, but you might lose some battery power. You need to find a good balance between flow and reactivity to get the best results.
Tip: Always test a small amount first to see how it works before making a lot.
Mesh size changes:
How well the powder works in batteries
How much energy the battery can hold
How well the powder flows
How well you can separate the powder
How good your final product is
Purity Considerations
Purity is very important for how well the powder works in batteries. If there are impurities in MnO₂ powder, the battery will not work as well. You should pick a mesh size that helps get rid of big unwanted pieces. Finer mesh can catch bigger impurities and make the powder more pure. This gives you better battery results and makes the battery last longer.
Always check how pure the powder is before using it in batteries or as a catalyst. High purity helps the battery hold more energy and work better. In sodium-ion batteries, both purity and mesh size decide how well the battery works. You get better results and more energy if you control both purity and mesh size.
Factor | Impact on Performance |
|---|---|
Mesh Size | Changes battery power, energy, and flow |
Purity | Makes battery work better and last longer |
Particle Separation | Helps you work faster and make better products |
Note: For more about purity rules, visit NIST.gov.
Mesh Size Chart
Micron Conversion
It is important to know how mesh size and micron size are connected when you use MnO₂ powder. Mesh size shows how many holes are in one inch of a screen. If the mesh number is higher, the holes are smaller and the powder is finer. Micron size tells you how wide each particle is in micrometers (μm). When you pick MnO₂ powder, you will see both mesh and micron numbers. These numbers help you choose the right powder for your job.
Here is a table to help you change mesh size to micron size:
Microns (μm) | Mesh (ASTM) | Mesh (TYLER) |
|---|---|---|
44 | 325 | 325 |
53 | 270 | 270 |
62 | 230 | 230 |
74 | 200 | 200 |
88 | 170 | 170 |
105 | 140 | 140 |
125 | 120 | 120 |
149 | 100 | 100 |
177 | 80 | 80 |
210 | 70 | 70 |
250 | 60 | 60 |
297 | 50 | 50 |
350 | 45 | 45 |
420 | 40 | 40 |
35 | 35 | |
590 | 30 | 30 |
710 | 25 | 25 |
840 | 20 | 20 |
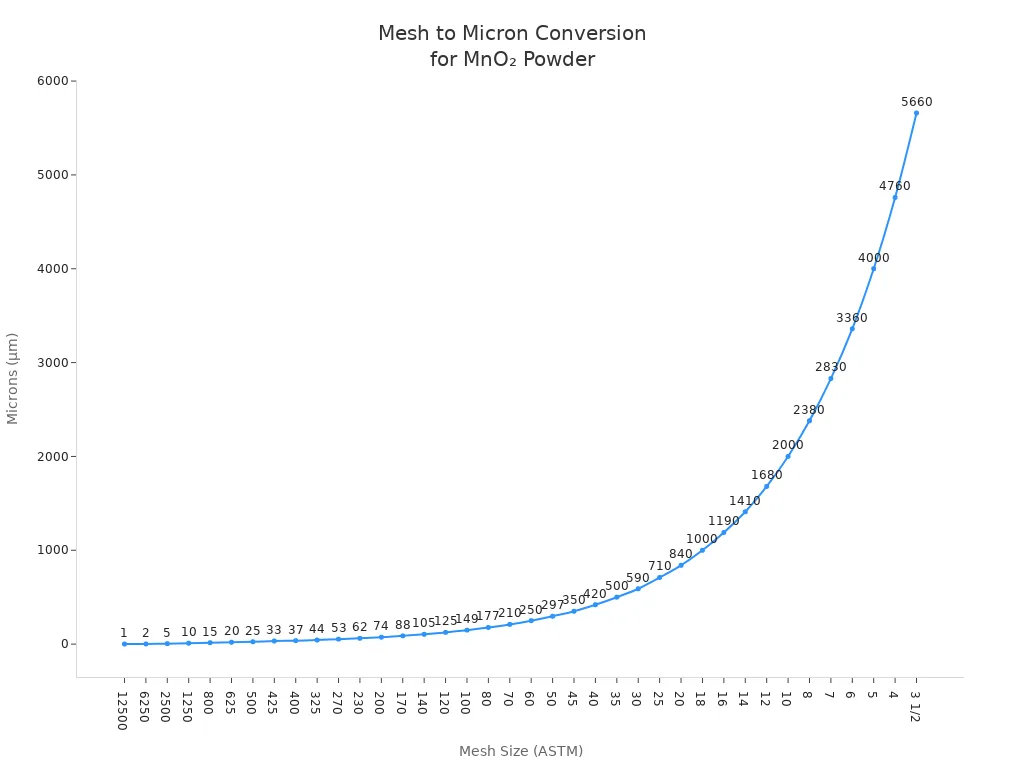
Tip: Always look at both mesh and micron numbers on your MnO₂ powder sheet. This helps you pick the right size for your machines and process.
Typical Ranges
Different mesh sizes work best for different steps when you process manganese oxide. Each mesh range changes how you separate, clean, or improve MnO₂ powder.
Minus 6-mesh ore is good for jigging, which makes better concentrates.
Plus 20-mesh ore is sent out as it is, but minus 20-mesh is saved for more work.
Gravity methods like jigs and tables use minus 8 or minus 10 mesh to get manganese well.
Flotation works with smaller particles, usually under 20 mesh, to get the most manganese.
Screening and crushing help control small pieces and stop too much slime, which can make separation harder.
You should always pick the mesh size that fits your process step. Coarse mesh helps powder flow better and saves money early on. Fine mesh gives more surface area for reactions in batteries or catalysts.
Note: To learn more about mesh rules and screening, visit NIST.gov or ASTM International.
Manganese Oxide Applications
Choosing for Batteries
When making sodium-ion batteries, you must pick the right mesh size for manganese oxide. Mesh size decides how big or small the powder pieces are. This changes how the battery works. Fine mesh gives you tiny particles. Tiny particles have more surface area. This helps the battery react better and work stronger. Fine mesh also helps the battery hold more energy and last longer. It lets the battery charge and discharge faster.
If you use coarse mesh, the particles are bigger. Bigger particles move easier but do not react as well. The battery might not hold as much energy or work as well. You need to find a balance between how the powder flows and how it reacts. Always test the powder in your battery process. Check how well the battery works, how much energy it holds, and if it stays stable. For sodium-ion battery cathodes, you want a mesh size that gives lots of surface area and good contact. This helps the battery work its best and last a long time.
Tip: Always look at the particle size distribution. This helps you control how well your sodium-ion batteries work and how much energy they can store.
Choosing for Catalysts
Manganese oxide is also used as a catalyst in many electrochemical jobs. Mesh size changes how well the catalyst works. Fine mesh gives more surface area. This makes reactions happen faster. You get better results in sodium-ion batteries and other systems. Fine mesh helps the catalyst speed up reactions and last longer.
Coarse mesh gives better flow and is easier to handle. But you lose some reaction power. Pick a mesh size that fits your process. Always test the catalyst in your system. Check how well it works, how fast reactions go, and how much it can do. For sodium-ion batteries, you want a mesh size that gives strong reaction power and steady results.
- Main uses that need special mesh sizes:
- Water treatment filtration media
- Pyrolusite ore media (8 x 20 to 20 x 40 mesh)
- Manufactured media like greensand (18 x 60 to 12 x 50 mesh)
- These mesh sizes help take out manganese, iron, and radium from water
Note: Most batteries, electronics, and farming do not need exact mesh sizes. Only water treatment filtration media need very specific mesh ranges to work best. For more details, visit NIST.gov.
You can pick the best mesh size for MnO₂ powder by using easy steps. First, think about what you need the powder to do. Then, match the particle size to your process. Always try to get good results and make the powder easy to use. Experts say you should:
- Check the particle size distribution of your powder.
- Use the right way to mix and prepare your samples.
- Pick milling equipment that gives you the size you want.
Look at mesh size charts to help you choose:
Mesh Size | Particle Size (μm) |
|---|---|
100 | 150 |
200 | 75 |
400 | 38 |
800 | 18 |

Tip: Try out small amounts first. This helps you make sure the powder works well and fits your process.
FAQ
What does mesh size mean for MnO₂ powder?
Mesh size tells you how many holes are in one inch of a screen. A higher mesh number means smaller particles. You can use mesh size to control powder quality and performance.
How do you convert mesh size to microns?
You can use this formula:Particle size (μm) ≈ 15000 / mesh number
For example, 200 mesh equals about 75 microns. Always check the supplier’s data sheet for exact values.
Why does mesh size affect battery performance?
Mesh size changes the surface area of MnO₂ powder. Finer mesh gives more surface area, which helps batteries store more energy and work better. Coarser mesh improves flow but may lower battery efficiency.
Where can you find official mesh size standards?
You can find mesh size standards at NIST.gov or ASTM International. These sites provide reliable, up-to-date information for your reference.
Related Posts

I am Edward lee, founder of manganesesupply( btlnewmaterial) , with more than 15 years experience in manganese products R&D and international sales, I helped more than 50+ corporates and am devoted to providing solutions to clients business.





