Alkaline manganese dioxide is very important for batteries. It helps batteries give steady power to things like remotes, flashlights, and toys. Many experts pick alkaline manganese dioxide because it gives more energy and makes batteries last longer.
btlnewmaterial gives battery makers pure manganese dioxide all over the world.
- Alkaline cells use this special manganese dioxide to meet the needs of new electronics.
- More people want strong, long-lasting batteries, so the market is growing.
Key Takeaways
Alkaline manganese dioxide helps batteries give steady power. It makes batteries last a long time in things like remotes and flashlights. Its special crystal shapes and purity help store more energy. This makes batteries work better and last longer. Alkaline batteries are safe and do not have mercury. They are made to stop leaks, but old or broken batteries need careful handling. Recycling alkaline batteries helps protect the environment. It stops harmful chemicals from getting into nature. Alkaline batteries give good energy and cost less than some others. They are easy to find and work well for many things.
Alkaline Manganese Dioxide
Properties
Alkaline manganese dioxide is special because of its chemical and physical features. Scientists know it comes in different crystal forms, like δ-, γ-, α-, β-, and ε-MnO2. Each form has its own crystal shape, which changes how it works in batteries. δ-MnO2 has layers with a big surface area and many oxygen gaps. This helps it store more energy and move ions fast, so batteries last longer and work better.
γ-MnO2 is also common. It has smaller tunnels but still a large surface area and many spots for energy reactions. The size and shape of these tunnels are important. Bigger tunnels help ions move faster, which gives the battery more power and smoother charging. Smaller tunnels, like in β-MnO2, still work but hold a little less energy.
Here are some main properties that make alkaline manganese dioxide good for batteries:
Many crystal forms, each with special shapes
High surface area for more energy reactions
Lots of oxygen gaps to help electricity flow
Tunnel sizes that change how ions move and how much energy the battery can hold
Can be changed to work even better
The shape and purity of manganese dioxide are very important for how much energy a battery gives and how long it lasts. Good types, like electrolytic manganese dioxide, help alkaline batteries work better and more reliably.
Role in Alkaline Cells
Manganese dioxide is the main part of alkaline cells. It is the key material at the cathode, which is the positive side. When you use a device with an alkaline battery, manganese dioxide takes electrons from the zinc anode. This makes electricity flow and powers the device.
When the battery is used, manganese dioxide acts as an oxidizing agent. It takes electrons and helps keep the battery’s voltage steady. The chemical reaction is:
Zn + 2MnO2 → ZnO + Mn2O3
This reaction shows how manganese dioxide changes as it stores and gives out energy. The special shape of manganese dioxide, especially when it is pure, lets it do these reactions well. This means alkaline cells can give steady energy for a long time.
Alkaline manganese dioxide technology helps batteries power things like toys and flashlights without losing power too fast. How manganese dioxide is made and shaped changes how well the battery works. When battery makers use pure manganese dioxide, the batteries last longer and give steady energy.
In short, manganese dioxide’s shape and chemistry are why alkaline cells are used in many devices. Its ability to take electrons and help fast energy reactions keeps alkaline batteries working well.
Alkaline Manganese Dioxide Cells
Battery Chemistry
Alkaline manganese dioxide cells have a simple but strong chemistry. Each cell has a zinc anode and a manganese dioxide cathode. There is also potassium hydroxide inside as the electrolyte. When you use the battery, zinc loses electrons. Manganese dioxide takes these electrons. This movement of electrons makes energy for your devices. Potassium hydroxide helps ions move between the anode and cathode. This keeps the battery working well.
Here’s a table that shows the main reactions when the battery is used:
Electrode | Reaction |
|---|---|
Anode | Zn + 2OH⁻ → Zn(OH)₂ + 2e⁻ |
| Zn(OH)₂ + 2OH⁻ → [Zn(OH)₄]²⁻ |
Cathode | 2MnO₂ + H₂O + 2e⁻ → Mn₂O₃ + 2OH⁻ |
| MnO₂ + 2H₂O + 2e⁻ → Mn(OH)₂ + 2OH⁻ (full discharge) |
Overall | Zn + 2MnO₂ → ZnO + Mn₂O₃ |
| Zn + MnO₂ + 2H₂O → Mn(OH)₂ + Zn(OH)₂ (full discharge) |
The manganese dioxide cathode changes in two steps as the battery is used. This helps the battery keep a steady voltage. It also helps the battery work well, even if you use it a lot. Potassium hydroxide as the electrolyte gives these cells more energy. It also helps them last longer and leak less than other batteries.
Construction
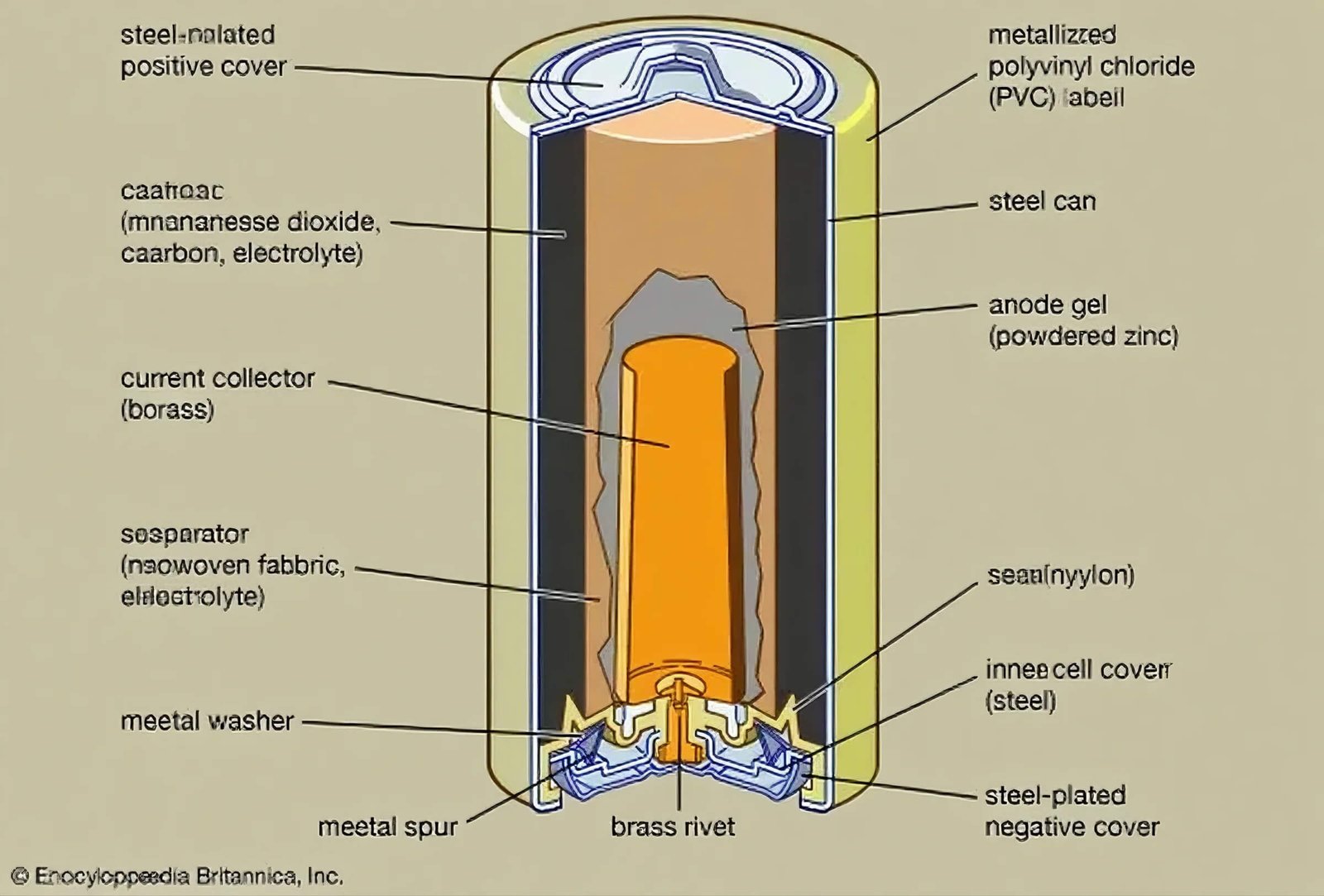
Manufacturers make alkaline manganese dioxide cells carefully. They want the batteries to give good energy and work well. The cathode has pure manganese dioxide mixed with graphite and a little acetylene black. The zinc anode is made from pure zinc powder. Sometimes, a small amount of lead is added to stop corrosion. Some batteries use gelled anodes. Others use porous anodes for better performance when used a lot.
A separator sits between the anode and cathode. It lets ions move but stops the battery from shorting out. Potassium hydroxide fills the cell as the electrolyte. This helps ions move fast and keeps the battery stable. Most alkaline batteries have a voltage of 1.5 volts. The voltage drops slowly as the battery is used. It goes down to about 0.9 volts at the end. This slow drop means these batteries can power things for a long time.
Alkaline manganese dioxide cells do not have mercury. This makes them safer for the environment. Their strong build and high energy make them a top choice for many devices.
Features of Alkaline Batteries
Performance
Alkaline batteries work well in many devices. People like them because they last a long time. They give steady power, so electronics work better. Alkaline batteries hold more charge than many other types. This means toys and remotes work longer before you need new batteries.
Let’s see how alkaline batteries and lithium batteries are different:
Feature | Alkaline Batteries | Lithium Batteries |
|---|---|---|
Energy Density | 150-500 Wh/kg | |
Shelf Life | About 5-7 years | Up to 12-15 years |
Self-Discharge Rate | 3-5% per month | 2-3% per month |
Voltage Stability | Drops under load | Stays flat during use |
Cost | Lower | Higher |
Alkaline batteries work best at room temperature. If it gets very cold, they do not work as well. At -30°C, they lose power and do not last long. In cold weather, other batteries like silver oxide work better.
Safety
Alkaline batteries are made to be safe, but there are still risks. Sometimes, old or broken batteries can leak. The liquid inside can hurt your skin or eyes. Manganese dioxide in the battery is harmful if you touch or breathe it in.
To stay safe, companies follow these steps:
Use the right battery for your device.
Change old batteries on time.
Look for leaks in battery holders.
Handle batteries carefully.
Recycle used batteries the right way.
Many factories use machines and AI to seal batteries tightly. This helps stop leaks and keeps batteries working well. btlnewmaterial gives battery makers very pure manganese dioxide. This helps batteries stay safe and work better.
Environmental Impact
Throwing away alkaline batteries makes waste. Most used batteries go to landfills. Chemicals like manganese, zinc, and potassium hydroxide can leak out. These chemicals can hurt plants, animals, and people. Only about half of alkaline batteries get recycled, so pollution is still a problem.
Recycling helps save metals and keeps waste out of landfills. Some recycling uses green materials to help the earth. btlnewmaterial follows strict rules for manganese dioxide. Their products help clean water and support green projects.
Tip: Always recycle old batteries. This helps the earth and saves energy.
Applications of Alkaline Cells
Everyday Devices
People use alkaline batteries in many things at home. These batteries power remotes, clocks, and flashlights. They work best in things that do not need much energy. For example, a remote only uses a little energy each time you press a button. Wall clocks can run for months or years on one battery. Flashlights use alkaline batteries because they give steady power and last long.
Alkaline batteries are cheap and easy to buy. Most stores have them in many sizes. People use them in toys, radios, and some medical tools. The battery chemistry makes them great for things that do not use much power. People trust alkaline batteries because they do not leak much and last a long time. This makes them a good choice for families who want safe and steady power.
Tip: Always keep some alkaline batteries at home. They are useful when you need to change a battery in a clock or flashlight.
Technology Impact
Alkaline batteries are used in more than just home items. In the 1950s, Lewis Urry made the first zinc-manganese dioxide alkaline battery. This changed how people used portable electronics. The new battery gave more energy and lasted longer than old ones. People could use radios, toys, and flashlights for more time.
Alkaline batteries made portable devices easier to use and more reliable.
Better designs, like porous electrodes, gave more energy and longer battery life.
Over time, alkaline batteries became the main power for many electronics.
The technology also led to new batteries, like nickel-cadmium and lithium-ion, which power laptops and phones today.
Alkaline batteries work in many things, from small gadgets to bigger tools. Their strong power and long life help new technology grow. People now have better and longer-lasting devices because of these battery advances.

Battery Comparison
Alkaline vs. Zinc-Carbon
Many people ask why alkaline cells are used more than zinc-carbon ones. The main reason is how each battery works and what it gives. Alkaline cells hold much more energy than zinc-carbon cells. They can store four to five times more energy. This means toys, remotes, and flashlights work longer before you need new batteries. Alkaline batteries can last up to 8 years on a shelf. Zinc-carbon batteries usually last only 1 or 2 years.
Here’s a quick way to see the differences:
Feature | Alkaline Battery | Carbon-Zinc Battery |
|---|---|---|
Cost per AA Unit | About $0.50 (lower) | |
Capacity (mAh) | 1,000 to 2,800 | 400 to 1,000 |
Shelf Life | Up to 8-10 years | 1-5 years |
High-Drain Use | Lasts about 3x longer | Shorter runtime |
Temp Range | -20°C to 54°C | -10°C to 50°C |
Leakage Risk | Lower | 25% higher after expiration |
Zinc-carbon cells cost less, so some people use them for things that do not need much power. But they leak more often and do not last as long. Alkaline cells are better for things that use more energy. They also leak less, so they are safer for homes.
Tip: For toys or gadgets that need steady power, alkaline batteries are the better pick.
Alkaline vs. Rechargeable
Now, many people think about using rechargeable batteries. You can use these batteries many times. Alkaline cells are single-use, so you throw them away after one use. In five years, a family might spend $20 to $40 on alkaline batteries. They would spend only about $15 on NiMH rechargeable batteries. Rechargeables make less waste—about 68% less—because you use fewer batteries.
Here’s how they compare:
Metric | Alkaline Batteries (5 Years) | NiMH Rechargeable Batteries (5 Years) |
|---|---|---|
Total Cost | $20 – $40 | $15 |
Battery Waste | 460 – 920 grams | 108 grams |
Packaging Waste | 25 – 50 grams | 5 grams |
Total Waste | 485 – 970 grams | 313 grams |
Rechargeable batteries work better in things that use a lot of power. They give steady power and can be charged many times. Alkaline cells are good for things that do not use much power and last a long time on the shelf. But they cost more for things like cameras or game controllers.
Alkaline cells are easy to buy and use.
Rechargeables need a charger but save money and make less waste.
For things you use every day, rechargeable batteries are a smart choice.
Alkaline manganese dioxide is important for modern devices. People pick these batteries because they last long and give strong power. They work well in many things we use every day.
Good suppliers like btlnewmaterial use pure materials. They check quality to help batteries last longer and work better.
The battery market is growing quickly, especially in Asia Pacific. More people want batteries that give steady energy for electronics and clean energy storage.
Now, people want batteries made with safe and earth-friendly materials. Picking a battery means you should think about how well it works and how it was made.

FAQ
What makes alkaline manganese dioxide better for batteries?
Alkaline manganese dioxide lets batteries give more power. It helps batteries last longer than other types. This keeps the battery’s voltage steady while you use it. Many people choose it because their devices work better. They also do not need to change batteries as often.
Can alkaline batteries be recharged?
No, you should not recharge regular alkaline batteries. These batteries are made for one-time use only. If you try to recharge them, they might leak or even burst. If you want to reuse batteries, pick rechargeable ones like NiMH.
Are alkaline batteries safe for the environment?
Alkaline batteries do not have mercury, so they are safer than old batteries. But they can still hurt the earth if you throw them away. People should recycle used batteries to help protect nature.
Why do some batteries leak?
Batteries can leak if they get old or damaged. Using them the wrong way can also cause leaks. The chemicals inside may escape and harm your devices. People should check batteries often and replace them when needed.
Where can people buy high-quality manganese dioxide?
Many battery makers trust suppliers like btlnewmaterial. They give pure manganese dioxide that helps batteries work better. People can contact them to learn more.
Related Posts

I am Edward lee, founder of manganesesupply( btlnewmaterial) , with more than 15 years experience in manganese products R&D and international sales, I helped more than 50+ corporates and am devoted to providing solutions to clients business.





