Manganese green sand is a special filter used to clean water. It takes out iron, manganese, and hydrogen sulfide from water. Many homes and businesses in the United States use this filter. This technology has helped treat water for over 30 years. People often pick manganese green sand for well water or groundwater. This filter works well with many pH levels. It is a trusted way to keep water clean.
Key Takeaways
Manganese green sand filters take out iron, manganese, and bad smells from water. This makes the water cleaner and safer to use. The filter changes harmful things into solids. These solids get stuck in the filter. The filter needs to be cleaned often. It also needs chemicals added to keep working well. Setting up the filter the right way is important. Taking care of it helps it last 4 to 8 years. You should backwash the filter and use potassium permanganate or chlorine. These filters work best when water pH is between 6.5 and 8.5. They are good for cleaning well water and groundwater. Manganese green sand filters have many good points. But they need the right water and care to work well and not have problems.
Manganese Green Sand Overview
What Is Manganese Greensand?
Manganese green sand is a special filter media for water. It comes from a mineral called glauconite. Glauconite is found as small green grains in old sea beds. Makers cover these grains with manganese dioxide. This coating makes the grains green and helps them clean water. Some new products use silica instead of glauconite. But the important part is still the manganese oxide coating.
People use manganese greensand to filter water and remove bad stuff. The coating helps change iron, manganese, and hydrogen sulfide into solids. These solids get stuck in the filter. This keeps water clear and safe to use. Manganese greensand is different from other filters because of its special chemistry and strong cleaning power.
Composition and Properties
The main part of manganese green sand is glauconite. Glauconite has silicon, aluminum, magnesium, potassium, and iron. Each grain gets a hard, shiny layer of manganese oxide. This layer has different types of manganese oxides like pyrolusite and cryptomelane. The manganese oxide layer gives the filter its special features.
Manganese greensand grains are about 0.3 to 0.35 millimeters wide. The grains are all about the same size. This helps them catch tiny particles in water. The manganese oxide layer lets the filter turn iron and manganese into solids. The filter can then trap these solids. The grains do not dissolve in water. They do not add extra minerals to the water.
Tip: The manganese dioxide coating pulls in bad stuff and makes chemical reactions happen faster. This makes manganese greensand work really well in water filters.
Washing and recharging the filter keeps it working well. The mix of physical and chemical features makes manganese greensand different from other filters.
Greensand Filtration Process
Oxidation and Filtration Mechanism
Greensand filtration is a way to clean water. Water moves through the greensand filter. The manganese dioxide coating on each grain acts like a helper. This coating starts chemical reactions. These reactions turn iron, manganese, and hydrogen sulfide into solids. The filter catches these solid pieces.
When water with iron or manganese touches the greensand, the coating works fast. It changes iron into rust-like bits. Manganese also changes, but it takes longer. This can take 10 to 30 minutes. Hydrogen sulfide smells bad, like rotten eggs. The filter changes it into solid sulfur or sulfate. The filter then removes these solids.
Note: Greensand filtration works best if water pH is between 6.7 and 8.8. It removes iron and manganese best when their total is under 15 ppm. For hydrogen sulfide, the filter can handle up to 5 ppm.
As water goes through the filter, solids build up inside. Backwashing gets rid of these trapped solids. This keeps the filter working well. Cleaning the filter is important for good water flow.
Key Points of the Oxidation and Filtration Process:
Manganese greensand changes iron, manganese, and hydrogen sulfide.
The filter holds the solid pieces.
Backwashing cleans out the solids.
The process depends on water pH and how long water touches the filter.
Regeneration Methods
After some time, the manganese dioxide coating gets weak. The filter cannot clean water as well. To fix this, users must restore the coating. The main way to do this is with potassium permanganate. This chemical brings back the filter’s cleaning power.
During regeneration, potassium permanganate is put into the filter. It soaks into the greensand and rebuilds the coating. This usually happens during backwashing. Doing this often keeps the filter strong. It helps remove iron, manganese, and hydrogen sulfide.
Potassium permanganate is the main chemical for this job.
Regeneration is needed every 1 to 3 months for most filters.
In homes or cities with normal iron and manganese, it may be needed every 30 to 36 hours of use.
Good regeneration helps the filter last 4 to 8 years.
Some new greensand types, like Greensand Plus, do not need potassium permanganate. These use a chlorine feed before the filter instead. Both ways help keep the filter media working.
Tip: Always be careful with potassium permanganate. It is strong and can stain things or hurt your skin.
Regeneration Method | Chemical Used | Frequency | Media Lifespan |
|---|---|---|---|
Standard Greensand | Potassium permanganate | Every 1-3 months | 4-8 years |
Greensand Plus (alt.) | Chlorine feed | As needed (pre-filter) | 4-8 years |
Doing regular care and correct regeneration helps the greensand filter last longer. This makes sure the filter keeps removing hydrogen sulfide and other bad stuff.

Contaminants Removed by Greensand Filters
Greensand filters help clean water from wells and underground sources. They remove harmful things that can make water unsafe.
Iron Removal Filters
Iron removal filters use greensand to take out iron. The manganese dioxide coating helps change iron into tiny solid pieces. The filter catches these pieces. Most filters lower iron to less than 0.3 ppm. This is safe for drinking water. Greensand filters work best when there is more iron than manganese. They can handle a lot of iron. If iron and manganese together are over 8–10 ppm, you may need extra steps. Greensand filters are reliable for many well water systems.
Feature | Greensand Filters | Manganese Oxide Filters | Birm Filters |
|---|---|---|---|
Iron Removal | Effective | More effective | Needs oxygen |
Manganese Removal | Good | Excellent | Limited |
Hydrogen Sulfide Odor | Yes | Yes | No |
Media Lifespan | 4–8 years | 10–15 years | 4–8 years |
Manganese and Hydrogen Sulfide
Greensand filters also take out manganese and hydrogen sulfide. The filter changes manganese in water into a solid. The solid gets stuck in the filter. This lowers manganese to less than 0.05 ppm. That makes water safe to drink. Hydrogen sulfide smells like rotten eggs. The filter changes it into solid sulfur or sulfate. This makes water taste and smell better. These filters work best when water pH is between 6.7 and 8.8. Studies show they can remove over 90% of manganese. Homes and businesses get clean water with no bad smell.
Note: You must backwash and recharge greensand filters often. This keeps them removing iron, manganese, and hydrogen sulfide well.
Arsenic and Radium
Some greensand filters can also remove arsenic and radium. The filter uses oxidation and adsorption to catch these. Arsenic sticks to iron particles made during filtering. Potassium permanganate or chlorine helps the filter change arsenic, iron, and manganese. The filter then traps them. Radium can also be lowered, but it depends on the water and system. For best results, water pH should be 6.7 to 8.8. Water should have low tannins and oil. Greensand filters often work with other treatments to remove arsenic and radium better.
Greensand filters remove iron, manganese, hydrogen sulfide, arsenic, and radium.
They work best for well water and groundwater with some contaminants.
Regular care keeps the filters working well.
Installation and Maintenance
System Setup
It is important to set up manganese greensand filters the right way. Most systems use pressure or gravity to move water. Pressure systems are good for homes and small businesses. Gravity systems work for big buildings or city plants. Installers pick the right tank size and media depth for the water. The bed should be 30 to 36 inches deep. Water should flow at 3 to 5 gallons per minute for each square foot. Sometimes, the flow can go up to 10 gallons per minute for a short time. Water moves down through the media. The pressure drop is usually less than 5 psi.
Parameter | Value / Range |
|---|---|
Service Flow Rate | 3-5 GPM per square foot (short term up to 8-10 GPM/ft²) |
Flow Direction | Downward |
Typical Pressure Drop | Less than 5 psi |
Backwash Flow Rate | 10-12 GPM per square foot |
Minimum Bed Depth | 30 inches |
Recommended Bed Depth | 30 to 36 inches |
Maximum Feed Temperature | 80°F |
Recommended pH Range | 6.2 to 8.5 |
Media Weight | About 85 lbs per cubic foot |
The tank size changes how fast water flows and how often you backwash. The chart below shows the best flow rates for different tank sizes:
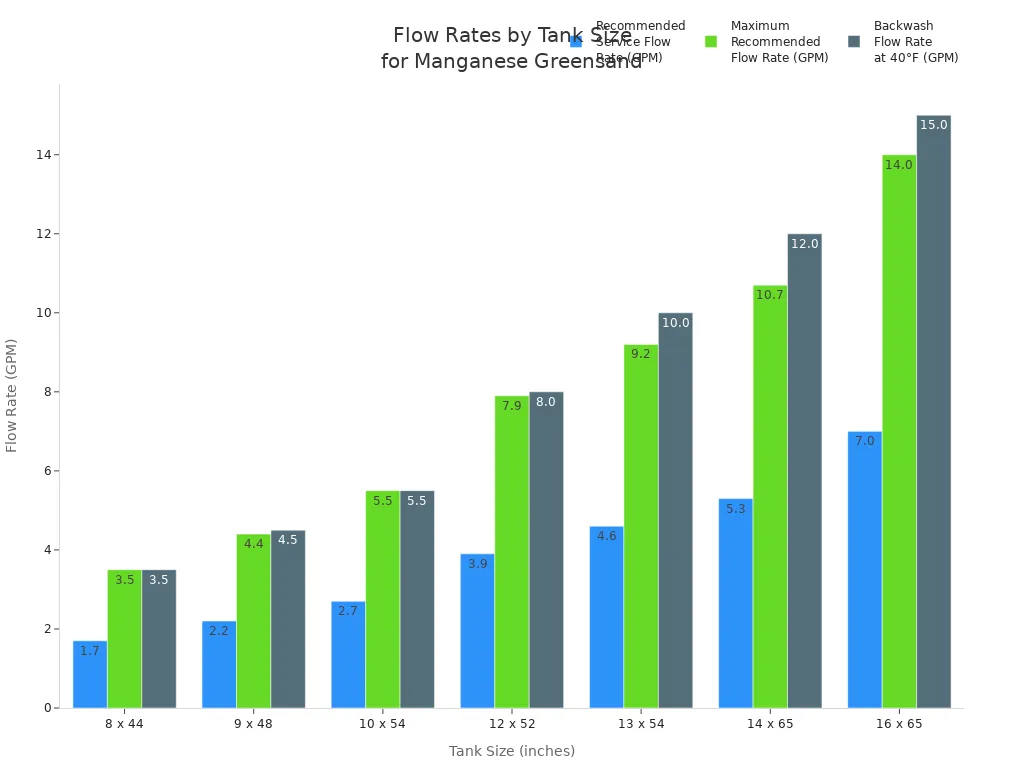
Pretreatment is an important part of setting up the system. Installers may add chlorine or potassium permanganate before the filter. This step helps change iron and manganese so they are easier to remove. Pretreatment also keeps the media from getting dirty and helps it last longer.
Backwashing and Lifespan
To keep the filter working, users must backwash it every few days or as needed. Backwashing gets rid of iron and manganese solids stuck in the filter. Each backwash uses a strong water flow, about 10 to 12 gallons per minute for each square foot. Potassium permanganate is used to recharge the media during this step. Users should add more potassium permanganate powder every 1 to 3 months, depending on how often they backwash.
Manganese greensand media usually lasts between 5 and 8 years. Many things can change how long it lasts. Water chemistry, flow speed, and iron bacteria can make it last longer or shorter. Doing regular care, using pretreatment, and having a good system design help the filter last longer.
Manganese greensand media should be replaced about every 5 years.
Solid manganese dioxide media lasts even longer.
Good care and pretreatment help the filter last more years.
Maintenance Tips
Facility managers and homeowners can do easy things to keep filters working:
Soak new media overnight in a 2-3% potassium permanganate solution before using it.
Recharge the filter media with potassium permanganate on a set schedule.
Keep chlorine above 0.5 mg/L at the filter outlet if using chlorine.
Backwash the filter often to stop iron solids from building up.
Watch flow rates and change regeneration times based on water use.
Add potassium permanganate to the tank when needed for recharging.
Plan yearly checkups and change the media every 4 to 8 years.
Tip: Using chlorine or potassium permanganate before the filter helps stop fouling and keeps the filter working well.
Taking care of the filter and doing pretreatment steps helps manganese greensand filters give clean water for many years.
Advantages and Limitations
Benefits of Manganese Greensand
Manganese greensand has many good points for cleaning water. Many experts pick this media because it works in many places. Here are some main benefits:
It takes out iron, manganese, and bad smells from water.
It does not need air injection. It uses chemicals like potassium permanganate or chlorine to recharge.
It removes iron better than some other filters, like Birm.
The media is light, so backwashing uses less water.
It costs less than solid manganese oxide media.
It can treat more than one contaminant at once.
It can handle chlorine and other oxidizers without losing power.
At the Pottawatomie County Water Treatment Plant, using manganese greensand filters made water better and saved money. Workers spent less time fixing things, and they changed filters less often.
The table below shows how manganese greensand compares to other filter media:
Feature | Manganese Greensand | Solid Manganese Oxide | Birm |
|---|---|---|---|
Iron Removal | Excellent | Excellent | Good |
Manganese Removal | Good | Excellent | Limited |
Hydrogen Sulfide Removal | Yes | Yes | No |
Backwash Water Needed | Low | High | Low |
Cost | Low | High | Low |
Media Lifespan | 5–8 years | 10–15 years | 4–8 years |
Limitations and Considerations
Manganese greensand also has some downsides that people should know about before picking this system:
It needs the right water chemistry, like pH and flow rate, to work best.
The media is heavy, so strong pumps are needed for backwashing.
Potassium permanganate can turn water pink or magenta if not used right.
Potassium permanganate is dangerous and can hurt valves if it builds up.
The media needs chemical recharging and must be replaced every few years.
It is not good for water with manganese over 1 mg/L because it costs more to run.
It does not work as well if the pH is too high or low or if there is a lot of carbon dioxide in the water.
If oxidation is not complete, iron or manganese can get through the filter.
Some people say it only gives basic results, especially with hard-to-treat water.
Tip: If your water has a lot of manganese, low pH, or lots of carbon dioxide, you may need a different system. Always test your water first and set up the system for your area.
Manganese greensand filters are good at taking out iron, manganese, and hydrogen sulfide. They need regular cleaning and chemical treatment to work well. People should test their water and check the pH often. They also need to follow a plan to keep the filter working.
These filters can be used in many homes and businesses.
If you set them up right and take care of them, they last 4 to 8 years.
Getting help from an expert helps you pick the best system.
Manganese greensand is still a trusted way to make water cleaner and safer.
FAQ
How often should users backwash a manganese greensand filter?
Most people backwash their filter every few days. If you use a lot of water or have lots of iron, you may need to clean it more often. Cleaning the filter often helps it work well and stops it from getting clogged.
Can manganese greensand remove all types of iron from water?
Manganese greensand takes out most dissolved iron. It works best with clear water iron. If your water has iron bacteria or iron stuck to other stuff, it might not remove all the iron.
Is potassium permanganate safe to use in the regeneration process?
Potassium permanganate is safe if you use it the right way. Keep it away from kids and always wear gloves. It can stain your skin and things it touches. Always follow the safety rules from the maker.
What signs show that the greensand media needs replacement?
If your water gets worse, or the flow slows down, or you need to recharge the filter a lot, the media may be worn out. Most media lasts 5 to 8 years. Checking the filter often helps you find problems early.
Does manganese greensand affect the taste or smell of water?
If you take care of your greensand filter, it will not change the taste or smell. It takes away bad smells like rotten eggs from hydrogen sulfide. If your water tastes strange, check the filter for problems.
Related Posts
Related Posts

I am Edward lee, founder of manganesesupply( btlnewmaterial) , with more than 15 years experience in manganese products R&D and international sales, I helped more than 50+ corporates and am devoted to providing solutions to clients business.






Venden arena de manganeso