Battery grade manganese dioxide is very pure and has small particles. This is important for batteries to work well and stay safe. This grade helps batteries like lithium ones that need a lot of energy. It is used more as electric cars and energy storage become popular. Industrial Grade Manganese Dioxide has more impurities. It is used for many power and industrial jobs. You should pick the right type based on what you need. If you need good battery chemistry, use battery grade. If you need it for general power, use industrial grade.
Key Takeaways
- Battery grade manganese dioxide is very pure and has tiny particles. This makes it great for strong and safe batteries. These batteries are used in electric cars and energy storage.
- Industrial grade manganese dioxide has more impurities and bigger particles. It works well for general industrial uses. People use it for water cleaning, ceramics, and making steel.
- Battery grade has smaller particles and higher purity. This helps batteries store more energy. It also gives steady power and makes batteries last longer.
- Battery grade costs more because it needs extra cleaning and quality checks. But it gives better performance and safety for tough battery jobs.
- Picking the right manganese dioxide grade for your needs is important. It helps you get the best mix of cost, safety, and performance for your project.
Key Differences
Purity
Purity is the biggest difference between battery grade and industrial grade manganese dioxide. Battery grade goes through more cleaning steps to get rid of things like calcium, magnesium, sodium, and potassium. These things can hurt lithium battery performance and make batteries not last as long. High purity helps batteries work better and last longer. Industrial grade manganese dioxide has more impurities because it does not need as much cleaning. This makes it good for general power and industrial jobs, but not for batteries that need to work really well.
Property | Battery Grade Manganese Dioxide | Industrial Grade Manganese Dioxide |
|---|---|---|
Typical Purity (%) | ≥99.5 | 80–90 |
Impurity Control | Very strict | Less strict |
Application Sensitivity | High (especially lithium) | Lower |
Note: High purity is needed for lithium batteries to stop bad reactions and keep them safe.
Particle Size
Particle size changes how well manganese dioxide works in batteries and factories. Battery grade manganese dioxide has much smaller particles, usually between 1 and 10 micrometers. Smaller particles give more surface area, so batteries can move electricity and ions faster. This means batteries can store more energy and give more power. Industrial grade manganese dioxide has bigger particles, often above 10 micrometers, with mesh sizes like -100 mesh (99.5% passing), -200 mesh (99.0% passing), and -325 mesh (95.0% passing). These bigger particles are good for things like making chemicals or cleaning water, but not for battery electrodes.
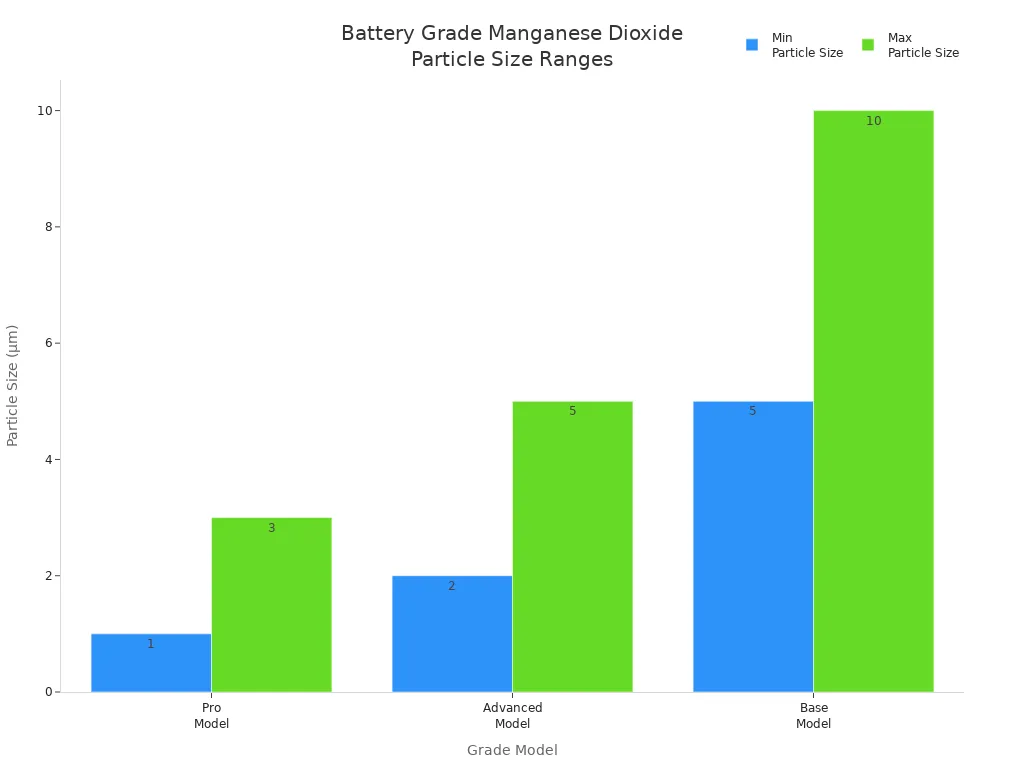
Grade Model | Particle Size Range (µm) | Notes on Application and Performance |
|---|---|---|
Pro Model | 1–3 | Smallest particles, highest purity (99.5%), best for high conductivity and ion movement |
Advanced Model | 2–5 | Small particles help ions move faster (30% better than 10 µm powders) |
Base Model | 5–10 | Bigger particles, standard battery grade for coating electrodes |
Smaller and even particles in battery grade manganese dioxide help lithium batteries store more energy. Industrial grade manganese dioxide with bigger particles is better for things like water cleaning or making ceramics, where you do not need fine control over reactions.
Application Needs
You should pick battery grade or industrial grade manganese dioxide based on what you need. Battery grade is needed for lithium and other strong batteries, where purity and particle size matter for energy, power, and safety. These batteries are used in electric cars, portable electronics, and energy storage. Industrial grade manganese dioxide is good for things that do not need strict control, like making potassium permanganate, cleaning water, or making ceramics. In these jobs, more impurities and bigger particles do not hurt how it works.
Battery Grade:
Used in lithium batteries, alkaline batteries, and energy storage.
Needs high purity and small particles for best power and energy.
Industrial Grade:
Used in water cleaning, ceramics, and chemical making.
Bigger particles and more impurities are okay.
Picking the right grade gives you the best results, safety, and saves money for each job.
Battery Grade Manganese Dioxide
Definition
Battery grade manganese dioxide is very pure and has tiny particles. Companies make it to meet strict rules for strong battery packs. This grade has very little metal that should not be there. This helps stop bad reactions inside the battery. High purity keeps the voltage steady and makes batteries last longer. It also helps batteries give steady power. Battery grade manganese dioxide is important for lithium manganese dioxide and other new battery types. The world’s battery makers need this grade, especially in Asia Pacific. There, more people want energy storage and electric cars.
Purification Process
Making battery grade manganese dioxide uses many steps to get rid of unwanted stuff. First, natural manganese dioxide turns into manganese(II) nitrate. Water is removed to make a salt that forms crystals. Then, heat at about 400 °C breaks it down and lets out gases. This leaves behind cleaner manganese dioxide. Next, carbothermic reduction makes manganese(II) oxide. This dissolves in sulfuric acid. Filtration takes out things that do not dissolve. Ammonium carbonate is added to make manganese carbonate. This is heated in air to make different manganese oxides. The mix is treated in sulfuric acid with sodium chlorate to turn it back into manganese dioxide. The last step uses electricity to put pure manganese dioxide on an anode. This makes it ready for strong battery packs. During all these steps, acid leaching and filtering keep metal impurities under 5%. This makes sure the material is good enough for batteries.
Change to manganese(II) nitrate
Remove water and make crystals
Heat to break down
Carbothermic reduction
Dissolve in sulfuric acid
Filter out solids
Make manganese carbonate
Heat to make oxides
Redox treatment
Use electricity to purify
Battery Applications
Battery grade manganese dioxide is a key part of many batteries. Lithium manganese dioxide batteries use it for high voltage and steady power. These batteries last a long time, so they are good for medical tools and electronics. Lithium manganese oxide batteries can be recharged. They have better ion flow, stay safe at high heat, and are safer to use. These batteries power tools, medical devices, and electric cars. Makers often mix lithium manganese oxide with NMC cathodes. This helps electric cars get more power and go farther. About 80% of battery grade manganese dioxide is used by the battery industry. Most of it goes into metal alkaline batteries.
Battery grade manganese dioxide helps batteries give steady energy and power for today’s needs.
Industrial Grade Manganese Dioxide
Definition
Industrial grade manganese dioxide is less pure than battery grade. It has more natural impurities like iron and silica. Makers do not clean out these impurities as much as for batteries. This grade is used in many ways because it does not need to be very pure. Many companies pick this grade because it costs less and can be used for many things.
Production Methods
Most producers use the electrolytic process to make this grade. They first heat manganese ore in a furnace or kiln. This changes the ore so it can dissolve in acid. Then, they use acid to make a manganese sulfate solution. Some impurities like iron and aluminum are removed to make it cleaner. Manganese dioxide forms on an anode using electricity. The last steps are neutralizing, drying, and packing the product. This method can make very pure material, but industrial grade keeps more impurities. The way it is made changes how pure it is and how much it costs. More cleaning and special steps make it cost more because of the equipment and care needed.
Industrial Uses
Industrial grade manganese dioxide is important in many industries. It is useful in different areas:
Industrial Application Sector | Description and Usage | Market Share / Usage Statistics |
|---|---|---|
Batteries | Used as cathode material in alkaline batteries for consumer electronics, electric vehicles, and renewable energy storage. Largest and fastest-growing segment driven by demand for portable devices and energy storage. | |
Glass & Ceramics Industry | Utilized in glass and ceramics manufacturing processes. | Significant but smaller than batteries |
Water Treatment | Used for purification and removal of impurities in drinking water and wastewater treatment. | Growing demand segment |
Steel Production | Acts as a deoxidizing agent in steel and iron alloy production. | Robust demand due to global steel production growth |
Electronics Manufacturing | Used in electronic components like diodes and transistors, especially high-purity (>99%) grade. | Fastest growth in >99% purity segment |
Others | Includes chemical oxidizing agent roles, environmental remediation (air purification), and specialty chemicals. | Smaller market share |
Batteries: Used in alkaline batteries for electronics, cars, and energy storage.
Ceramics and Glass: Used in making glass and ceramics because it helps with reactions.
Environmental Remediation: Helps clean water and air.
Electronics: Used to make parts like diodes and transistors.
Dry-cell Batteries: Helps batteries work better and last longer.
Industrial grade manganese dioxide is used in many jobs. Batteries use the most, but more is needed for water cleaning, ceramics, and electronics.
Performance and Cost
Discharge Capacity
Discharge capacity tells us how much energy a battery gives before it needs charging again. Batteries with battery grade manganese dioxide have higher open circuit voltage. They also keep their voltage higher while working. But, these batteries do not always hold as much energy as ones with industrial grade electrolytic manganese dioxide. Both grades make the same lithium intercalated manganese dioxide phase when used. The difference in how much energy they give comes from their phase makeup, water inside, and particle size. If you want high energy density and steady power, battery grade manganese dioxide gives better voltage. Sometimes, industrial grade can give more total energy.
Electrochemical Activity
Electrochemical activity shows how well manganese dioxide helps lithium ions and electrons move in a battery. Battery grade manganese dioxide has smaller and more even particles. This helps ions move faster and gives better power. High purity means fewer bad reactions, so batteries are safer and last longer. Industrial grade manganese dioxide has bigger particles and more impurities. It cannot give as much power or energy density. It works well for things like water cleaning or ceramics, where high energy is not needed. For strong batteries, battery grade manganese dioxide is still the best for high energy and steady power.
Cost Comparison
The price of manganese dioxide depends on how pure it is, how it is made, and the market. Battery grade manganese dioxide costs more because it needs extra cleaning and careful checks. Industrial grade is cheaper because it is easier to make and does not need to be as pure. Many things change the final price:
Manganese ore prices going up or down change how much it costs to make both grades.
Problems in the supply chain, like world events or new mining rules, can make prices go up.
High-purity manganese dioxide, used in new battery tech, always costs more to make.
Tip: If your project needs high power and energy, battery grade manganese dioxide is worth the higher price for better results.
Choosing the Right Grade
Industrial Grade Battery Suitability
Industrial grade battery products are used in many areas. These batteries are fine for backup power and emergency lights. Some factories also use them. They cost less, so they are good for small budgets. But, they have more impurities. This can make batteries not work as well or last as long. Industrial grade li-ion batteries may not be safe enough for electric cars or sensitive gadgets. Rules for making batteries are getting stricter. Now, companies must use less harmful stuff in batteries. Because of this, many pick purer grades for car and electronics batteries.
Tip: Pick industrial grade batteries when saving money is more important than having the most energy or longest life.
Application-Based Selection
The right manganese dioxide grade depends on how it will be used. Battery makers pick high-purity grades for lithium-ion batteries in cars and small devices. These grades help meet safety and green rules. Lower-purity grades are okay for things like water cleaning, ceramics, and steel making. Rules also affect which grade is picked. For example, green rules for throwing away batteries push for grades that are safer to recycle. The table below shows how different jobs follow rules and pick the right grade:
Industry Sector | Regulatory Influence | Impact on Grade Selection |
|---|---|---|
Battery Manufacturing | Strict safety and purity rules | High-purity grades for stable performance |
Environmental Regulations | Push for cleaner production and disposal | Cleaner grades for compliance |
Industrial Applications | Fewer purity restrictions | Industrial grade fits most needs |
Safety and green rules change how mining and battery trash are handled.
What is popular and the price of materials also matter when picking a grade.
Purity can be high (≥99%) or lower for industrial grade (≥80%).
Makers should match the manganese dioxide grade to what the battery or product needs. This helps get the best mix of price, safety, and how well it works.
Battery grade manganese dioxide is very pure and has tiny particles. This makes it important for new batteries. Industrial grade is used for more things but is less pure. You should pick the right grade for your job. Here are some good tips:
Make sure purity and type fit your use.
Pick powdered, pure grades for storing energy or starting fires.
Choose the mix that gives the performance you want.
If you need special help, companies like CAMAL Group and OLI Systems can give advice. They help you find and use the best manganese dioxide for your needs.
FAQ
What is the main difference between battery grade and industrial grade manganese dioxide?
Battery grade manganese dioxide is much purer. It also has smaller particles. This type is best for batteries that need to work well and stay safe. Industrial grade has more impurities and bigger particles. It is used for many factory jobs.
Can industrial grade manganese dioxide be used in batteries?
Industrial grade can be used in simple batteries. These are things like flashlights or backup lights. It does not meet the tough rules for strong or rechargeable batteries. Battery makers pick battery grade for safer and longer-lasting batteries.
Why does particle size matter in manganese dioxide?
Battery grade has smaller particles. This gives more surface area. It helps batteries move ions faster and store more energy. Industrial grade has bigger particles. These are better for making chemicals or cleaning water.
How does cost compare between the two grades?
Battery grade manganese dioxide costs more money. It needs extra cleaning and careful checks. Industrial grade is cheaper. It is good for jobs that do not need high purity.
Related Posts

I am Edward lee, founder of manganesesupply( btlnewmaterial) , with more than 15 years experience in manganese products R&D and international sales, I helped more than 50+ corporates and am devoted to providing solutions to clients business.