Activated manganese dioxide is very important in industry today. Companies like it because it is cheap and easy to find. It also works well and does not cost much. In 2023, the world market for manganese oxide was about $2.5 billion. This number is getting bigger because people want it for batteries and farming. Industries pick this compound because it is simple to make and good for the environment. It also works great for storing energy and cleaning up the environment. Its special structure and strong electrochemical activity help make better products. These products are used for many different things.
Key Takeaways
Activated manganese dioxide is cheap and good for the environment. It is used a lot in batteries, water cleaning, and making chemicals. Its tiny size and high purity make it a strong catalyst. It helps chemical reactions go faster and lowers pollution. Factories make it by treating natural manganese ore with chemicals. Then, they dry it carefully to keep it working well and stable. It helps by making oxidation and catalysis happen faster. It breaks down bad substances and helps store energy better. Workers must be safe when using activated manganese dioxide. They control dust and wear protective gear to stay safe.
Activated Manganese Dioxide
Properties
Activated manganese dioxide is special because of its physical and chemical features. It looks like a brown-black powder or a solid. People like it because it is very pure, usually between 72% and 90%. Its chemical formula is MnO₂. The density is about 5.026 g/cm³. This material does not dissolve in water. It stays stable up to about 535°C.
Here’s a simple table with some key properties:
Property | Details/Range |
|---|---|
Chemical Formula | MnO₂ |
Appearance | Brown-black powder/solid |
Purity Range | 72% to 90% MnO₂ |
Particle Size | 75% passing -200 B.S. or as specified |
Density | Approx. 5.026 g/cm³ |
pH Range | 4 to 6 |
Max Fe Content | 2% to 9% (by grade) |
Max SiO₂ Content | 2% to 8% (by grade) |
Activity | 18+ to 24+ (varies with grade) |
Voltage | Around 1.6 V+ |
When the particles are smaller, the surface area gets bigger. This gives more spots for chemical reactions to happen. It helps activated manganese dioxide work better as a catalyst. People use it in batteries, water cleaning, and glass making. The β-manganese dioxide type helps electricity move better. This is good for batteries.
Tip: Smaller particles can make reactions happen faster. But they might stick together after a while. This can make them work less well, so it is important to control the size.
Preparation
Industries have a few ways to make activated manganese dioxide. They often start with natural manganese ore. Workers mix the ore with a catalyst and manganese sulfate. Then they heat it with chemicals like sulfuric acid and sodium chlorate. This step turns the manganese into its active form. Next, they wash the mix with hot water, make it neutral, and dry it. Drying is very important. Taking out water helps make the material active.
Another way uses a reaction between manganese sulfate and potassium permanganate in hot water. After the reaction, workers filter, wash, and dry the solid at about 100-125°C. Sometimes, special liquids help pull out water. This makes the manganese dioxide even more active and stable.
Newer ways include mixing manganese with biochar or using special oxidation steps. These new methods help make the catalyst stronger and safer for the environment.
Note: Drying and removing water are very important. If water stays, the activity goes down and the material does not last as long.

Industrial Uses
Chemical Manufacturing
Many chemical plants use activated manganese dioxide as a catalyst. This material helps reactions go faster. For example, it helps change alcohols into aldehydes or ketones. It does this without making a lot of extra waste. Factories also use it to break down things like toluene and formaldehyde. This helps stop pollution. In green chemistry, it changes plant chemicals into useful things. It works under gentle conditions. This makes the process safer and better for nature.
Here’s a quick look at some common uses:
| Process/Application Area | Role of Activated Manganese Dioxide | Key Details/Outcomes |
|---|---|---|
| Oxidation of Alcohols | Catalyst | High selectivity, fewer by-products |
| VOC Degradation | Catalyst | Breaks down pollutants, protects environment |
| Biomass Conversion | Catalyst | Converts renewable materials, supports green chemistry |
| Fuel Cells | Cathode catalyst | Cost-effective, good conductivity, alternative to platinum |
Tip: Using this catalyst can save money and make chemical work cleaner.
Water Treatment
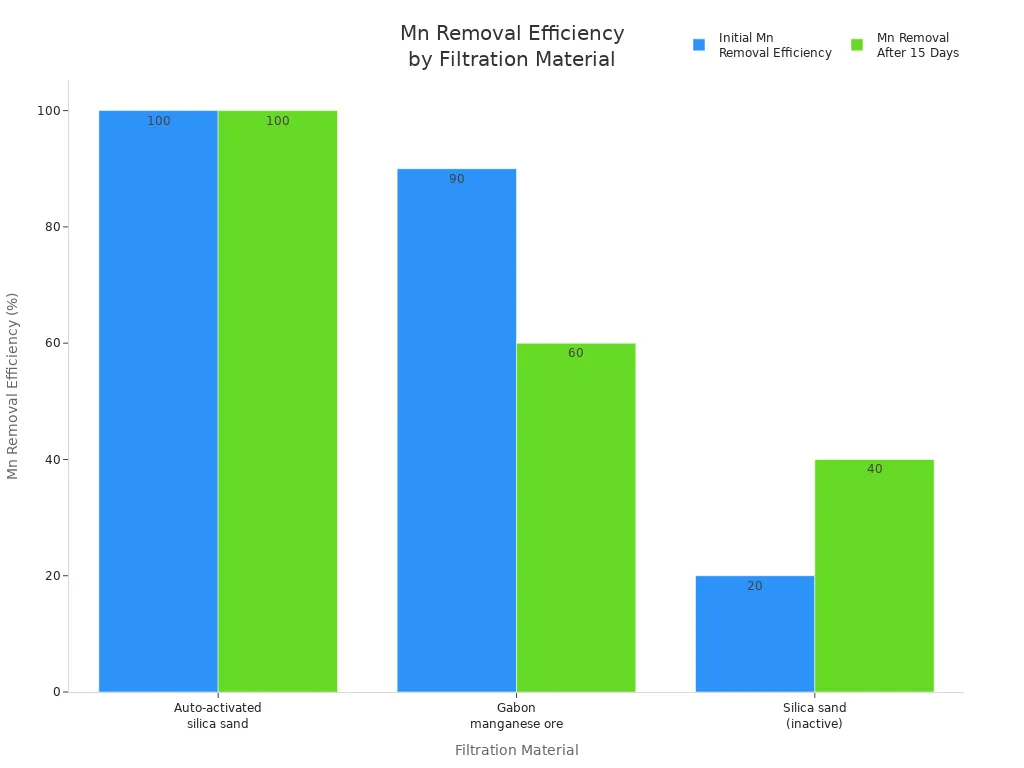
Water treatment plants use activated manganese dioxide to take out harmful metals. It is very good at removing manganese from groundwater. When used as a filter, it has lots of tiny holes and a big surface area. This helps it catch and change bad stuff in the water. It keeps working well for a long time. It does not lose its power fast.
The chart above shows that auto-activated silica sand, which gets a layer of manganese dioxide, removes manganese better and stays strong longer than other materials. This makes it a great choice for safe and steady water cleaning.
Batteries
Battery makers use activated manganese dioxide as a main part in batteries. It is important for dry batteries, like the ones in flashlights and toys. In rechargeable batteries, it helps store and give out energy. It lets zinc ions move in and out. This makes batteries hold more power and last longer. Special liquids can help it work even better. This means batteries can work well for more time. Because it is cheap and easy to find, many companies use it instead of pricier materials.
How It Works
Oxidation
Activated manganese dioxide helps factories clean up chemicals faster. It does this by making oxidation reactions happen more quickly. Oxidation is when something loses electrons. This can help break down bad materials. In factories, this material uses two main ways to help with oxidation. These are called radical and non-radical pathways.
Radical Pathways:
Some manganese oxides, like Mn3O4, make strong particles called sulfate radicals. This happens when they react with chemicals like peroxydisulfate (PDS). These radicals are great at breaking down hard-to-remove pollutants.Non-Radical Pathways:
Other types, like α-Mn2O3 and γ-MnOOH, use singlet oxygen or work with PDS on their surface. This way does not make radicals. But it still changes bad chemicals into safer ones.Other Factors:
How well these reactions work depends on things like pH and the shape of the manganese dioxide. It also depends on what other metals or carbon are mixed in. For example, adding iron or silver can help electrons move faster. This makes the process work better.
Note: Factories use activated manganese dioxide to take out dangerous metals and chemicals from water. It works best when dry and when the pH is close to 5.
Here is a table that shows the best conditions for oxidation:
Parameter | Best Condition or Description |
|---|---|
Drying Temperature | 100–130 °C for 12–24 hours (125 °C for 52 hours is optimal) |
Water Content | Less water is better; too much water blocks the active sites |
pH Level | Around 5 is effective for many reactions |
Additives | Bisulfite can change how well it works |
Safety | Avoid using Mn2O7 because it can explode |
When these things are just right, activated manganese dioxide can break down many pollutants fast and safely.
Catalysis
Catalysis means making a chemical reaction go faster without using up the helper. The helper is called a catalyst. Activated manganese dioxide is a strong catalyst in many factories. It helps turn harmful gases and liquids into safer ones.
One important job is breaking down hydrogen peroxide (H2O2). This reaction makes water and oxygen, which are safe. Manganese dioxide does this with less energy than other materials. This saves power and money.
Factories also use this material to clean up gases like carbon monoxide (CO) and formaldehyde (HCHO). When it is mixed with platinum, it works even better. The platinum spreads out on the manganese dioxide. Together, they give off active oxygen to break down these gases. This teamwork helps keep the air cleaner in factories and cities.
Tip: Catalysts made with manganese dioxide and platinum can remove dangerous gases at lower temperatures than other catalysts. This means less energy is used and there are fewer bad leftovers.
Some manganese catalysts, especially those with special coatings or mixed with other elements, can even work better than expensive metals like gold or silver in some reactions. For example, a manganese catalyst with halogen and nitrogen can turn carbon dioxide (CO2) into useful products faster than any other known catalyst.
Here are some important reactions where this catalyst works well:
Breaking down hydrogen peroxide to make clean water and oxygen.
Changing carbon monoxide into carbon dioxide, which is safer.
Taking formaldehyde out of air in factories and homes.
Because it is electrochemically active, activated manganese dioxide also helps in batteries and fuel cells. It moves electrons quickly, so these devices work better and last longer.
Chemically Activated Manganese Dioxide vs Manganese Dioxide
Key Differences
Chemically activated manganese dioxide is different from regular manganese dioxide in a few ways. The biggest difference is how they are made. Regular manganese dioxide comes from natural ore or simple chemical steps. Chemically activated manganese dioxide gets extra chemical treatments and drying. These extra steps make it more active.
The crystal structure and particle size are also not the same. Activated types have smaller particles and more surface area. This helps them react faster and work better as catalysts. The table below shows how each type works for activity and selectivity:
MnO2 Form | Catalytic Activity (Oxidation) | Selectivity and Stability Notes |
|---|---|---|
α-MnO2 | High for benzene oxidation | Superior catalytic performance and stability |
γ-MnO2 | High for benzene oxidation | Comparable to α-MnO2 in catalytic activity |
δ-MnO2 | More active for formaldehyde | Different selectivity profile compared to α and γ phases |
β-MnO2 | Lower activity | Less effective in oxidation reactions |
Commercial activated MnO2 | Enhanced catalytic ability | Improved surface properties and catalytic selectivity |
Chemically activated manganese dioxide has a larger specific surface area. This helps it do better in reactions like oxidation and dehydrogenation. Its steady quality comes from careful steps during production.
Industrial Advantages
Industries pick chemically activated manganese dioxide for many reasons. It works faster and gives better results in chemical reactions. This means factories can make more products with less waste.
The activated type makes reactions go faster, saving time and energy.
Its small, even particles are good for coatings and sprays.
Factories get steady quality because the process is controlled.
It is useful in batteries, water cleaning, and making chemicals.
In fuel and chemical making, manganese-based catalysts help make longer hydrocarbon chains. This means more fuel and chemical feedstocks are made. In the chemical industry, α-Mn2O3-based catalysts help make nitriles without using dangerous cyanides. This makes the process safer and better for the environment.
Tip: Using activated types can lower dangerous byproducts and make products better.
Chemically activated manganese dioxide gives industries a strong and reliable choice for many important jobs.
Safety and Handling
Toxicity
Activated manganese dioxide is safe if you use it correctly. But breathing in its dust or touching it a lot can be harmful. Workers might get headaches or feel weak if they breathe too much dust. Over time, it can also make it hard to remember things. The small particles can go deep into the lungs. They might hurt the nervous system.
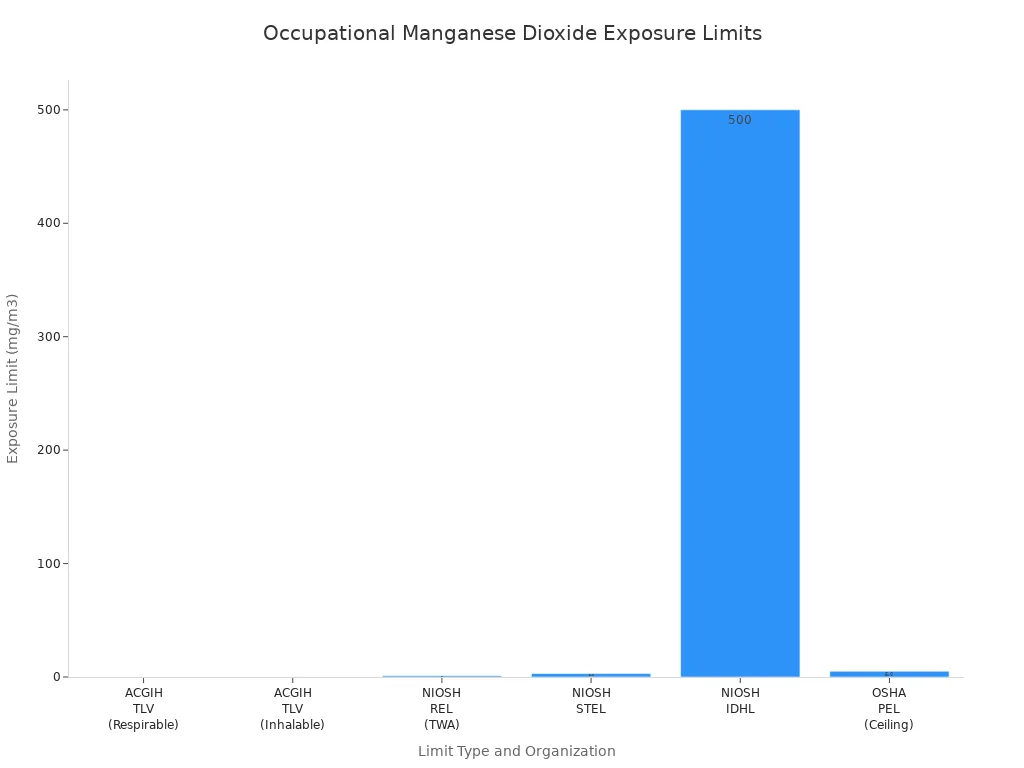
Different safety groups set rules for how much dust workers can breathe. These rules help keep people safe at work. The table below shows what some groups say is safe:
| Organization | Exposure Limit Type | Value (mg/m³) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| ACGIH | TLV (Respirable) | 0.02 | Time-weighted average (TWA), respirable particulate matter (≤4 µm) |
| ACGIH | TLV (Inhalable) | 0.1 | TWA, inhalable particulate matter (≤100 µm) |
| NIOSH | REL (TWA) | 1.0 | Recommended exposure limit, 10-hour TWA |
| NIOSH | STEL | 3.0 | Short-term exposure limit (15 minutes) |
| NIOSH | IDLH | 500 | Immediately Dangerous to Life or Health level |
| OSHA | PEL (Ceiling) | 5.0 | Permissible exposure limit, ceiling value, considered outdated |
ACGIH has the strictest rules. OSHA allows more dust, so it is less safe. The smallest particles are the most dangerous. They can reach deep inside the lungs.
Best Practices
Companies can keep workers safe by doing some easy things:
- Store activated manganese dioxide in a cool, dry place with good air flow.
- Use containers that seal tight and do not react, like HDPE or stainless steel.
- Put labels on all containers with the name, batch, and date.
- Check containers often for water, damage, or dirt.
- Keep it away from chemicals that could react with it.
- Use the oldest material first so it stays fresh.
- Wear gloves, goggles, special clothes, and masks when working with dust.
- Make sure work areas have good air flow to lower dust.
- Teach workers how to handle, store, and deal with emergencies.
- Use strong, water-proof packaging and the right warning labels for shipping.
- Have plans ready for spills, fires, or if someone is exposed.
- Throw away waste the right way and talk to groups like the EPA if needed.
- Keep notes about storage, checks, accidents, and training.
Doing these things keeps workers safe, protects the product, and follows safety rules.
Activated manganese dioxide is special in industry because it works better and saves money. It also helps companies care for the environment. Many businesses use it in energy, cars, and making things. It helps them work faster and reach green goals.
- It works with new tools like AI and IoT.
- It helps control energy use and lower pollution.
- It can be used in many ways, like in batteries and cleaning water.
In the future, scientists think it will work even better with electricity. They also see new uses in health and farming. Factories may find safer ways to make it. The future is bright as companies want smarter and cleaner ways to do things.
FAQ
How is activated manganese dioxide not the same as regular manganese dioxide?
Activated manganese dioxide has more surface area and smaller pieces. This helps it work better as a catalyst. Factories like it because it makes reactions faster and gives good results.
Can factories use activated manganese dioxide again in their work?
Yes, many factories use it more than once. It stays active for a long time if workers keep it dry and clean. When it does not work well anymore, they get new material.
Is activated manganese dioxide okay for the environment?
Activated manganese dioxide is safer than many other chemicals. It does not mix with water or make harmful waste. Companies still need to handle and throw it away the right way to keep nature safe.
Where do factories use activated manganese dioxide the most?
Cleaning water
Chemical plants
These places use it because it helps clean things, store energy, and make products faster.
Related Posts

I am Edward lee, founder of manganesesupply( btlnewmaterial) , with more than 15 years experience in manganese products R&D and international sales, I helped more than 50+ corporates and am devoted to providing solutions to clients business.





