Many global buyers—especially in battery materials, fertilizers, ceramics, and water treatment—face the same problem when buying manganese carbonate (MnCO₃) from international suppliers:
The product quality they receive is often inconsistent, purity is lower than promised, and documents are incomplete.
This is not a small issue. It impacts cost, production yield, and safety.
Here are the biggest pain points in today’s manganese carbonate market:
(1) Mn Content Is Often Lower Than Sellers Claim
Many suppliers claim Mn = 44%, but USGS and Chinese industry reports show that real commercial-grade MnCO₃ varies:
Typical range: 41%–44% Mn (USGS Mineral Commodity Summary, 2024)
Unreliable suppliers fluctuate: 39%–42%
Stable manufacturers control at: ≥ 43.5% ±0.2%
This means factories may need 5–8% more material to reach the same Mn input when the content is low.
(2) COA Data Is Not Verified or Uses Wrong Methods
Some suppliers use outdated wet-chemical testing, which creates a 0.5–1% Mn content bias compared with modern ICP-MS methods (ISO 17025 lab data comparison).
(3) Trading Companies Pretend To Be Factories
A 2023 industry survey from China Nonferrous Metals Association reported:
About 60% of MnCO₃ exporters are trading companies
Only 20–25% have real production facilities
Only 10–15% follow standard batch control management
(4) Shipment Delays and Poor Packaging
MnCO₃ can absorb moisture easily. Poor packaging causes:
Caking
Lower purity
Increased LOI (Loss on Ignition)
UN Transport Guidance (UN/TCS/208, 2023) recommends:
Inner plastic liner
Outer polypropylene woven bag
Moisture-proof palletization
These are often ignored by low-level suppliers.
2. What Quality Standards Should Manganese Carbonate Meet?
Below is a simplified table showing common industrial standards with verified sources.
Table 1 — Industry Standards for Manganese Carbonate Quality
| Parameter | Typical Standard | Good Supplier | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mn Content | ≥ 43% | 43.5–44% | USGS 2024; GB/T 24203-2009 |
| Fe (Iron) | ≤ 0.005% | ≤ 0.003% | GB/T 24203-2009 |
| Ca + Mg | ≤ 0.2% | ≤ 0.15% | Chinese Industrial Standard |
| Heavy Metals (Pb, As, Cd, Hg) | Follow ISO 11014 | Low and stable | ISO 11014 |
| Moisture | ≤ 0.5% | ≤ 0.3% | SGS Testing |
| LOI (Loss on Ignition) | ≤ 20% | 18–19% | GB/T 24203-2009 |
| Particle Size (D50) | 5–20 µm | Stable curve | Factory QC |
These standards help buyers identify real manufacturers from unreliable resellers.
3. Step-by-Step: How to Evaluate a Manganese Carbonate Supplier
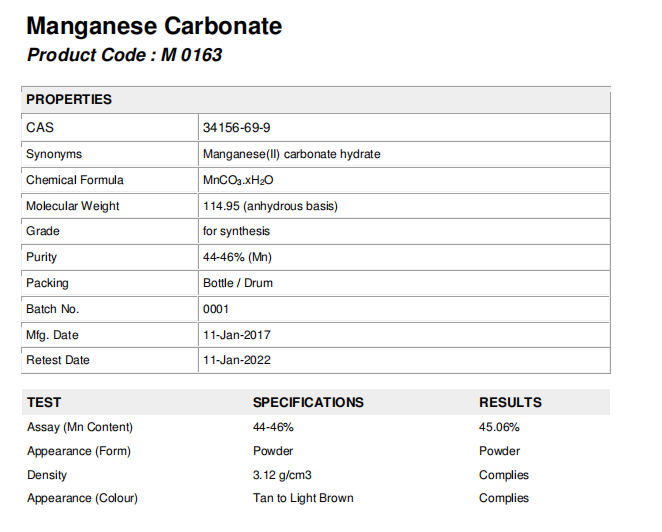
1) Verify Mn Content Stability with Real COA Data
A reliable supplier should provide:
Batch number
Testing method: ICP-MS, AAS, or titration
Testing date
Laboratory name (prefer ISO 17025 accredited)
According to ISO 17025 comparisons:
ICP-MS deviation: ±0.1%
Titration deviation: ±0.5–1.0%
If a supplier refuses to share the testing method → red flag.
2) Check Whether They Are Real Manufacturers
Ask for these documents or proofs:
| Verification Item | What You Should See | Why It Matters |
|---|---|---|
| Factory License | Local production certificate | Proof of real factory |
| Environmental Permit | Required for Mn-related production | Ensures legal production |
| Production Video or Photos | Reactors, drying system, packaging | Confirms manufacturing |
| Capacity Data | Tons/day or tons/month | Shows long-term stability |
| Export Records | Bills of lading | Proves they can export safely |
Factories can always explain the chemical process.
Trading companies often cannot.
3) Evaluate Production Capacity and Batch Stability
Large factories typically offer:
Daily output: 20–60 tons/day
Stable batch-to-batch Mn fluctuation: ±0.2%
Automated drying and sieving systems
12-month retain sample policy
Why this matters:
Data from SGS 2023 shows that batch inconsistency is the No.1 cause of failed QC in MnCO₃ supply chains.
4) Confirm Packaging Quality (Often Ignored but Critical)
According to UN/TCS/208 Transport Standard and GB 190 for chemical packaging:
Recommended Packaging
Inner: 0.1–0.15 mm PE liner
Outer: PP woven bag
Weight: 25 kg or 50 kg
With pallet: optional but best for moisture protection
Why it matters:
SGS moisture absorption tests show:
Poor packaging: up to 1.8% moisture absorption in 7 days
Standard packaging: < 0.4% in 7 days
This affects both purity and flowability.
5) Review Export Capability and Compliance
A reliable supplier should provide:
COA
MSDS (following ISO 11014)
TDS
REACH compliance (if selling to EU)
Hazard classification
MnCO₃ is not classified as dangerous goods (UN Model Regulations), but must follow standard packing rules.
6) Evaluate Communication and Transparency
Reliable suppliers usually:
Answer technical questions clearly
Provide detailed testing methods
Share photos/videos of sample preparation
Provide shipping timeline
Allow third-party inspections (SGS, BV, Intertek)
Poor suppliers often:
Avoid COA details
Give inconsistent answers
Refuse SGS testing
Overpromise and underdeliver
4. COA Verification: How to Confirm the Data Is Real
A real COA should include:
Batch No.
Mn content (e.g., 43.8%)
Fe, Ca, Mg, LOI
Testing method
Testing date
Lab or factory stamp
How to detect fake COAs
Red flags:
No testing method listed
No date or batch
All numbers rounded (e.g., Fe=0.00 always)
No responsible person signature
Format identical across different batches
ISO 17025 labs can detect fake COAs within minutes.
5. Factory vs Trading Company: Quick Identification Table

Table 2 — How to Identify True Manufacturers
| Criteria | Real Factory | Trading Company |
|---|---|---|
| Can explain production process | ✔️ | ❌ |
| Has reactor/drying line video | ✔️ | ❌ |
| Batch retention samples | ✔️ | ❌ |
| Stable Mn 43.5–44% | ✔️ | ❌ (often 41–43%) |
| Offers bulk shipment photos | ✔️ | ❌ |
| Response to technical questions | Clear | Vague |
If a supplier says:
“We can supply any purity you want.”
→ This usually means they are not a factory.
6. A Complete Checklist for Evaluating MnCO₃ Suppliers
Ask for real COA with testing method
Confirm factory license and environmental permit
Request production line photos/videos
Check batch-to-batch Mn stability (look for ±0.2%)
Confirm Fe, Ca, Mg levels
Require MSDS + COA + TDS
Check packaging (PE liner + PP woven)
Ask about monthly capacity
Confirm previous export experience
Ask for sample (verify if sample ≈ bulk)
7. Conclusion
Evaluating manganese carbonate suppliers is not just about price.
The key is quality stability, real manufacturing capability, proper documentation, and transparent testing.
A reliable supplier should have:
Stable Mn content ≥ 43.5%
Clear heavy metal and impurity control
ISO 17025 testing or equivalent
Real factory facilities
Export experience
Moisture-proof packaging
Consistent communication
When a supplier meets all these points, buyers achieve lower risk, better yield, and long-term stability.
FAQ
1. How do I know if a manganese carbonate supplier is a real factory?
A real factory can provide production videos, reactor photos, batch numbers, production licenses, and technical explanations. Trading companies cannot.
2. What is the acceptable Mn content for high-quality manganese carbonate?
Good-quality MnCO₃ should have Mn ≥ 43.5%, based on GB/T 24203-2009 and USGS data.
3. Why is batch stability so important?
Poor stability can cause differences in Mn input, affecting fertilizer formulation, battery performance, or ceramic color. Good factories maintain Mn fluctuation within ±0.2%.
4. Is manganese carbonate considered dangerous goods?
No. MnCO₃ is not classified as DG under UN Model Regulations. However, moisture-proof packaging is required.
5. Should I request a sample first?
Yes. Always verify sample Mn content, impurities, and moisture. A reliable supplier will provide consistent results between sample and bulk.
Related Posts

I am Edward lee, founder of manganesesupply( btlnewmaterial) , with more than 15 years experience in manganese products R&D and international sales, I helped more than 50+ corporates and am devoted to providing solutions to clients business.